flowering plants
... • ancestors of modern day plants were aquatic organism similar to green algae. • to grow on land, plants have developed: • an embryo – reproductive structure which develops directly into a plant. ...
... • ancestors of modern day plants were aquatic organism similar to green algae. • to grow on land, plants have developed: • an embryo – reproductive structure which develops directly into a plant. ...
Native Plants of Groton Informational Poster
... [1] Stritch, Larry. "Plant of the Week." American Witchhazel. USDA, n.d. Web. 14 Nov. 2016..
[2] "Mountain-Laurel." Mountain-Laurel on the Tree Guide at Arborday.org. Arbor Day Foundation, n.d. Web.
05 Dec. 2016.
... [1] Stritch, Larry. "Plant of the Week." American Witchhazel. USDA, n.d. Web. 14 Nov. 2016.
Discovering Plants
... is the male reproductive organ. • Anther- ovoid structure at its tip • Pollen Grainsbear by anther • Filament-stalk of the flower ...
... is the male reproductive organ. • Anther- ovoid structure at its tip • Pollen Grainsbear by anther • Filament-stalk of the flower ...
Basic Agriculture Curriculum Map Plant Science
... are aesthetically pleasing. Plants utilize energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide to sugar. A person working with plants requires knowledge of basic plant anatomy and processes to grow, manage, and market plant products. ...
... are aesthetically pleasing. Plants utilize energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide to sugar. A person working with plants requires knowledge of basic plant anatomy and processes to grow, manage, and market plant products. ...
Chapter 10 - cloudfront.net
... a microscope. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know that mitochondria liberate energy for the work that cells do and that chloroplasts capture sunlight energy for photosynthesis. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic instructions that specify its traits. Those traits may ...
... a microscope. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know that mitochondria liberate energy for the work that cells do and that chloroplasts capture sunlight energy for photosynthesis. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic instructions that specify its traits. Those traits may ...
File - wentworth science
... • they are abrasive due to deposits of silica in their outer layer of cells • club mosses are commonly called “ground pine” • all are only a few centimeters tall ...
... • they are abrasive due to deposits of silica in their outer layer of cells • club mosses are commonly called “ground pine” • all are only a few centimeters tall ...
Chapter 9 - cloudfront.net
... a microscope. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know that mitochondria liberate energy for the work that cells do and that chloroplasts capture sunlight energy for photosynthesis. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic instructions that specify its traits. Those traits may ...
... a microscope. As a basis for understanding this concept: Students know that mitochondria liberate energy for the work that cells do and that chloroplasts capture sunlight energy for photosynthesis. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic instructions that specify its traits. Those traits may ...
3.6.1 Asexual Reproduction in Plants
... • Different growth regulators are then added so that this tissue develops into a plantlet • Plantlet can be divided up again to produce many identical plants • Entire plant can be grown from a small piece of stem, leaf or root tissue • Used in mass production of house plants and crops such as banana ...
... • Different growth regulators are then added so that this tissue develops into a plantlet • Plantlet can be divided up again to produce many identical plants • Entire plant can be grown from a small piece of stem, leaf or root tissue • Used in mass production of house plants and crops such as banana ...
Chapter 21 - SPS186.org
... What evidence is there that present-day plants and present-day green algae have common ancestry? ...
... What evidence is there that present-day plants and present-day green algae have common ancestry? ...
Created by G. Baker www.thesciencequeen.net
... 39. A plant's life cycle describes how long a plant lives or how long it takes to grow, flower, and set seed. Plants can be either an ________________, ____________________, or ____________________. 40. Annual plants are plants that completes its life cycle in __________________________. It will gro ...
... 39. A plant's life cycle describes how long a plant lives or how long it takes to grow, flower, and set seed. Plants can be either an ________________, ____________________, or ____________________. 40. Annual plants are plants that completes its life cycle in __________________________. It will gro ...
Name
... __________3. Type of plant that is usually taller (longer) and has vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) that provides support _______________4. ...
... __________3. Type of plant that is usually taller (longer) and has vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) that provides support _______________4. ...
Plants – Part 2
... Animals, wind, and water can o Seeds dispersed by animals can have o Seeds dispersed by wind can have Seeds begin to grow when environmental conditions are o Seed dormancy is a Dormancy may end when ...
... Animals, wind, and water can o Seeds dispersed by animals can have o Seeds dispersed by wind can have Seeds begin to grow when environmental conditions are o Seed dormancy is a Dormancy may end when ...
Dante Matero
... Chapter 38 related to Chapter 1 because it utilizes information like species and genuses to help convey its information about GM plants. Chapter One gives much information on hypotheses and If-Then thinking, and Chapter 38 certainly uses a lot of this mentality when it tries to figure out the danger ...
... Chapter 38 related to Chapter 1 because it utilizes information like species and genuses to help convey its information about GM plants. Chapter One gives much information on hypotheses and If-Then thinking, and Chapter 38 certainly uses a lot of this mentality when it tries to figure out the danger ...
