Kingdom Plantae - Bakersfield College
... C. Stores food for embryo D. Protection from predators ...
... C. Stores food for embryo D. Protection from predators ...
Angiosperms, which evolved in the Cretaceous period
... Angiosperms evolved during the late Cretaceous Period, about 125100 million years ago. Angiosperms have developed flowers and fruit as ways to attract pollinators and protect their seeds, respectively. Flowers have a wide array of colors, shapes, and smells, all of which are for the purpose of attr ...
... Angiosperms evolved during the late Cretaceous Period, about 125100 million years ago. Angiosperms have developed flowers and fruit as ways to attract pollinators and protect their seeds, respectively. Flowers have a wide array of colors, shapes, and smells, all of which are for the purpose of attr ...
Biology H/Pre-IB
... What is the difference between monocot and dicot? What does a seed consist of? Mosses are nonvascular plants. Describe two adaptations they have to still survive successfully without vascular tissue. 6. Know and be able to identify the steps in the life cycles of mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angi ...
... What is the difference between monocot and dicot? What does a seed consist of? Mosses are nonvascular plants. Describe two adaptations they have to still survive successfully without vascular tissue. 6. Know and be able to identify the steps in the life cycles of mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and angi ...
ss 1 biology - Danbo International Schools
... Plant kingdom are usually could plantae. The divisions of plantae includes a. Thallophyta _ They are the earliest group of plants which are called Algae or thallopytes. They lack true roots e.g Spirogyra. b. Bryophyta – They are called Bryophytes. They possess rhizoids or false root e.g moss plant. ...
... Plant kingdom are usually could plantae. The divisions of plantae includes a. Thallophyta _ They are the earliest group of plants which are called Algae or thallopytes. They lack true roots e.g Spirogyra. b. Bryophyta – They are called Bryophytes. They possess rhizoids or false root e.g moss plant. ...
Study Guide: Plants
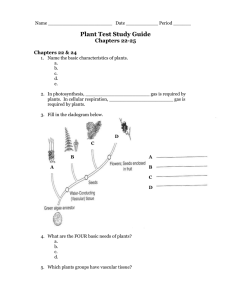
... 22. Name the methods of seed dispersal. a. b. c. 23. What is seed dormancy? ...
... 22. Name the methods of seed dispersal. a. b. c. 23. What is seed dormancy? ...
biology 104
... 1. When did plants evolve? Which group of organisms did plants evolve from? 2. What adaptations did plants have to survive on land? 3. What are mycorrhizae? Are they fungi or plants? 4. Define a plant. Which kingdom do they belong to? Are they eukaryotes or prokaryotes? Name a few characteristics th ...
... 1. When did plants evolve? Which group of organisms did plants evolve from? 2. What adaptations did plants have to survive on land? 3. What are mycorrhizae? Are they fungi or plants? 4. Define a plant. Which kingdom do they belong to? Are they eukaryotes or prokaryotes? Name a few characteristics th ...
Plants
... These plants have cones and needles The largest group of gymnosperms are Conifers (California Redwoods) ...
... These plants have cones and needles The largest group of gymnosperms are Conifers (California Redwoods) ...
flowers
... 1) pollen grain adheres to stigma, germinates, and extends a pollen tube toward the ovary; 2) generative cell divides (mitosis) to form 2 sperm; 3) directed by a chemical attractant, pollen tube enters and discharges its 2 sperm nuclei into the embryo sac; 4) 1 sperm unites with the egg ZYGOTE; 5) ...
... 1) pollen grain adheres to stigma, germinates, and extends a pollen tube toward the ovary; 2) generative cell divides (mitosis) to form 2 sperm; 3) directed by a chemical attractant, pollen tube enters and discharges its 2 sperm nuclei into the embryo sac; 4) 1 sperm unites with the egg ZYGOTE; 5) ...
File ap notes chapter 38
... megaspores (n) In most angiosperms: 1 of 4 megaspores survives Surviving megaspore divides without cytokinesis to form a large cell with 8 haploid nuclei Large cell partitioned in gametophyte embryo sac Embryo sac has 3 cells at one end ...
... megaspores (n) In most angiosperms: 1 of 4 megaspores survives Surviving megaspore divides without cytokinesis to form a large cell with 8 haploid nuclei Large cell partitioned in gametophyte embryo sac Embryo sac has 3 cells at one end ...
Figure 38.2 Review of an idealized flower
... Pollination • Pollination is the transfer of the pollen from the anther to the stigma • If the pollen lands on a flower on the SAME plant it is called self-pollination – If it lands on a different individual then it is called cross-pollination ...
... Pollination • Pollination is the transfer of the pollen from the anther to the stigma • If the pollen lands on a flower on the SAME plant it is called self-pollination – If it lands on a different individual then it is called cross-pollination ...
Cattleya skinneri
... Native of: Central America. It is the national flower of Costa Rica. Habitat: We have seen this growing in Costa Rica at 1000m on large trees in seasonally dry forest. Description: Stout pseudobulbs up to 30cm high carry two leathery leaves up to 15cm long. The inflorescence appears from a dry sheat ...
... Native of: Central America. It is the national flower of Costa Rica. Habitat: We have seen this growing in Costa Rica at 1000m on large trees in seasonally dry forest. Description: Stout pseudobulbs up to 30cm high carry two leathery leaves up to 15cm long. The inflorescence appears from a dry sheat ...
Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
... sepal: small, green leaves below the petal that cover and protect the flower bud pistil: female organ of the flower that creates and forms egg cells stamen: male part of the flower that makes pollen ovary: thick bottom of the pistil fertilization: process by which egg and sperm cells combine to deve ...
... sepal: small, green leaves below the petal that cover and protect the flower bud pistil: female organ of the flower that creates and forms egg cells stamen: male part of the flower that makes pollen ovary: thick bottom of the pistil fertilization: process by which egg and sperm cells combine to deve ...
Kingdom: Plantae
... Haploid spores produce plants which eventually produce gametes which fuse to produce diploid zygote that grows into a sporophyte plant ...
... Haploid spores produce plants which eventually produce gametes which fuse to produce diploid zygote that grows into a sporophyte plant ...
Plant Reproduction
... 19. Outer whorl of flower parts that may appear green and leaf-shaped 23. Production of one type of spore as in moss and ferns 24. A sugar solution made by plants to attract insect pollinators 25. Larger, female spore 28. Producing two types of spores such as gymnosperms 30. Transfer of pollen to fe ...
... 19. Outer whorl of flower parts that may appear green and leaf-shaped 23. Production of one type of spore as in moss and ferns 24. A sugar solution made by plants to attract insect pollinators 25. Larger, female spore 28. Producing two types of spores such as gymnosperms 30. Transfer of pollen to fe ...
Plants junior
... plant has a different function: roots help to anchor the plant and absorb water and mineral salts from the soil; leaves produce the plant’s food and flowers contain the reproductive organs. Many flowers are colourful and sweet-smelling to attract birds and insects that feed on the nectar that they f ...
... plant has a different function: roots help to anchor the plant and absorb water and mineral salts from the soil; leaves produce the plant’s food and flowers contain the reproductive organs. Many flowers are colourful and sweet-smelling to attract birds and insects that feed on the nectar that they f ...
Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... • Some plants use their roots for asexual reproduction. The dandelion is a common example. Trees, such as the poplar or aspen, send up new stems from their roots. In time, an entire forest of trees may form — all part of a clone of the original tree. • Apple seeds are planted only for the root and s ...
... • Some plants use their roots for asexual reproduction. The dandelion is a common example. Trees, such as the poplar or aspen, send up new stems from their roots. In time, an entire forest of trees may form — all part of a clone of the original tree. • Apple seeds are planted only for the root and s ...
Control of Flowering
... In daylight, Pfr is rapidly converted to back to Pr In darkness, Pfr is very slowly converted back to Pr The slow conversion of Pfr to Pr helps plants time the ...
... In daylight, Pfr is rapidly converted to back to Pr In darkness, Pfr is very slowly converted back to Pr The slow conversion of Pfr to Pr helps plants time the ...
Obj. 8: Describe characteristics of marine plant and algae divisions
... 1. Horizontal stems (rhizomes) that grow beneath the sediment 2. Roots and stems grow from the rhizomes 3. Leaves are called blades ...
... 1. Horizontal stems (rhizomes) that grow beneath the sediment 2. Roots and stems grow from the rhizomes 3. Leaves are called blades ...
20.3 Diversity of Flowering Plants
... Flowering plants have unique adaptations that allow them to dominate in today’s world. • Flowers allow for efficient pollination. – animals feed on pollen or nectar – pollen is spread from plant to plant in process ...
... Flowering plants have unique adaptations that allow them to dominate in today’s world. • Flowers allow for efficient pollination. – animals feed on pollen or nectar – pollen is spread from plant to plant in process ...
flowering plants - VCE
... their discoveries on photoperiodism and felt it was the length of daylight that was critical, but it was later discovered that the length of the night was the controlling factor. Photoperiodic flowering plants are classified as ...
... their discoveries on photoperiodism and felt it was the length of daylight that was critical, but it was later discovered that the length of the night was the controlling factor. Photoperiodic flowering plants are classified as ...
Section 1 Plant Kingdom P. 104-111 Main Ideas Details What is a
... Female reproductive parts sticky tip of pistil ( collects pollen) slender tube protects the seeds as it’s developing ( holds ovules) ...
... Female reproductive parts sticky tip of pistil ( collects pollen) slender tube protects the seeds as it’s developing ( holds ovules) ...
Note on the Growing of Xeronema Callistemon
... FROM a sowing of 1966/67 seed, Mr John Moreland has at this date some 50 plants about a year and a quarter old, 4 or 5 inches high, with seven leaves in a fan. They take 2 i to 3 months to germinate, have grown most noticeably in the last six months and are still growing slowly. These seedlings are ...
... FROM a sowing of 1966/67 seed, Mr John Moreland has at this date some 50 plants about a year and a quarter old, 4 or 5 inches high, with seven leaves in a fan. They take 2 i to 3 months to germinate, have grown most noticeably in the last six months and are still growing slowly. These seedlings are ...
Pollination There are two main groups of plants on planet Earth
... female part of the flower and it has two main parts; a sticky end called the stigma and a hollow structure called an ovary that holds eggs or ovules. ...
... female part of the flower and it has two main parts; a sticky end called the stigma and a hollow structure called an ovary that holds eggs or ovules. ...
Angiosperms
... parsley, carrot, dill, giant Astraceae – rich family; some of them produce latex in their tissues; inflorescence – head; fruit – achene, sunflower, daisy, marguerite, dahlia ...
... parsley, carrot, dill, giant Astraceae – rich family; some of them produce latex in their tissues; inflorescence – head; fruit – achene, sunflower, daisy, marguerite, dahlia ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.