Plants & Photosynthesis - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... quantities, that is produced one place and has its effects elsewhere • Auxinsroot formation, apical dominance • Giberellins seed germination, stem elongation • Cytokinins cell division, differentiation • Abscisic Acid ab secare plant maturation, leaf abscission (what time of year?) • Ethylene ...
... quantities, that is produced one place and has its effects elsewhere • Auxinsroot formation, apical dominance • Giberellins seed germination, stem elongation • Cytokinins cell division, differentiation • Abscisic Acid ab secare plant maturation, leaf abscission (what time of year?) • Ethylene ...
12 Angiosperm Reproduction
... Active Y and X : autosome systems present. V. Di Stilio, 1998. PhD dissertation. Genome 41 (2): 141-147 (1997). ...
... Active Y and X : autosome systems present. V. Di Stilio, 1998. PhD dissertation. Genome 41 (2): 141-147 (1997). ...
Kingdom Plantae
... water vapor form the leaves that is a result of cellular respiration-draws water up through the xylem. Xylem is like a straw with a one way flow of water and minerals ...
... water vapor form the leaves that is a result of cellular respiration-draws water up through the xylem. Xylem is like a straw with a one way flow of water and minerals ...
VOCABULARY FOR UNIT B CHAPTER 2 MOSS – a very short
... VOCABULARY FOR UNIT B CHAPTER 2 1. MOSS – a very short, green plant that doesn’t have true roots, stems, or leaves. It is non-vascular so it doesn’t have xylem or phloem. 2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION – plant reproduction stage, which doesn’t involve the joining of a sperm and egg cell. 3. SPORE – the str ...
... VOCABULARY FOR UNIT B CHAPTER 2 1. MOSS – a very short, green plant that doesn’t have true roots, stems, or leaves. It is non-vascular so it doesn’t have xylem or phloem. 2. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION – plant reproduction stage, which doesn’t involve the joining of a sperm and egg cell. 3. SPORE – the str ...
Chapter 34
... STRUCTURE OF THE FLOWER • Egg formation occurs in the ovary, which contains the ovule. – Each ovule contains a megaspore mother cell that undergoes meiosis. • Only one megaspore survives to undergo repeated mitotic divisions that produce eight ...
... STRUCTURE OF THE FLOWER • Egg formation occurs in the ovary, which contains the ovule. – Each ovule contains a megaspore mother cell that undergoes meiosis. • Only one megaspore survives to undergo repeated mitotic divisions that produce eight ...
Seed dispersal
... I shall call you the Lookouts and you could help me by looking out for some of your local plants. Perhaps you could draw and write about their leaves, flowers and stems like I do. ...
... I shall call you the Lookouts and you could help me by looking out for some of your local plants. Perhaps you could draw and write about their leaves, flowers and stems like I do. ...
plant class notes
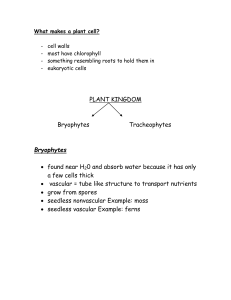
... Tracheophytes Seed plants- have roots, stem, leaves, and vascular tissue seed is reproductive part of a plant that contains plant embryo and stored food 2 Types of seed plants ...
... Tracheophytes Seed plants- have roots, stem, leaves, and vascular tissue seed is reproductive part of a plant that contains plant embryo and stored food 2 Types of seed plants ...
Evolution of Flowering Plants
... Although flowers and their components are the major innovations of angiosperms, they are not the only ones. Angiosperms also have more efficient vascular tissues. Additionally, in many flowering plants the ovaries ripen into fruits. Fruits are often brightly colored, so animals are likely to see and ...
... Although flowers and their components are the major innovations of angiosperms, they are not the only ones. Angiosperms also have more efficient vascular tissues. Additionally, in many flowering plants the ovaries ripen into fruits. Fruits are often brightly colored, so animals are likely to see and ...
PLANT REPRODUCTION
... The sporophyte is the dominant generation, but multicellular male and female gametophytes are produced within the flowers of the sporophyte. Cells of the microsporangium within the anther undergo meiosis to produce microspores. Subsequent mitotic divisions are limited, but the end result is a multic ...
... The sporophyte is the dominant generation, but multicellular male and female gametophytes are produced within the flowers of the sporophyte. Cells of the microsporangium within the anther undergo meiosis to produce microspores. Subsequent mitotic divisions are limited, but the end result is a multic ...
Male Parts Anther
... • Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it and down the style into the ...
... • Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it and down the style into the ...
