Chapter 7 How are Plants Classified
... With a partner, answer the following questions and WRITE down what you come up with! You will have approximately 15 minutes to do this (and do it WELL!) You will be sharing your thoughts! ...
... With a partner, answer the following questions and WRITE down what you come up with! You will have approximately 15 minutes to do this (and do it WELL!) You will be sharing your thoughts! ...
Coffee Plant - Sargent Welch
... • Soil: African Violet or Tropical Plant Potting Soil 20 W 8306 should be used. • Propagation: From seed or cuttings during spring or winter. ...
... • Soil: African Violet or Tropical Plant Potting Soil 20 W 8306 should be used. • Propagation: From seed or cuttings during spring or winter. ...
Dahlia Dahlietta
... grown in a bigger pot, pinching to 3- 4 leaf pairs can be used 2 weeks after planting. This will give a better branch growth from the base and therefore increase the number of flowers. The flowering will be delayed by 7 to 10 days. ...
... grown in a bigger pot, pinching to 3- 4 leaf pairs can be used 2 weeks after planting. This will give a better branch growth from the base and therefore increase the number of flowers. The flowering will be delayed by 7 to 10 days. ...
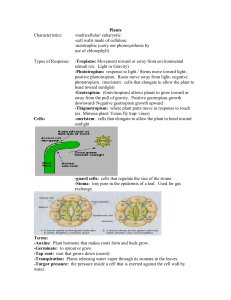
Plant classification
... Flower: contains the reproductive organs of a plant. The main parts of a flower are the calyx, corolla, staments and pistil. ...
... Flower: contains the reproductive organs of a plant. The main parts of a flower are the calyx, corolla, staments and pistil. ...
plants - Cloudfront.net
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
Plants
... minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant. •Xylem Xylem contains vessels, which are made up of cells that conduct water only after they lose their cytoplasm. Water flows between cells through pits and perforations in their cell walls. •Phloem Phloem contains sieve tubes, which are made up ...
... minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant. •Xylem Xylem contains vessels, which are made up of cells that conduct water only after they lose their cytoplasm. Water flows between cells through pits and perforations in their cell walls. •Phloem Phloem contains sieve tubes, which are made up ...
Plants
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
... Xylem-a transport subsystem containing key cells called tracheids. This system carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. Tracheids are hollow cells with thick cell walls that resist pressure (example- drinking straw). Phloem-transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates pro ...
Parts of Flowers Test Review 2014 (1)
... 22) _______ are special features that allow a plant or animal to 22) live in a particular place or habitat. 23) When a seed does not germinate immediately after leaving 23) the parent plant, it goes into a period of ______, or inactivity. 24) In order for a seed to come out of this dormancy state, ...
... 22) _______ are special features that allow a plant or animal to 22) live in a particular place or habitat. 23) When a seed does not germinate immediately after leaving 23) the parent plant, it goes into a period of ______, or inactivity. 24) In order for a seed to come out of this dormancy state, ...
Plantae: Anthophyta
... (photosynthesis). This food is either stored in the roots, used to grow new plant tissue, or fuel production of flowers and seeds. • Roses only make food when their leaves are present. In late fall and winter, the plant is dormant, although food reserves in the roots allow some root growth when the ...
... (photosynthesis). This food is either stored in the roots, used to grow new plant tissue, or fuel production of flowers and seeds. • Roses only make food when their leaves are present. In late fall and winter, the plant is dormant, although food reserves in the roots allow some root growth when the ...
Unit 4 Powerpoint
... Plants with seeds have a greater chance at reproductive success than seedless plants. Why? Two main groups of seed-bearing plants: gymnosperms (“naked” seed) and angiosperms (seed ...
... Plants with seeds have a greater chance at reproductive success than seedless plants. Why? Two main groups of seed-bearing plants: gymnosperms (“naked” seed) and angiosperms (seed ...
Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves
... Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves Directions: 1. )Uses pressed plants, at least six.. ...
... Dichotomous Key for MN Leaves Directions: 1. )Uses pressed plants, at least six.. ...
Capturing Light Energy -Photosynthesis-the process
... -light energy is used to help form glucose molecules; oxygen gas is given off by plant cells -six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water are needed to form one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. -Getting Energy from Sugar -glucose molecules store energy; plant cells use ...
... -light energy is used to help form glucose molecules; oxygen gas is given off by plant cells -six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water are needed to form one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen. -Getting Energy from Sugar -glucose molecules store energy; plant cells use ...
Plants with Seeds
... Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
... Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
Chapter 21 and 22 Notes - Plants
... Notes – Chapter 21-22 – Plants – Kingdom Plantae Plant Adaptation to Life on Land • Plants need water and minerals • Usually get water and minerals from soil • Most fruits, leaves, and stems are covered with a protective, waxy layer called the cuticle. • Leaves are the area in which photosynthesis u ...
... Notes – Chapter 21-22 – Plants – Kingdom Plantae Plant Adaptation to Life on Land • Plants need water and minerals • Usually get water and minerals from soil • Most fruits, leaves, and stems are covered with a protective, waxy layer called the cuticle. • Leaves are the area in which photosynthesis u ...
ECOSYSTEMS GLOSSARY Adaptations: the way in which
... Heather (calluna vulgaris): common plant on upland moorlands Moorland: a high upland ecosystem, which is of international importance, characterized by Muirburn: a method of upland management using controlled burning, o National Park: an area which has protected status, and provides a Niche: the stat ...
... Heather (calluna vulgaris): common plant on upland moorlands Moorland: a high upland ecosystem, which is of international importance, characterized by Muirburn: a method of upland management using controlled burning, o National Park: an area which has protected status, and provides a Niche: the stat ...
SCIENCE 7 TOPIC 5 NOTES - Stillwater Christian School
... A. Bryophytes rely on osmosis and diffusion to transport materials and are, therefore, small is size. B. Bryophytes are nonflowering, seedless plants and reproduce differently from flowering, seed bearing plants: 1. Sporophytes release spores which develop into male and female gametophytes. 2. The m ...
... A. Bryophytes rely on osmosis and diffusion to transport materials and are, therefore, small is size. B. Bryophytes are nonflowering, seedless plants and reproduce differently from flowering, seed bearing plants: 1. Sporophytes release spores which develop into male and female gametophytes. 2. The m ...
Dipladenia / Mandevilla - The Von Trapp Greenhouse
... Mandevilla sanderi (dipladenia) and Mandevilla x amabilis (mandevilla) are easy care tropical plants native to Brazil. Both thrive in full, blazing hot sun and reward the gardener with a profusion of bright blooms that do not require deadheading. They are drought tolerant and are therefore the perfe ...
... Mandevilla sanderi (dipladenia) and Mandevilla x amabilis (mandevilla) are easy care tropical plants native to Brazil. Both thrive in full, blazing hot sun and reward the gardener with a profusion of bright blooms that do not require deadheading. They are drought tolerant and are therefore the perfe ...
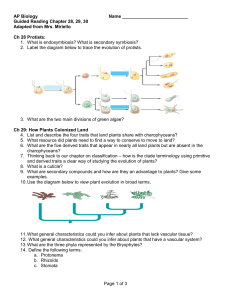
AP Biology
... 6. What are the five derived traits that appear in nearly all land plants but are absent in the charophyceans? 7. Thinking back to our chapter on classification – how is the clade terminology using primitive and derived traits a clear way of studying the evolution of plants? 8. What is a cuticle? 9. ...
... 6. What are the five derived traits that appear in nearly all land plants but are absent in the charophyceans? 7. Thinking back to our chapter on classification – how is the clade terminology using primitive and derived traits a clear way of studying the evolution of plants? 8. What is a cuticle? 9. ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.