
CPB748_JK Nervous
... • The membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. TECHNIQUE A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive salt solution. One end ...
... • The membrane potential of a cell can be measured APPLICATION Electrophysiologists use intracellular recording to measure the membrane potential of neurons and other cells. TECHNIQUE A microelectrode is made from a glass capillary tube filled with an electrically conductive salt solution. One end ...
Nervous System
... • If membrane potential becomes less negative, it has depolarized • Graded (or proportional) to intensity of stimulation, meaning the greater the stimulation, the greater the depolarization • if the depolarization is great enough, reach threshold potential ...
... • If membrane potential becomes less negative, it has depolarized • Graded (or proportional) to intensity of stimulation, meaning the greater the stimulation, the greater the depolarization • if the depolarization is great enough, reach threshold potential ...
Unit 4 - cloudfront.net
... 5. If the cell voltage is positive (_________________ cell), then the reaction is spontaneous, therefore the G= _____. If G is positive, then the reaction requires an input of energy to make it occur (_______________________ cell). If G = 0, then the reaction is at equilibrium. 6. Determine the ...
... 5. If the cell voltage is positive (_________________ cell), then the reaction is spontaneous, therefore the G= _____. If G is positive, then the reaction requires an input of energy to make it occur (_______________________ cell). If G = 0, then the reaction is at equilibrium. 6. Determine the ...
Building Blocks File
... • Cells are surrounded by …………..and have fluid inside them • The concentration of substances inside and outside the cell is usually the same/different (delete one) • To enter a cell, a substance may have to move AGAINST its ………………………………..gradient LCSC06 | Biosciences for SLT ...
... • Cells are surrounded by …………..and have fluid inside them • The concentration of substances inside and outside the cell is usually the same/different (delete one) • To enter a cell, a substance may have to move AGAINST its ………………………………..gradient LCSC06 | Biosciences for SLT ...
The Nervous System
... • Graded potentials by themselves cannot trigger activation of large neurons and muscle fibers – Referred to as having excitable membranes ...
... • Graded potentials by themselves cannot trigger activation of large neurons and muscle fibers – Referred to as having excitable membranes ...
Lecture12 PPT
... shifts to a value between +40 and +50 mV. • Then, voltage-activated potassium channels open, allowing K+ to rush out. ...
... shifts to a value between +40 and +50 mV. • Then, voltage-activated potassium channels open, allowing K+ to rush out. ...
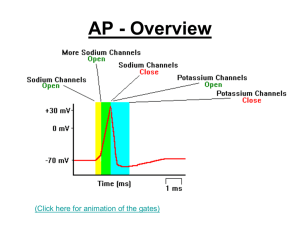
AP – All or nothing
... • During the action potential, the membrane is depolarised. • Following the impulse K+ ions move out of the membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
... • During the action potential, the membrane is depolarised. • Following the impulse K+ ions move out of the membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
NeuroMuscular Junction and Excitation Coupling IP
... 3. (P 3.) How are skeletal muscle cells electrically insulated from each other? _______________________________ 4. (P 3.) What is a motor neuron? 5. (P3.) What part of the motor neuron carries impulses to the muscle? Describe its structure. 6. (P 4.) Match the following terms to their description: A ...
... 3. (P 3.) How are skeletal muscle cells electrically insulated from each other? _______________________________ 4. (P 3.) What is a motor neuron? 5. (P3.) What part of the motor neuron carries impulses to the muscle? Describe its structure. 6. (P 4.) Match the following terms to their description: A ...
[j26]Chapter 7#
... The Na+/K+ pumps are not directly involved in the formation of an action potential; rather they are required to maintain the proper, opposing concentration gradients of these two ions. Within a collection of axons (or nerves), a low-intensity stimulus will only activate those few fibers with low thr ...
... The Na+/K+ pumps are not directly involved in the formation of an action potential; rather they are required to maintain the proper, opposing concentration gradients of these two ions. Within a collection of axons (or nerves), a low-intensity stimulus will only activate those few fibers with low thr ...
[j26]Chapter 7#
... ___ 35. The Na+/K+ pumps are not directly involved in the formation of an action potential; rather they are required to maintain the proper, opposing concentration gradients of these two ions. ___ 36. Within a collection of axons (or nerves), a low-intensity stimulus will only activate those few fi ...
... ___ 35. The Na+/K+ pumps are not directly involved in the formation of an action potential; rather they are required to maintain the proper, opposing concentration gradients of these two ions. ___ 36. Within a collection of axons (or nerves), a low-intensity stimulus will only activate those few fi ...
Academic Half-Day Neurophysiology 101
... outward currents result in hypperpolarization of membrane further away from threshold for action potential generation ...
... outward currents result in hypperpolarization of membrane further away from threshold for action potential generation ...
effects of inhibitors of cell membrane calcium channels
... Muscle Biology and Physiopathology Unit, Padova, Italy. This work investigated the role of extracellular Ca2+ influx through cell membrane Ca2+ channels during high-frequency fatigue (HFF) in slow and fast skeletal muscles of mice. The study was performed in both innervated and in 14-day denervated ...
... Muscle Biology and Physiopathology Unit, Padova, Italy. This work investigated the role of extracellular Ca2+ influx through cell membrane Ca2+ channels during high-frequency fatigue (HFF) in slow and fast skeletal muscles of mice. The study was performed in both innervated and in 14-day denervated ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... - open in response to the presence of specific chemicals (e.g. ACh) at a binding site - found on the dendrites and cell body of a neuron 2. voltage-regulated channels: - respond to changes in the transmembrane potential - characteristic of excitable membrane - found in axons of neurons, sarcolemma o ...
