PD233-Lecture6
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
... Potential difference leads to flow of current flow when two points with different electric potential are connected with conducting media. ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... regeneration tube + NGF & adhesion proteins – tube guides sprout to original target – connection reestablished & soma shrinks to normal size ...
... regeneration tube + NGF & adhesion proteins – tube guides sprout to original target – connection reestablished & soma shrinks to normal size ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... 1. The trigger zone of an axon is the first part or initial segment of an ____________. 2. The _____________ zone contains many voltage-gated sodium channels. 3. At the resting membrane potential, sodium channels are closed but when threshold is reached, sodium channels __________. 4. As sodium ions ...
... 1. The trigger zone of an axon is the first part or initial segment of an ____________. 2. The _____________ zone contains many voltage-gated sodium channels. 3. At the resting membrane potential, sodium channels are closed but when threshold is reached, sodium channels __________. 4. As sodium ions ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... When ion channels are open, ions diffuse across the membrane, creating electrical currents. C. The Resting Membrane Potential (pp. 396–398; Figs. 11.7–11.8) ...
... When ion channels are open, ions diffuse across the membrane, creating electrical currents. C. The Resting Membrane Potential (pp. 396–398; Figs. 11.7–11.8) ...
Neuron Physiology Notes
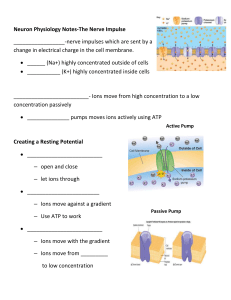
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
... Neuron Physiology Notes-The Nerve Impulse _________________-nerve impulses which are sent by a change in electrical charge in the cell membrane. ______ (Na+) highly concentrated outside of cells ___________ (K+) highly concentrated inside cells ...
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS
... wire to an amplifier 3. The voltage difference between the electrode placed inside the axon and a reference electrode outside the axon is detected… ...
... wire to an amplifier 3. The voltage difference between the electrode placed inside the axon and a reference electrode outside the axon is detected… ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... neuron - A highly specialized cell that communicates with another cell of its kind and with other types of cells by electrical or chemical signals. ...
... neuron - A highly specialized cell that communicates with another cell of its kind and with other types of cells by electrical or chemical signals. ...
Special Senses
... a) basilar membrane -separates cochlear duct from scala tympani b) vestibular membrane -separates scala vestibuli from cochlear duct ...
... a) basilar membrane -separates cochlear duct from scala tympani b) vestibular membrane -separates scala vestibuli from cochlear duct ...
Neural Communication
... from one neuron to another. As we will find out, the steps that lead to this process are far from simple and one of the most important factors is the movement of molecules across the neuronal membrane. I'm not just referring to the movement of neurotransmitters across the membrane, but the movement ...
... from one neuron to another. As we will find out, the steps that lead to this process are far from simple and one of the most important factors is the movement of molecules across the neuronal membrane. I'm not just referring to the movement of neurotransmitters across the membrane, but the movement ...
VII. The Nervous System
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
Chapter 2
... for segregation of molecules involved in cellular processes (smooth); lipid molecules are made here (smooth) Golgi apparatus – wraps around products of a secretory cell (secretion = ...
... for segregation of molecules involved in cellular processes (smooth); lipid molecules are made here (smooth) Golgi apparatus – wraps around products of a secretory cell (secretion = ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
Action Potential Web Quest
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
... 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 major types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: ...
BGYB30 Mammalian Physiology • Today: • Next Lecture:
... Course Goals: • Understand the underlying mechanisms that contribute to nerve, muscle, and endocrine function • Understand the cellular basis for higher order physiological systems • Appreciate the experimental foundations of physiological knowledge ...
... Course Goals: • Understand the underlying mechanisms that contribute to nerve, muscle, and endocrine function • Understand the cellular basis for higher order physiological systems • Appreciate the experimental foundations of physiological knowledge ...
Transport through plasma membranes
... Water molecules are polar, but are small enough to pass through cell membranes. Because O2 and CO2 are soluble in lipids, they can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Because the size and polarity of Glucose and sucrose, they cannot diffuse directly through ...
... Water molecules are polar, but are small enough to pass through cell membranes. Because O2 and CO2 are soluble in lipids, they can diffuse directly through the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. Because the size and polarity of Glucose and sucrose, they cannot diffuse directly through ...
A. Cellular Physiology a. Describe the cell membrane and its
... composed of 2 α (95 kd binds ATP and digoxin) and 2 ß 3Na+ (40 kd glycoprotein) subunits. Na+ binding is associated with phosphorylation generates a membrane potential rate-limited by intracellular Na+ responsible for most of BMR symport transport coupled to an electrical or chemical gradient e.g. N ...
... composed of 2 α (95 kd binds ATP and digoxin) and 2 ß 3Na+ (40 kd glycoprotein) subunits. Na+ binding is associated with phosphorylation generates a membrane potential rate-limited by intracellular Na+ responsible for most of BMR symport transport coupled to an electrical or chemical gradient e.g. N ...
the nervous sys. The function of neuron & Glia
... These differences in ion concentrations are known as ion concentration gradients. The fact that membrane is permeable to K but barely permeable to Na produces a voltage across the membrane called a resting membrane potential ( = RMP). This is usually 1/14 of a volt inside negative (or -70mV) and is ...
... These differences in ion concentrations are known as ion concentration gradients. The fact that membrane is permeable to K but barely permeable to Na produces a voltage across the membrane called a resting membrane potential ( = RMP). This is usually 1/14 of a volt inside negative (or -70mV) and is ...
Chapter 11 - Nervous Tissue
... not a continuous region to region depolarization instead, a “jumping” depolarization myelinated axons transmit an Action Potential differently the myelin sheath acts as an insulator preventing ion flows in and out of the membrane neurofibral nodes (node of Ranvier) interrupt the myelin she ...
... not a continuous region to region depolarization instead, a “jumping” depolarization myelinated axons transmit an Action Potential differently the myelin sheath acts as an insulator preventing ion flows in and out of the membrane neurofibral nodes (node of Ranvier) interrupt the myelin she ...
Neuron Function
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
Biology Notes: The Nervous System and Neurons
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
Types of neurons
... With inputs to dendrites inside becomes more positive if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
... With inputs to dendrites inside becomes more positive if resting potential rises above threshold an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon Figure shows resting axon being approached by an AP ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.