nerve_pharmacy_(mana..
... Causes of RMP: • 1. RMP is 100 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. K+ tends to leak out of the cell down its conc gradient, carrying +ve charge with it. (through K leak channels). • 2. non-diffusible anions (proteins, sulphate and phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na ...
... Causes of RMP: • 1. RMP is 100 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. K+ tends to leak out of the cell down its conc gradient, carrying +ve charge with it. (through K leak channels). • 2. non-diffusible anions (proteins, sulphate and phosphate ions) cannot leave the cell. • 3. very small amount of Na ...
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular
... left arrives at left ear first 2. Phase difference: ex., continuous sound waves will reach each ear at slightly different phases of the oscillating sound waves - these mechanisms work best with sounds of moderate frequencies 3. Intensity difference: ex., sound generated to the left are sensed slight ...
... left arrives at left ear first 2. Phase difference: ex., continuous sound waves will reach each ear at slightly different phases of the oscillating sound waves - these mechanisms work best with sounds of moderate frequencies 3. Intensity difference: ex., sound generated to the left are sensed slight ...
Chapter 48 Nervous System
... The nervous, endocrine and immune systems often cooperate and interact in regulating internal body functions to maintain homeostasis. The ability of an organism to survive and maintain homeostasis depends largely on how it responds to internal and external stimuli. A stimulus is an agent or a change ...
... The nervous, endocrine and immune systems often cooperate and interact in regulating internal body functions to maintain homeostasis. The ability of an organism to survive and maintain homeostasis depends largely on how it responds to internal and external stimuli. A stimulus is an agent or a change ...
Questions for Exam #3
... One of the TRP channels, call it TRPQ, opens in response to heat. TRPQ is a nonspecific cation channel. TRPQ is found in the sensory neurons that detect heat; these neurons can fire APs. Exposure to the compound capsaicin, the active ingredient in hot peppers, also opens TRPQ channels in sensory neu ...
... One of the TRP channels, call it TRPQ, opens in response to heat. TRPQ is a nonspecific cation channel. TRPQ is found in the sensory neurons that detect heat; these neurons can fire APs. Exposure to the compound capsaicin, the active ingredient in hot peppers, also opens TRPQ channels in sensory neu ...
Total Internal reflection Fluorescence Microscopy: Instrumentation
... proportional to evanescent intensity I(z). If fluorophore moves from z1 to z2, z= z1- z2 = dln (I2/I1) This relationship is valid even in those cases where there are multiple fluorophores attached to the same structure or irregularly shaped fluorophores. ...
... proportional to evanescent intensity I(z). If fluorophore moves from z1 to z2, z= z1- z2 = dln (I2/I1) This relationship is valid even in those cases where there are multiple fluorophores attached to the same structure or irregularly shaped fluorophores. ...
Feedback — Exam
... strengthens/weakens as a function of the timing of prevs. postsynaptic spikes (STDP). Mark the correct sentences. When the pre synaptic cell fires a spike immediately after the post synaptic cell – no change in the synaptic strength When the postsynaptic spike fires before the pre-synaptic spike, th ...
... strengthens/weakens as a function of the timing of prevs. postsynaptic spikes (STDP). Mark the correct sentences. When the pre synaptic cell fires a spike immediately after the post synaptic cell – no change in the synaptic strength When the postsynaptic spike fires before the pre-synaptic spike, th ...
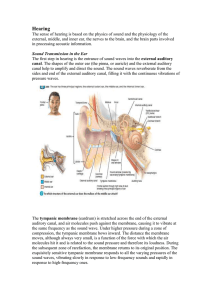
Ear
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary
... Value of the resting membrane potential on a “resting” neuron: ____________________ Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: _______ ...
... Value of the resting membrane potential on a “resting” neuron: ____________________ Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: _______ ...
File
... has mitochondria, ribosomes, a cell membrane, a nucleus, etc. This is because the cell needs to survive just like any other Similar cell. Different ...
... has mitochondria, ribosomes, a cell membrane, a nucleus, etc. This is because the cell needs to survive just like any other Similar cell. Different ...
The Nervous System
... Conducted by Axons ● hyperpolarization: increase in the magnitude of the membrane potential ○ caused by opening of gated K+ channels ● depolarization: reduction of the magnitude of the membrane potential ○ caused by opening of gated Na+ channels ● graded potentials: changes in membrane potential ● t ...
