SCIENCE 4 – 3rd Term UT1 REVIEWER MODIFIED TRUE OR
... 15. A fertilized ovule develops into a seed, while a mature ovary develops into a _________ that protects the seed. III. MULTIPLE CHOICE ...
... 15. A fertilized ovule develops into a seed, while a mature ovary develops into a _________ that protects the seed. III. MULTIPLE CHOICE ...
2. No vascular tissue
... or generations: a gametophyte generation and a sporophyte generation. The stage that produces gametes (sperm and eggs) is the gametophyte generation. It is haploid. The stage that produces spores is the sporophyte generation. It is diploid. ...
... or generations: a gametophyte generation and a sporophyte generation. The stage that produces gametes (sperm and eggs) is the gametophyte generation. It is haploid. The stage that produces spores is the sporophyte generation. It is diploid. ...
Seed Plants - Madison Station Elementary
... • A hormone is a chemical that affects how the plant grows • Auxin is a hormone that helps a plant’s cells ...
... • A hormone is a chemical that affects how the plant grows • Auxin is a hormone that helps a plant’s cells ...
Eating plants
... Many seeds are used as food. Examples include peas, sweetcorn and rice. We grind coffee beans to make coffee and wheat seeds to make flour and products like cornflakes. Seeds contain starch which is used in glues and pastes like wallpaper paste; and oils which are used in many things including cooki ...
... Many seeds are used as food. Examples include peas, sweetcorn and rice. We grind coffee beans to make coffee and wheat seeds to make flour and products like cornflakes. Seeds contain starch which is used in glues and pastes like wallpaper paste; and oils which are used in many things including cooki ...
2003 North Dakota State FFA
... 10. Most of the feeding roots of a tree can be found between __________ inches deep. A. 1 and 12 C. 10 and 50 B. 10 and 30 D. 10 and 60 11. Plants such as Ginkgo and Holly have only male or female flowers on a single plant are called __________. A. imperfect C. monecious B. perfect D. dioecious 12. ...
... 10. Most of the feeding roots of a tree can be found between __________ inches deep. A. 1 and 12 C. 10 and 50 B. 10 and 30 D. 10 and 60 11. Plants such as Ginkgo and Holly have only male or female flowers on a single plant are called __________. A. imperfect C. monecious B. perfect D. dioecious 12. ...
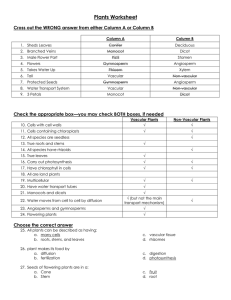
Plants Worksheet_answer key - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... 12. All species are seedless 13. True roots and stems ...
... 12. All species are seedless 13. True roots and stems ...
Kingdom Plantae - Porterville Unified School District
... Flowering plants • Most plants are angiosperms • Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant – Some have separate male and female plants – Some have male and female flowers on the same plant – Most have flowers with male and female parts ...
... Flowering plants • Most plants are angiosperms • Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant – Some have separate male and female plants – Some have male and female flowers on the same plant – Most have flowers with male and female parts ...
Kingdom Plantae - Cloudfront.net
... Flowering plants • Most plants are angiosperms • Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant – Some have separate male and female plants – Some have male and female flowers on the same plant – Most have flowers with male and female parts ...
... Flowering plants • Most plants are angiosperms • Flowers are the reproductive part of the plant – Some have separate male and female plants – Some have male and female flowers on the same plant – Most have flowers with male and female parts ...
Plant Project Rubrics
... Have cell walls Have life cycles with two phases (alternation of generations---a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase) ...
... Have cell walls Have life cycles with two phases (alternation of generations---a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase) ...
Classification Puzzles
... parts called a head, a thorax and an abdomen. I have I a skeleton on the outside of my body called an exoskeleton, which Am isn’t made from bone. Fertilisation of my eggs takes placeAn inside my body and my young are laid in soft eggs. insect I can fly. Which group in the animal kingdom do I belong ...
... parts called a head, a thorax and an abdomen. I have I a skeleton on the outside of my body called an exoskeleton, which Am isn’t made from bone. Fertilisation of my eggs takes placeAn inside my body and my young are laid in soft eggs. insect I can fly. Which group in the animal kingdom do I belong ...
Plants
... Plants: which one is it? I have got five flowerpots. Which one do I grow in each flowerpot? ...
... Plants: which one is it? I have got five flowerpots. Which one do I grow in each flowerpot? ...
06-PlantsCN
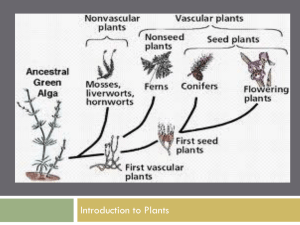
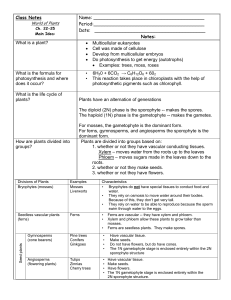
... For mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant form. For ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte is the dominant form. Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars m ...
... For mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant form. For ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms the sporophyte is the dominant form. Plants are divided into groups based on: 1. whether or not they have vascular conducting tissues. Xylem – moves water from the roots up to the leaves Phloem – moves sugars m ...
From Cell to Seed p. 134-‐138 1. List 4 things plants do for us. 2.
... ability to use Sulfur compounds, CO 2, and energy from the sun to make food 6. What substance was abundant at this Kme? Water 7. How did oxygen increase in the atmosphere? cells that used H 2 O, CO2, and sun to make food released oxygen as waste (pho ...
... ability to use Sulfur compounds, CO 2, and energy from the sun to make food 6. What substance was abundant at this Kme? Water 7. How did oxygen increase in the atmosphere? cells that used H 2 O, CO2, and sun to make food released oxygen as waste (pho ...
The Colonization of Land - Western Washington University
... The Colonization of Land The Evolution of Land Plants ...
... The Colonization of Land The Evolution of Land Plants ...
Tropism - Cloudfront.net
... are independent of the direction of the stimuli. These movements are regulated by changes in the water pressure of certain plants. ...
... are independent of the direction of the stimuli. These movements are regulated by changes in the water pressure of certain plants. ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... photosynthetic organs Stems – lift leaves and reproductive structures ...
... photosynthetic organs Stems – lift leaves and reproductive structures ...
Lysichiton americanus factsheet - Q-bank
... American Skunk-cabbage Ecology: American Skunk-cabbage can grow in both shallow water or on very moist soils such as stream sides in forests and wet woodlands; which are found to be particularly suitable. It develops both in sunny and in shaded locations, but the latter will result in fewer inflores ...
... American Skunk-cabbage Ecology: American Skunk-cabbage can grow in both shallow water or on very moist soils such as stream sides in forests and wet woodlands; which are found to be particularly suitable. It develops both in sunny and in shaded locations, but the latter will result in fewer inflores ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.