Chapter 5 Gases - Bethel Local Schools
... • Cnidarians and echinoderms have a simple nervous system, a nerve net with no central integrating organ. • Bilateral animals have three types of neurons: sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. • Flatworms have paired ganglia that serve as an integrating center. Other invertebrates have m ...
... • Cnidarians and echinoderms have a simple nervous system, a nerve net with no central integrating organ. • Bilateral animals have three types of neurons: sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. • Flatworms have paired ganglia that serve as an integrating center. Other invertebrates have m ...
Worksheet - Nervous System I Lecture Notes Page
... must open then close in sequence along the entire length of the cell membrane. This results in a relative ________________ (slower/faster) rate of conduction. In contract, myelinated neurons are capable of ___________________________(continuous/saltatory) conduction. In this type of conduction only ...
... must open then close in sequence along the entire length of the cell membrane. This results in a relative ________________ (slower/faster) rate of conduction. In contract, myelinated neurons are capable of ___________________________(continuous/saltatory) conduction. In this type of conduction only ...
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION
... the mechanism behind various events. For example, How does drinking alcohol increase urinary output? How does muscle get bigger when it’s put under mechanical stress (i.e. ...
... the mechanism behind various events. For example, How does drinking alcohol increase urinary output? How does muscle get bigger when it’s put under mechanical stress (i.e. ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... In the neuron, ions are moved by two forces (potential energy): Concentration Gradients: difference in distribution for various ions between the inside and outside of the membrane Electrical Gradient: the difference in positive and negative ...
... In the neuron, ions are moved by two forces (potential energy): Concentration Gradients: difference in distribution for various ions between the inside and outside of the membrane Electrical Gradient: the difference in positive and negative ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... - gap junctions link the cytosol of two cells - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important in some reflexes - chemical synaps ...
... - gap junctions link the cytosol of two cells - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important in some reflexes - chemical synaps ...
HERE
... 1. Neurons maintain different concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. What ion is in high concentration outside the neuron? _____________________ 2. Which ion is in high concentration inside the neuron? ___________________ 3. What specialized protein exists in the neural cell mem ...
... 1. Neurons maintain different concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. What ion is in high concentration outside the neuron? _____________________ 2. Which ion is in high concentration inside the neuron? ___________________ 3. What specialized protein exists in the neural cell mem ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-14
... Salt and sour receptors -chemically gated ion channels *salt and sour work directly on ion channel Sweet, bitter and umani receptors -gustducins – g proteins *use a second messenger cascade that will eventually affect ion channel ...
... Salt and sour receptors -chemically gated ion channels *salt and sour work directly on ion channel Sweet, bitter and umani receptors -gustducins – g proteins *use a second messenger cascade that will eventually affect ion channel ...
1. If a significant amount of Cl - entered the body of a motor neuron
... 15. When the sodium potassium pump breaks down a molecule of ATP, ______ K+ ions are moved into the cell and ______ Na+ are moved out of the cell. a. 2-3 b. 3-2 c. 3-4 d. 4-3 e. None of the above 16. The influx of sodium will cause the membrane potential of a neuron to: a. Increase b. Decrease c. S ...
... 15. When the sodium potassium pump breaks down a molecule of ATP, ______ K+ ions are moved into the cell and ______ Na+ are moved out of the cell. a. 2-3 b. 3-2 c. 3-4 d. 4-3 e. None of the above 16. The influx of sodium will cause the membrane potential of a neuron to: a. Increase b. Decrease c. S ...
Nerve Cells PPT
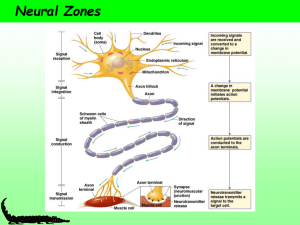
... DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential (electrical charges) of the neuron builds up before it trans ...
... DENDRITES function to receive the signal and carry the nerve conduction toward the cell body. SOMA (cell body) is where the nucleus, ribosomes, and most organelles are located AXON HILLOCK is the area on the soma where the action potential (electrical charges) of the neuron builds up before it trans ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... • Direct synaptic transmission Neurotransmitter binds directly to ligand-gated channels Channel opens for Na+, K+ or both ...
... • Direct synaptic transmission Neurotransmitter binds directly to ligand-gated channels Channel opens for Na+, K+ or both ...
Lecture #13 * Animal Nervous Systems
... • Direct synaptic transmission Neurotransmitter binds directly to ligand-gated channels Channel opens for Na+, K+ or both ...
... • Direct synaptic transmission Neurotransmitter binds directly to ligand-gated channels Channel opens for Na+, K+ or both ...
Terms being described
... 9. It refers to the action potential firing to maximum amplitude or not at all. [3 words] 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change t ...
... 9. It refers to the action potential firing to maximum amplitude or not at all. [3 words] 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change t ...
Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... Concept 48.3: Action potentials (nerve impulses) are the signals conducted by axons • Neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli • You’ll want to review this pic after you understand the action potential ...