Introduction to Plants
... _____________________ are also a common structure on roots. They make the roots look fuzzy and help in the ____________________________________________. 38. The majority of the plant you see is made up of ________ and ___________. Think about a tree. The stems are the trunks and branches. Leaves are ...
... _____________________ are also a common structure on roots. They make the roots look fuzzy and help in the ____________________________________________. 38. The majority of the plant you see is made up of ________ and ___________. Think about a tree. The stems are the trunks and branches. Leaves are ...
Angelonia angustifolia
... of fertilizer or some compost in a garden bed is usually all that is needed for these plants to thrive. Due to their heat-loving nature they are one of the plants that can be planted even during the heat of mid-summer Angelonia is an erect little perennial with smooth stems and narrow leaves with to ...
... of fertilizer or some compost in a garden bed is usually all that is needed for these plants to thrive. Due to their heat-loving nature they are one of the plants that can be planted even during the heat of mid-summer Angelonia is an erect little perennial with smooth stems and narrow leaves with to ...
Parts of the Flower
... In some plants, seeds plop on the ground and begin to sprout. Animals may spread seeds that are inside tasty fruit (ex.-berries) Once the seed is moved from the parent plant, the embryo (new plant) will stay in the seed until conditions are right (temperature/moisture)...can’t wait too long, o ...
... In some plants, seeds plop on the ground and begin to sprout. Animals may spread seeds that are inside tasty fruit (ex.-berries) Once the seed is moved from the parent plant, the embryo (new plant) will stay in the seed until conditions are right (temperature/moisture)...can’t wait too long, o ...
6-2.4 Summarize the basic functions of the structures of a flowering
... •The style- a stalk down which the pollen tube grows after pollination has taken place ...
... •The style- a stalk down which the pollen tube grows after pollination has taken place ...
BioD Exam Plants Structure and Function
... b. An embryo grows into a seedling. c. Egg and sperm join. 9. What is the endosperm? a. A food supply for a developing plant embryo. b. The egg that has been fertilized b y a sperm c. The female part of the plant. 10. When a plant embryo inside a seed has stopped growing, the seed is said to be in a ...
... b. An embryo grows into a seedling. c. Egg and sperm join. 9. What is the endosperm? a. A food supply for a developing plant embryo. b. The egg that has been fertilized b y a sperm c. The female part of the plant. 10. When a plant embryo inside a seed has stopped growing, the seed is said to be in a ...
Common Native and Exotic Aquatic Plants Of Indiana Waters
... Emergent Plants – These plants have all or most of the vegetative structure, including reproductive and flowering parts, above the water’s surface. The root system can be under water but will survive during periods of low water level. Emergent plants are found along shorelines and in shallow waters ...
... Emergent Plants – These plants have all or most of the vegetative structure, including reproductive and flowering parts, above the water’s surface. The root system can be under water but will survive during periods of low water level. Emergent plants are found along shorelines and in shallow waters ...
Plant Life Cycle Notes
... 11. Some plants (like ferns) grow from spores instead of seeds. A spore is much smaller and simpler than a seed. 12. Spores are very hardy. They can stay dormant (inactive) in dry conditions for many years. Just like a seed, when the conditions are right, a spore grows into a new plant. In order to ...
... 11. Some plants (like ferns) grow from spores instead of seeds. A spore is much smaller and simpler than a seed. 12. Spores are very hardy. They can stay dormant (inactive) in dry conditions for many years. Just like a seed, when the conditions are right, a spore grows into a new plant. In order to ...
A B C - admms
... Unit Review, Introduction to Plants 1. During which process do plants capture light energy and carbon dioxide along with water to produce glucose? a. fertilization b. reproduction c. photosynthesis d. cellular respiraton 2. Where would you expect to see a plant that does not have a vascular system? ...
... Unit Review, Introduction to Plants 1. During which process do plants capture light energy and carbon dioxide along with water to produce glucose? a. fertilization b. reproduction c. photosynthesis d. cellular respiraton 2. Where would you expect to see a plant that does not have a vascular system? ...
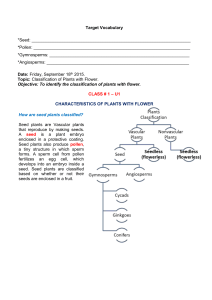
Target Vocabulary *Seed: *Pollen: *Gymnosperms: *Angiosperms
... Conifers They are the most common type of gymnosperm. This group that includes pine trees, cedars, and redwoods, also produce cones. The wood of conifer trees is used for building and for paper products. Pine trees also produce a sticky fluid called resin used to make soap, paint, and ink. ...
... Conifers They are the most common type of gymnosperm. This group that includes pine trees, cedars, and redwoods, also produce cones. The wood of conifer trees is used for building and for paper products. Pine trees also produce a sticky fluid called resin used to make soap, paint, and ink. ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.