Nervous System Neuron: nerve cell, functional unit of nervous
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
... Purpose of the refractory period is to make the stimulus reach the end because of the potassium. Parts of axon not covered by myelin the action potential jumps Nodes of Ranvier which have voltage gated channels. This is known as the refractory period. Cell begins to Reset Once refectory, +40 mV is r ...
The Resting Potential II
... also, conductances are much more easily measured than permeablities o permeability describes the ease with which an ion can move through the membrane o conductance describes the ability of a given ion species to carry electrical current across the membrane conductance depends on permeability, bu ...
... also, conductances are much more easily measured than permeablities o permeability describes the ease with which an ion can move through the membrane o conductance describes the ability of a given ion species to carry electrical current across the membrane conductance depends on permeability, bu ...
To allow an immediate response to stimuli in the
... -Often, axons will be wrapped in a “Myelin sheath” (fat) -Gaps in this sheath are known as “nodes of Ranvier” B. Neuroglia -“supporting” cells; support, insulate and protect neurons -“Schwann cells” = neuroglia which produce the myelin sheath ...
... -Often, axons will be wrapped in a “Myelin sheath” (fat) -Gaps in this sheath are known as “nodes of Ranvier” B. Neuroglia -“supporting” cells; support, insulate and protect neurons -“Schwann cells” = neuroglia which produce the myelin sheath ...
04-21-06
... The resting membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive TECHNIQUE salt solution. On ...
... The resting membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive TECHNIQUE salt solution. On ...
Lecture_29_noquiz
... The Goldman Equation extends the Nernst Equation to consider the relative permeabilities of the ions (P): Ions with higher P have a larger effect on Emembrane ...
... The Goldman Equation extends the Nernst Equation to consider the relative permeabilities of the ions (P): Ions with higher P have a larger effect on Emembrane ...
Neural transmission
... Multiple Sclerosis is an incurable debilitating disease of the central nervous system. MS affects young to middle aged adults. Approximately 4 million worldwide have this disease. 400,000 of these people live in the United States. It can affect anyone, and can strike at anytime without warning. Once ...
... Multiple Sclerosis is an incurable debilitating disease of the central nervous system. MS affects young to middle aged adults. Approximately 4 million worldwide have this disease. 400,000 of these people live in the United States. It can affect anyone, and can strike at anytime without warning. Once ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
The nervous system
... Positively charged ions move both into and out of the cell The diffusion is not equal and the resting membrane is about 50 times more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium. ...
... Positively charged ions move both into and out of the cell The diffusion is not equal and the resting membrane is about 50 times more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium. ...
The nervous system
... Positively charged ions move both into and out of the cell The diffusion is not equal and the resting membrane is about 50 times more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium. ...
... Positively charged ions move both into and out of the cell The diffusion is not equal and the resting membrane is about 50 times more permeable to potassium ions than to sodium. ...
Gated Channels
... (a) In a bare plasma membrane (without voltage-gated channels), as on a dendrite, voltage decays because current leaks across the membrane. Voltage-gated ...
... (a) In a bare plasma membrane (without voltage-gated channels), as on a dendrite, voltage decays because current leaks across the membrane. Voltage-gated ...
File
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
... Neurons either fire maximally or not at all, this is referred to as the “all or none” response Increasing neuronal stimulation beyond a critical level will not result in an increased response Neurons response to increased stimulation by increasing the frequency of firing, not the intensity at wh ...
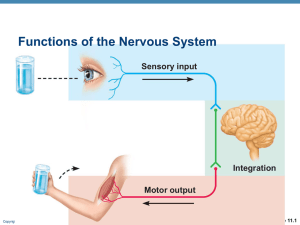
We have seen how the Nervous System plays an important role in
... This needs A LOT of help. Good diagrams are a must for this topic!!! I’m not sure if this is too specific and needs to be more general, or if it is too general and needs to be more specific???????? We have seen how the nervous system plays an important role in reaction time, stability and balance, h ...
... This needs A LOT of help. Good diagrams are a must for this topic!!! I’m not sure if this is too specific and needs to be more general, or if it is too general and needs to be more specific???????? We have seen how the nervous system plays an important role in reaction time, stability and balance, h ...
Chap 28 – Nervous System Part 2 – Synaptic Transmission
... Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Unit 8 Nervous System
... Resting membrane potential Differences in ionic makeup ICF has lower concentration of Na+ and Cl- than ECF ICF has higher concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins (A-) than ECF ...
