General Biology II Lecture Plants Land Plants – monophyletic group
... Micropores (produced in LARGE numbers in microsporangia) develop into microgametophyte (pollen grain) ...
... Micropores (produced in LARGE numbers in microsporangia) develop into microgametophyte (pollen grain) ...
SOL Study Book
... Some plants do not have flowers or produce seeds. Plants such as mosses and ferns use spores. A spore is a cell in a seedless plant. A spore can grow into a new plant. The moss plant has two separate stages in its life cycle. In the first stage, it produces spores. The moss spores grow into moss pla ...
... Some plants do not have flowers or produce seeds. Plants such as mosses and ferns use spores. A spore is a cell in a seedless plant. A spore can grow into a new plant. The moss plant has two separate stages in its life cycle. In the first stage, it produces spores. The moss spores grow into moss pla ...
Practice Exam 2 Below are sample questions from your book (of
... Adaptations associated with transitioning from an aquatic to a terrestrial environment Understand alternation of generations using bryophytes as an example Understand the adaptations that foster stable internal water content (the rise of vascular plants) Be able to discuss the changes in plant life ...
... Adaptations associated with transitioning from an aquatic to a terrestrial environment Understand alternation of generations using bryophytes as an example Understand the adaptations that foster stable internal water content (the rise of vascular plants) Be able to discuss the changes in plant life ...
Plant Diversity Or: Why plants are cooler than you think
... PLANT LIFE CYCLEALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS ...
... PLANT LIFE CYCLEALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS ...
Bio10Lab7 0609
... have been human. Plants enrich the beauty of the world, have inspired and taught us. ...
... have been human. Plants enrich the beauty of the world, have inspired and taught us. ...
Control
... VOCABULARY Transpiration- the process by which water is given off from plants through evaporation Variable- what you change in an experiment (what you are testing!) Control- the standard to which an experiment is compared; it is not subjected to the variable (the change) Controlled Experiment- only ...
... VOCABULARY Transpiration- the process by which water is given off from plants through evaporation Variable- what you change in an experiment (what you are testing!) Control- the standard to which an experiment is compared; it is not subjected to the variable (the change) Controlled Experiment- only ...
class_outlines_-_vegetable_families
... o Farmers are very familiar with alliums and can generally list all of them. Introduce the idea that smell can be used to help identify alliums Cucurbits Solanaceae o Talk about tomatillos as being more like a cousin than a sibling Legumes o Nitrogen fixers, very good for your soil o There are man ...
... o Farmers are very familiar with alliums and can generally list all of them. Introduce the idea that smell can be used to help identify alliums Cucurbits Solanaceae o Talk about tomatillos as being more like a cousin than a sibling Legumes o Nitrogen fixers, very good for your soil o There are man ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... Plant Reproduction Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer document. 1.Plants who take two years to complete their life cycles are called a. sporophyte c. biennials b. annuals d. perennials 2.Which is a disadvantage of reproducing asexually a. one parent can quickly pro ...
... Plant Reproduction Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on your answer document. 1.Plants who take two years to complete their life cycles are called a. sporophyte c. biennials b. annuals d. perennials 2.Which is a disadvantage of reproducing asexually a. one parent can quickly pro ...
File
... Plants rely on pollinators (birds, insects, and other animals), wind or water to help move the pollen to the pistil. ...
... Plants rely on pollinators (birds, insects, and other animals), wind or water to help move the pollen to the pistil. ...
Chapter 9 - biology4friends
... 13 Stomata open and close because of changes in the turgor pressure of the guard cells. Abscisic acid causes potassium ions to move out of guard cells, resulting in stomatal closure. Stomata usually occur on leaves; however, some plants have stomata on their stems. 14 The movement of organic molecu ...
... 13 Stomata open and close because of changes in the turgor pressure of the guard cells. Abscisic acid causes potassium ions to move out of guard cells, resulting in stomatal closure. Stomata usually occur on leaves; however, some plants have stomata on their stems. 14 The movement of organic molecu ...
Name
... A) the conversion of ammonia to nitrate. B) the conversion of nitrate to ammonia. C) the production of ammonium from decomposing organic matter. D) the conversion of N2 to ammonia. E) the conversion of N2 to ammonia or nitrate. 29) Legumes, such as beans or peas, A) form mutualistic associations wit ...
... A) the conversion of ammonia to nitrate. B) the conversion of nitrate to ammonia. C) the production of ammonium from decomposing organic matter. D) the conversion of N2 to ammonia. E) the conversion of N2 to ammonia or nitrate. 29) Legumes, such as beans or peas, A) form mutualistic associations wit ...
Plants
... Plant Characteristics 1. Range in size 2. Most have roots or rootlike structures 3. Are adapted to live in any environment 4. All plants need water ...
... Plant Characteristics 1. Range in size 2. Most have roots or rootlike structures 3. Are adapted to live in any environment 4. All plants need water ...
22.2-22.5 Kinds of Plants
... Xylem- dead tubular tissue that transport water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots to the leaves 2. Phloem- living tubular cells that transport sugars from the leaves to all parts of the cells 3. Produce spores and exhibit alternation of ...