... Conducted by Axons ● hyperpolarization: increase in the magnitude of the membrane potential ○ caused by opening of gated K+ channels ● depolarization: reduction of the magnitude of the membrane potential ○ caused by opening of gated Na+ channels ● graded potentials: changes in membrane potential ● t ...
Regulation Systems: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... •Cell body – contains nucleus and other organelles •Dendrite – receives impulse from another neuron •Axon – sends impulses to other neurons, muscles or glands •The axons of some neurons have a myelin sheath for protection and faster transmission. ...
... •Cell body – contains nucleus and other organelles •Dendrite – receives impulse from another neuron •Axon – sends impulses to other neurons, muscles or glands •The axons of some neurons have a myelin sheath for protection and faster transmission. ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
File
... • An action potential can travel long distances by regenerating itself along the axon. • At the site where the action potential is generated, usually the axon hillock, an electrical current depolarizes the neighboring region of the axon membrane. • Inactivated Na+ channels behind the zone of depolar ...
... • An action potential can travel long distances by regenerating itself along the axon. • At the site where the action potential is generated, usually the axon hillock, an electrical current depolarizes the neighboring region of the axon membrane. • Inactivated Na+ channels behind the zone of depolar ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... – motor commands: control activities of peripheral organs (e.g., skeletal muscles) – higher functions of brain: intelligence, memory, learning, emotion ...
... – motor commands: control activities of peripheral organs (e.g., skeletal muscles) – higher functions of brain: intelligence, memory, learning, emotion ...
Chapter 10b
... 4 The fluid waves push on the 5 Neurotransmitter release onto sensory neurons flexible membranes of the creates action potentials cochlear duct. Hair cells bend that travel through the and ion channels open, cochlear nerve to creating an electrical signal that the brain. alters neurotransmitter rele ...
... 4 The fluid waves push on the 5 Neurotransmitter release onto sensory neurons flexible membranes of the creates action potentials cochlear duct. Hair cells bend that travel through the and ion channels open, cochlear nerve to creating an electrical signal that the brain. alters neurotransmitter rele ...
Chapter 48 Presentation
... This equation applies to any membrane that is permeable to a single type of ion. All you need to know is the ion concentration inside and outside of the membrane. A minus sign indicates the inside is more negative than the outside. travismulthaupt.com ...
... This equation applies to any membrane that is permeable to a single type of ion. All you need to know is the ion concentration inside and outside of the membrane. A minus sign indicates the inside is more negative than the outside. travismulthaupt.com ...
Systems Neuroscience Auditory system
... The up-and-down motion of the basilar membrane causes the organ of Corti to vibrate up-and-down, which, in turn causes the stereocilia to bend back-and-forth. Polarization of the stereocilia (B) When the organ of Corti moves upward, the stereocilia bend away from the limbus and ...
... The up-and-down motion of the basilar membrane causes the organ of Corti to vibrate up-and-down, which, in turn causes the stereocilia to bend back-and-forth. Polarization of the stereocilia (B) When the organ of Corti moves upward, the stereocilia bend away from the limbus and ...
Title: Nervous System
... Binding of a signal molecule – into an intracellular response that modifies the behavior of target cell a) Phase I – binding of first messenger (transmitter) to the receptor (T+R) b) Phase II – transduction of a signal into the intracellular compartment. T+R complex interacts with a specific G-prote ...
... Binding of a signal molecule – into an intracellular response that modifies the behavior of target cell a) Phase I – binding of first messenger (transmitter) to the receptor (T+R) b) Phase II – transduction of a signal into the intracellular compartment. T+R complex interacts with a specific G-prote ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Types of gated ions. • Chemically-gated ion channels open or close in response to a chemical stimulus. • Voltage-gated ion channels open or close in response to a change in membrane potential. ...
... • Types of gated ions. • Chemically-gated ion channels open or close in response to a chemical stimulus. • Voltage-gated ion channels open or close in response to a change in membrane potential. ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... – K+ inside and outside of the cell are attracted to the negative charges on the inside of the cell membrane, and repelled by the positive charges on the outside of the cell membrane • indicated in white on the next slide ...
... – K+ inside and outside of the cell are attracted to the negative charges on the inside of the cell membrane, and repelled by the positive charges on the outside of the cell membrane • indicated in white on the next slide ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.