... Resting membrane potential Differences in ionic makeup ICF has lower concentration of Na+ and Cl- than ECF ICF has higher concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins (A-) than ECF ...
Neurophysiology Neurotransmitter and Nervous System
... membranes of dendrites and cell bodies do not have action potentials. Instead, any depolarizing stimulus causes a post synaptic potential (PSP) which spreads out across the membrane. The depolarization is weaker the further it gets from the stimulus. When the stimulus is turned off, the PSP disappea ...
... membranes of dendrites and cell bodies do not have action potentials. Instead, any depolarizing stimulus causes a post synaptic potential (PSP) which spreads out across the membrane. The depolarization is weaker the further it gets from the stimulus. When the stimulus is turned off, the PSP disappea ...
The Nervous System 35-2
... outside the cell and a negative charge inside the cell. This is caused by sodium and potassium pump which pumps sodium out and potassium into the cell. Potassium can leak out of the cell faster than sodium which leaves a negative charge on the inside of the cell. ...
... outside the cell and a negative charge inside the cell. This is caused by sodium and potassium pump which pumps sodium out and potassium into the cell. Potassium can leak out of the cell faster than sodium which leaves a negative charge on the inside of the cell. ...
Cell Review ppt with Anwwers
... a 50% sugar solution. Sugar molecules are very big, and cannot pass through the membrane. If I want to make the cell gain weight, which beaker should I place it into? **Explain your choice** a. beaker of 70% sugar solution b. beaker of water c. beaker of 90% sugar solution d. beaker of any type of s ...
... a 50% sugar solution. Sugar molecules are very big, and cannot pass through the membrane. If I want to make the cell gain weight, which beaker should I place it into? **Explain your choice** a. beaker of 70% sugar solution b. beaker of water c. beaker of 90% sugar solution d. beaker of any type of s ...
electrochemical impulse
... • When a sensory neuron detects a change in the environment known as a stimulus, it has to be strong enough to trigger the depolarization of the membrane. • The intensity of the stimulus must reach a set level called the threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for ...
... • When a sensory neuron detects a change in the environment known as a stimulus, it has to be strong enough to trigger the depolarization of the membrane. • The intensity of the stimulus must reach a set level called the threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for ...
Action Potential
... How does the action potential have an effect ? propagation- action potential progresses down the cell membrane by segments. one region is stimulated, then the region next to it is, etc. electrical current changes shape of channels in adjacent regions * Na+ channels ...
... How does the action potential have an effect ? propagation- action potential progresses down the cell membrane by segments. one region is stimulated, then the region next to it is, etc. electrical current changes shape of channels in adjacent regions * Na+ channels ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... receive messages from other neurons. The dendrites and cell body are covered with synapses formed by the ends of axons of other neurons. Neurons signal by transmitting electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch to three or more feet. Glia cells: ...
... receive messages from other neurons. The dendrites and cell body are covered with synapses formed by the ends of axons of other neurons. Neurons signal by transmitting electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch to three or more feet. Glia cells: ...
The NERVOUS System
... E. Characteristics of Nerves • Nerves (Neurons) • amitotic: they do not divide (cannot be replaced if destroyed) -high metabolic rate-require constant O2 and glucose, die within a few minutes without O2 ...
... E. Characteristics of Nerves • Nerves (Neurons) • amitotic: they do not divide (cannot be replaced if destroyed) -high metabolic rate-require constant O2 and glucose, die within a few minutes without O2 ...
Sxn 2 Objectives
... Predict the movement of an ion based on its charge (e.g. negative towards positive) State the membrane potential difference of a cell given intracellular and extracellular fluid absolute and relative charges. Explain how the resting membrane potential is generated and the role of ATP transport ...
... Predict the movement of an ion based on its charge (e.g. negative towards positive) State the membrane potential difference of a cell given intracellular and extracellular fluid absolute and relative charges. Explain how the resting membrane potential is generated and the role of ATP transport ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... o Increases the positive charge outside the cell o Depolarization becomes harder to achieve More Na+ channels must open for it to occur Many neural transmitters can be both excitatory and inhibitory Summation The effect produced by the accumulation of a variety of neurotransmitters from two or ...
... o Increases the positive charge outside the cell o Depolarization becomes harder to achieve More Na+ channels must open for it to occur Many neural transmitters can be both excitatory and inhibitory Summation The effect produced by the accumulation of a variety of neurotransmitters from two or ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.