LS Seeded Vascular Plants Booklet PP
... Large fan shaped leaves Only found in some parts of the U.S. and China Trees contain either all male cones or all female cones. Seeds are large and red, and produce an awful smell. ...
... Large fan shaped leaves Only found in some parts of the U.S. and China Trees contain either all male cones or all female cones. Seeds are large and red, and produce an awful smell. ...
plants review key - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... phloem); T: vascular (have xylem and phloem) Where do each of these types of plants live? B: land/moist environments; T: land or water Give 3 examples of each type. B: moss, liverwort, hornwort; T: ferns (seedless), gymnosperms and angiosperms. 5. What are the adaptations that plants have acquired f ...
... phloem); T: vascular (have xylem and phloem) Where do each of these types of plants live? B: land/moist environments; T: land or water Give 3 examples of each type. B: moss, liverwort, hornwort; T: ferns (seedless), gymnosperms and angiosperms. 5. What are the adaptations that plants have acquired f ...
Kingdom Plantae Test Review Pre-AP Spring 2008
... phloem); T: vascular (have xylem and phloem) Where do each of these types of plants live? B: land/moist environments; T: land or water Give 3 examples of each type. B: moss, liverwort, hornwort; T: ferns (seedless), gymnosperms and angiosperms. 5. What are the adaptations that plants have acquired f ...
... phloem); T: vascular (have xylem and phloem) Where do each of these types of plants live? B: land/moist environments; T: land or water Give 3 examples of each type. B: moss, liverwort, hornwort; T: ferns (seedless), gymnosperms and angiosperms. 5. What are the adaptations that plants have acquired f ...
Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
... – During the late Mesozoic the major branches of the clade diverged from their common ancestor ...
... – During the late Mesozoic the major branches of the clade diverged from their common ancestor ...
Plant Reproduction
... • Plants have a double life cycle with two distinct forms: • Sporophyte: diploid, produce haploid spores by meiosis. • Gametophyte: haploid, produce gametes by mitosis. ...
... • Plants have a double life cycle with two distinct forms: • Sporophyte: diploid, produce haploid spores by meiosis. • Gametophyte: haploid, produce gametes by mitosis. ...
Chapter 24: Reproduction of Seed Plants
... – Carpel (Pistil)- produce female gametophytes. – Ovary- base of the pistil. – Style- stalk of the pistil. – Stigma- top of the style where pollen lands. ...
... – Carpel (Pistil)- produce female gametophytes. – Ovary- base of the pistil. – Style- stalk of the pistil. – Stigma- top of the style where pollen lands. ...
Plants
... • Use flowers (attract animals) and fruits (protect seeds) for reproduction. • Flowering plants provide food for animals. ...
... • Use flowers (attract animals) and fruits (protect seeds) for reproduction. • Flowering plants provide food for animals. ...
Seed Plants
... Angiosperm Life Cycle Double fertilization – one sperm unites with egg – one sperm unites with polar nuclei develops into endosperm (3n) Fruit and Seed development – ovule = seed – ovary = fruit ...
... Angiosperm Life Cycle Double fertilization – one sperm unites with egg – one sperm unites with polar nuclei develops into endosperm (3n) Fruit and Seed development – ovule = seed – ovary = fruit ...
seed
... Plants that produce “Naked” seeds (exposed on the scales of cones) can reproduce without free-standing water, via pollination – ADAPTATIONS – Seeds (embryo & food supply) – seeds allow plants to disperse to new places ...
... Plants that produce “Naked” seeds (exposed on the scales of cones) can reproduce without free-standing water, via pollination – ADAPTATIONS – Seeds (embryo & food supply) – seeds allow plants to disperse to new places ...
6-2.4 notes Plants - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... Parts of the flowering plant that function in reproduction include: Flowers Produce seeds. Many contain both male and female parts needed to produce new flowers. Flower petals are often colorful or have a scent so as to attract insects and other animals. Stamem The male part of a flower that ...
... Parts of the flowering plant that function in reproduction include: Flowers Produce seeds. Many contain both male and female parts needed to produce new flowers. Flower petals are often colorful or have a scent so as to attract insects and other animals. Stamem The male part of a flower that ...
Plants
... 10) Gametophyte (haploid) is the dominant generation in Bryophytes 11) Bryophytes have a mat-like structure. What the advantages to having this? Close to the ground so doesn’t have to transport nutrients very far 12) What are the two vascular tissues and what do they do? Xylem – moves minerals from ...
... 10) Gametophyte (haploid) is the dominant generation in Bryophytes 11) Bryophytes have a mat-like structure. What the advantages to having this? Close to the ground so doesn’t have to transport nutrients very far 12) What are the two vascular tissues and what do they do? Xylem – moves minerals from ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.