... Xylem- dead tubular tissue that transport water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots to the leaves 2. Phloem- living tubular cells that transport sugars from the leaves to all parts of the cells 3. Produce spores and exhibit alternation of ...
The New England Carnivorous Plant Society www
... How They Trap Food: The tiny trapping devices of Utricularia are usually buried within the soil, or in the case of aquatic species, tangled in floating masses of aquatic weeds. Tiny though it may be, its complexity is unrivalled in the world of carnivorous plants. It consists of a sac, (usually betw ...
... How They Trap Food: The tiny trapping devices of Utricularia are usually buried within the soil, or in the case of aquatic species, tangled in floating masses of aquatic weeds. Tiny though it may be, its complexity is unrivalled in the world of carnivorous plants. It consists of a sac, (usually betw ...
notes
... ¨It is customarily capitalized when written with a species name. ¨For example: Grain sorghums genus is sorghum Species ¨A group of plants or animals that all share similar structure, common ancestors and maintain their characteristics ¨The subgroup under genus ¨Generally not capitalized when written ...
... ¨It is customarily capitalized when written with a species name. ¨For example: Grain sorghums genus is sorghum Species ¨A group of plants or animals that all share similar structure, common ancestors and maintain their characteristics ¨The subgroup under genus ¨Generally not capitalized when written ...
Chapter 22 The Plant Kingdom
... Antheridium is made up of a jacket of cells surrounding the developing sperm Archegonium is a flask shaped structure that produces the egg When sperm mature, antheridian opens and sperm will swim through a film of dew or rainwater to archegonium Sperm and egg nuclei fuse, diploid zygote is produced ...
... Antheridium is made up of a jacket of cells surrounding the developing sperm Archegonium is a flask shaped structure that produces the egg When sperm mature, antheridian opens and sperm will swim through a film of dew or rainwater to archegonium Sperm and egg nuclei fuse, diploid zygote is produced ...
Prairie Blazing Star: Liatris pycnostachya
... Cultivation: The preference is full sun and moist to mesic conditions. Established plants can tolerate some drought, but seedlings and transplants are vulnerable. The soil should consist of a rich loam or clay loam, and can contain rocky material. There is a tendency for the lower leaves to turn yel ...
... Cultivation: The preference is full sun and moist to mesic conditions. Established plants can tolerate some drought, but seedlings and transplants are vulnerable. The soil should consist of a rich loam or clay loam, and can contain rocky material. There is a tendency for the lower leaves to turn yel ...
World of Plants – Summary
... same flower on the same plant. b) Cross pollination is the transfer of pollen between two different plants of the same species. (From the anther of one flower to the stigma of a different flower on a different plant of the same species). 15. * A wind-pollinated plant depends on the wind to transfer ...
... same flower on the same plant. b) Cross pollination is the transfer of pollen between two different plants of the same species. (From the anther of one flower to the stigma of a different flower on a different plant of the same species). 15. * A wind-pollinated plant depends on the wind to transfer ...
Mandeville - WSU Extension
... and creates an obsession to seek and find. Several years ago the mandevilla vine was one such obsession. Locating one was not that easy, but happily it is on its second winter inside brightening the gray days with hope of spring. Known for its showy flowers, the genus Mandevilla includes plants that ...
... and creates an obsession to seek and find. Several years ago the mandevilla vine was one such obsession. Locating one was not that easy, but happily it is on its second winter inside brightening the gray days with hope of spring. Known for its showy flowers, the genus Mandevilla includes plants that ...
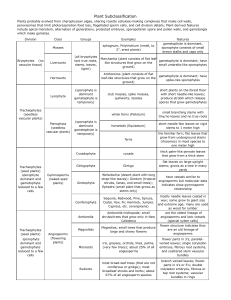
Plant Subclassification
... peroxisomes that limit photorespiration food loss, flagellated sperm cells, and cell division details; Plant derived features include apical meristem, alternation of generations, protected embryos, sporopollenin spore and pollen walls, and gametangia which make gametes. Division ...
... peroxisomes that limit photorespiration food loss, flagellated sperm cells, and cell division details; Plant derived features include apical meristem, alternation of generations, protected embryos, sporopollenin spore and pollen walls, and gametangia which make gametes. Division ...
Name: Date: Period: ____ Notes: Major Plant Groups Group 1
... – Nourishment: ____________ inside feed embryo – Protection: Hard ____________ ...
... – Nourishment: ____________ inside feed embryo – Protection: Hard ____________ ...
Slide 1
... eukaryotic cells! In this unit we will discuss the systems in plants, specifically transport, reproduction, and response. ...
... eukaryotic cells! In this unit we will discuss the systems in plants, specifically transport, reproduction, and response. ...
Plant Cell Biology and Biochemistry
... Learning outcomes This module will provide an understanding of the unique features of plant cells and a general grounding on plant physiology and growth. In addition it will provide a brief introduction to the various physiological, molecular, and biochemical mechanisms plants use to respond to envi ...
... Learning outcomes This module will provide an understanding of the unique features of plant cells and a general grounding on plant physiology and growth. In addition it will provide a brief introduction to the various physiological, molecular, and biochemical mechanisms plants use to respond to envi ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.