... - open in response to the presence of specific chemicals (e.g. ACh) at a binding site - found on the dendrites and cell body of a neuron 2. voltage-regulated channels: - respond to changes in the transmembrane potential - characteristic of excitable membrane - found in axons of neurons, sarcolemma o ...
AP Biology Chapter 48 Neurons Guided Notes
... Graded Potentials and Action Potentials • ___________________ are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with the strength of the stimulus • These are not the nerve signals that travel along axons, but they do have an effect on the generation of nerve signals ...
... Graded Potentials and Action Potentials • ___________________ are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with the strength of the stimulus • These are not the nerve signals that travel along axons, but they do have an effect on the generation of nerve signals ...
primary motor Cortex
... Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Initially, a stimulus will cause the membrane to depolarize toward threshold. When this occurs, voltage-gated Na+ channels begin to open. As a result, Na+ ions enter the cell down their concentration and electri ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Initially, a stimulus will cause the membrane to depolarize toward threshold. When this occurs, voltage-gated Na+ channels begin to open. As a result, Na+ ions enter the cell down their concentration and electri ...
neuro jeopardy
... A membrane maintains its resting potential mainly due to _________. a. the sodium-potassium pump b. chemically gated sodium channels c. potassium leak channels d. calcium leak channels BACK TO GAME ...
... A membrane maintains its resting potential mainly due to _________. a. the sodium-potassium pump b. chemically gated sodium channels c. potassium leak channels d. calcium leak channels BACK TO GAME ...
The Special Senses Accessory Structures of the - dr
... Tympanic cavity Ossicles- malleus, incus, stapes (merge onto oval window)- transmit sound from external ear to internal ear. Increase force but not the amplitude of vibrations transmitted by tympanic membrane eustachian tube/ auditory tube- equalizes air pressure Oval window (stapes) Round window – ...
... Tympanic cavity Ossicles- malleus, incus, stapes (merge onto oval window)- transmit sound from external ear to internal ear. Increase force but not the amplitude of vibrations transmitted by tympanic membrane eustachian tube/ auditory tube- equalizes air pressure Oval window (stapes) Round window – ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... potential contributing to Na+, K+ or leak channel ion flow we take the difference between the potential and the Nernst potential. The Nernst potential is the membrane potential at which there is no ion flow between the intracellular space and the extracellular space[4]. The Nernst potential is denot ...
... potential contributing to Na+, K+ or leak channel ion flow we take the difference between the potential and the Nernst potential. The Nernst potential is the membrane potential at which there is no ion flow between the intracellular space and the extracellular space[4]. The Nernst potential is denot ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • At the same time, voltage-gated K+ channels slowly begin to open. Most of these channels open at about the time that the membrane potential is about +50mV. At this point, K+ ions are driven out by the +50mV charge and by their high internal concentration; this repolarizes the neuron and leaves it ...
... • At the same time, voltage-gated K+ channels slowly begin to open. Most of these channels open at about the time that the membrane potential is about +50mV. At this point, K+ ions are driven out by the +50mV charge and by their high internal concentration; this repolarizes the neuron and leaves it ...
48 BIOLOGY 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014
... Graded Potentials Graded potentials are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with strength of the stimulus ...
... Graded Potentials Graded potentials are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with strength of the stimulus ...
Chapter 48
... Conduction of Action Potentials At the site where the action potential is generated (usually the axon hillock) an electrical current depolarizes the neighboring region of the axon membrane Action potentials travel in only one direction: toward the synaptic terminals ...
... Conduction of Action Potentials At the site where the action potential is generated (usually the axon hillock) an electrical current depolarizes the neighboring region of the axon membrane Action potentials travel in only one direction: toward the synaptic terminals ...
Biopsychology 2012 – sec 002
... The study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and on behavior. What is a drug? An exogenous chemical not necessary for normal cellular functioning that significantly alters the functions of certain cells of the body when taken in relatively low doses (in this context, cells of the nervous ...
... The study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and on behavior. What is a drug? An exogenous chemical not necessary for normal cellular functioning that significantly alters the functions of certain cells of the body when taken in relatively low doses (in this context, cells of the nervous ...
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis part 1
... of ions across their membranes. Sodium ions are pumped out and potassium ions are pumped in. There are chloride ions, DNA and other negatively charged ions inside the neuron that are fairly large and have a tendency to stay inside which creates a net negative charge inside the neuron as compared wit ...
... of ions across their membranes. Sodium ions are pumped out and potassium ions are pumped in. There are chloride ions, DNA and other negatively charged ions inside the neuron that are fairly large and have a tendency to stay inside which creates a net negative charge inside the neuron as compared wit ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
... level and an action potential will be produced, then the signal will travel along the second nerve or muscle cell. In summation, if there are enough IPSPs to keep the membrane potential of the post-synaptic cell negative (hyperpolarized) and cancel out the EPSPs, then the post-synaptic neuron will N ...
... level and an action potential will be produced, then the signal will travel along the second nerve or muscle cell. In summation, if there are enough IPSPs to keep the membrane potential of the post-synaptic cell negative (hyperpolarized) and cancel out the EPSPs, then the post-synaptic neuron will N ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.







![[j26]Chapter 7#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015520931_1-d3d263c2c8c221955c9bc7f03ee94039-300x300.png)
![[j26]Chapter 7#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009487154_1-bf88061009d68b903e2c1573596f45de-300x300.png)