... Concept 48.3: Action potentials (nerve impulses) are the signals conducted by axons • Neurons contain gated ion channels that open or close in response to stimuli • You’ll want to review this pic after you understand the action potential ...
Action_ Resting_Potential
... resting state. In the resting state, the inside of a neuron has a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions than the outside does. This situation creates a slight negative charge inside the neuron, which acts as a store of potential energy called the resting potential. The resting pot ...
... resting state. In the resting state, the inside of a neuron has a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions than the outside does. This situation creates a slight negative charge inside the neuron, which acts as a store of potential energy called the resting potential. The resting pot ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... • Propagated changes in transmembrane potential • Affect an entire excitable membrane • Link graded potentials at cell body with motor end plate actions • They are “all-or-none” ...
... • Propagated changes in transmembrane potential • Affect an entire excitable membrane • Link graded potentials at cell body with motor end plate actions • They are “all-or-none” ...
Biology 12 Nervous System Major Divisions of Nervous System 1
... • a nerve impulse along a neuron consists of a wave of change of polarity or charge along it's length. • This change can be measured by using an oscilloscope which shows the voltage changes along the neuron. It records changes in polarity. Resting Potential: • When a neuron is not conducting a nerve ...
... • a nerve impulse along a neuron consists of a wave of change of polarity or charge along it's length. • This change can be measured by using an oscilloscope which shows the voltage changes along the neuron. It records changes in polarity. Resting Potential: • When a neuron is not conducting a nerve ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... by the binding of an inhibitory neurotransmitter from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic receptor; makes it more difficult for a postsynaptic neuron to generate an action potential ...
... by the binding of an inhibitory neurotransmitter from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic receptor; makes it more difficult for a postsynaptic neuron to generate an action potential ...
1. When the reaction Cu + HNO3 → Cu2+ + NO + H2O is balanced
... 14. The pair _____ has the better oxidizing agent listed first. A) Au3+, Br2 B) H2, Ag+ C) Cr3+, Cd2+ D) O2 in basic media, O2 in acidic media 15. The pair _____ has the better reducing agent listed first. A) H2, I2 B) Ag, Fe2+ C) Co2+, Brฏ D) Na, Li 16. The relation connecting ∆Gฐ and Eฐ is _____. ...
... 14. The pair _____ has the better oxidizing agent listed first. A) Au3+, Br2 B) H2, Ag+ C) Cr3+, Cd2+ D) O2 in basic media, O2 in acidic media 15. The pair _____ has the better reducing agent listed first. A) H2, I2 B) Ag, Fe2+ C) Co2+, Brฏ D) Na, Li 16. The relation connecting ∆Gฐ and Eฐ is _____. ...
Membrane potential moves toward the K equilibrium
... High Resistance, low permeability to ions Salt solution (ICF and ECF): Low Resistance, easy for ions to move ...
... High Resistance, low permeability to ions Salt solution (ICF and ECF): Low Resistance, easy for ions to move ...
Notes of Neuronal Firing
... A graded potential can only travel a short distance because the change in voltage spreads by the passive movement of ions in a process called electrotonic conduction. As the current moves further from the site of stimulation, the membrane potential decreases because the ions diffuse and the ions pas ...
... A graded potential can only travel a short distance because the change in voltage spreads by the passive movement of ions in a process called electrotonic conduction. As the current moves further from the site of stimulation, the membrane potential decreases because the ions diffuse and the ions pas ...
Nervous System
... Different regions of the vertebrate brain have different functions. On the diagram below, label the parts of the brain responsible for vision, ...
... Different regions of the vertebrate brain have different functions. On the diagram below, label the parts of the brain responsible for vision, ...
barriers pores pumps and gates gapped notes
... creates the K+ and Na+ gradients • K+ movement down its gradient creates the membrane potential • - because K+ ions only can cross the membrane. • What is important is not that the membrane is K+ permeable but rather that it is ……………… to other ions. • The value of the membrane potential may be calcu ...
... creates the K+ and Na+ gradients • K+ movement down its gradient creates the membrane potential • - because K+ ions only can cross the membrane. • What is important is not that the membrane is K+ permeable but rather that it is ……………… to other ions. • The value of the membrane potential may be calcu ...
action potential
... 4. During the falling phase, voltage-gated Na+ channels become inactivated; voltage-gated K+ channels open, and K+ flows out of the cell ...
... 4. During the falling phase, voltage-gated Na+ channels become inactivated; voltage-gated K+ channels open, and K+ flows out of the cell ...
Chapter 04: The Action Potential
... the next AP once an AP is initiated ~ 1 msec - Relative refractory period : for a few miliseconds after the end of absolute refractory period, current needed to reach threshold is above normal ...
... the next AP once an AP is initiated ~ 1 msec - Relative refractory period : for a few miliseconds after the end of absolute refractory period, current needed to reach threshold is above normal ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.