Chronic Administration of Statins Alters Multiple Gene Expression
... including pravastatin, and therefore statin levels were determined in cerebral cortex of mice acutely and chronically administered statins. Statin quantification was accomplished using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). We demonstrate that statins have pleiotropic effects on ...
... including pravastatin, and therefore statin levels were determined in cerebral cortex of mice acutely and chronically administered statins. Statin quantification was accomplished using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). We demonstrate that statins have pleiotropic effects on ...
Regulation of rCBF by Diffusible Signals: An Analysis of Constraints
... tween neural activity and hemodynamics are not, at appropriate distribution. The source geometry modthe present time, fully known. However the empirical elled in this paper was a distribution of point sources observations above provide constraints on the proper- on the nodes of an infinitely large r ...
... tween neural activity and hemodynamics are not, at appropriate distribution. The source geometry modthe present time, fully known. However the empirical elled in this paper was a distribution of point sources observations above provide constraints on the proper- on the nodes of an infinitely large r ...
PROJECTIONS OF THE AMYGDALOID BODY TO THE INSULAR
... (Fig. 1). It is usually divided into agranular insular cortex, localized around the rhinal sulcus and granular insular cortex lying mainly on the surface of the anterior sylvian gyrus. There are two parts of the insular granular cortex: anterior and posterior; that partition. seems to have mainly to ...
... (Fig. 1). It is usually divided into agranular insular cortex, localized around the rhinal sulcus and granular insular cortex lying mainly on the surface of the anterior sylvian gyrus. There are two parts of the insular granular cortex: anterior and posterior; that partition. seems to have mainly to ...
Physiology of the Striate Cortex
... • Map of the visual field onto a target structure (retina, LGN, superior colliculus, striate cortex) - overrepresentation of central visual field • Discrete point of light: Activates many cells in the target structure • Perception: Based on the brain’s interpretation of distributed patterns of activ ...
... • Map of the visual field onto a target structure (retina, LGN, superior colliculus, striate cortex) - overrepresentation of central visual field • Discrete point of light: Activates many cells in the target structure • Perception: Based on the brain’s interpretation of distributed patterns of activ ...
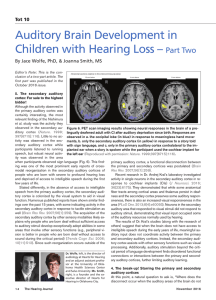
Auditory Brain Development in Children with Hearing Loss – Part Two
... plains why people who are born deaf without sufficient access The results of Dr. Kral’s studies (along with the research of to auditory stimuli develop exceptionally adept abilities in some others) suggest that when the brain does not have access to areas that involve other sensory functions (e.g., ...
... plains why people who are born deaf without sufficient access The results of Dr. Kral’s studies (along with the research of to auditory stimuli develop exceptionally adept abilities in some others) suggest that when the brain does not have access to areas that involve other sensory functions (e.g., ...
Model of autism: increased ratio of excitationinhibition in key neural
... In both of these hypothetical ‘noisy processing’ developmental scenarios, the auditory/aural speech cortex would mature through the critical period of development and pass into the ‘adult’ epoch of development in a highly undifferentiated and relatively unstable state. Such experiments indicate that ...
... In both of these hypothetical ‘noisy processing’ developmental scenarios, the auditory/aural speech cortex would mature through the critical period of development and pass into the ‘adult’ epoch of development in a highly undifferentiated and relatively unstable state. Such experiments indicate that ...
Motor pathway injury in patients with
... measured neuronal g-aminobutyric acidA receptor binding potential with dynamic positron emission tomography scans (n = 27) and compared the binding potential map of the patient group with controls (n = 20). In the current study, white matter volume reduction did not show significant correlation with ...
... measured neuronal g-aminobutyric acidA receptor binding potential with dynamic positron emission tomography scans (n = 27) and compared the binding potential map of the patient group with controls (n = 20). In the current study, white matter volume reduction did not show significant correlation with ...
~ Pergamon
... similar laminar definition to determine whether regional differences in the distribution of labelled neurons were related to differences in laminar characteristics noted previously/4 Categories were constructed on the basis of number of layers and laminar definition, and are shown in Table 1. At one ...
... similar laminar definition to determine whether regional differences in the distribution of labelled neurons were related to differences in laminar characteristics noted previously/4 Categories were constructed on the basis of number of layers and laminar definition, and are shown in Table 1. At one ...
Identification and characterisation of regionally enriched cortex
... The highly complex neocortex is a mammalian specific region of the brain. In humans, several areas of the neocortex have been linked to normal cognitive functioning. Importantly, abnormalities in the neocortex are associated with serious psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia and bipolar affec ...
... The highly complex neocortex is a mammalian specific region of the brain. In humans, several areas of the neocortex have been linked to normal cognitive functioning. Importantly, abnormalities in the neocortex are associated with serious psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia and bipolar affec ...
BRAINSTEM
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
Exam 1
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
... Crossing-over of corticospinal (motor) tract at the level of the transition between medulla and spinal cord. Visible on the ventral brainstem surface. As a result of the decussation, one side of the brain controls the muscles of the opposite side. Ascending afferent axonal pathway in the brainstem ( ...
State-Dependent TMS Reveals a Hierarchical
... RTs (minus number of excluded error trials). In each of the 2 experiments, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed with the 3 within-subjects variables: ‘‘stimulation modality’’ (6 levels in Experiment 1: no TMS, SPL, left SMG, left PMv, right SMG, and right PMv and 3 levels in Experiment 2: l ...
... RTs (minus number of excluded error trials). In each of the 2 experiments, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed with the 3 within-subjects variables: ‘‘stimulation modality’’ (6 levels in Experiment 1: no TMS, SPL, left SMG, left PMv, right SMG, and right PMv and 3 levels in Experiment 2: l ...
Finding a face in the crowd: parallel and serial neural mechanisms
... stimulus outside the RF. More specifically, the response to an unselected RF stimulus with the neuron’s preferred or nonpreferred color was compared on trials during which the cue was of the preferred or nonpreferred color for the neuron (Fig. 2A). When a stimulus of the preferred color was in the RF ...
... stimulus outside the RF. More specifically, the response to an unselected RF stimulus with the neuron’s preferred or nonpreferred color was compared on trials during which the cue was of the preferred or nonpreferred color for the neuron (Fig. 2A). When a stimulus of the preferred color was in the RF ...
Cerebrum - CM
... • Neocortex is divided into three areas: primary motor cortex, primary sensory cortices, and association areas (continued): • Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement • Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input • Association areas integrate different typ ...
... • Neocortex is divided into three areas: primary motor cortex, primary sensory cortices, and association areas (continued): • Primary motor cortex – plans and executes movement • Primary sensory cortices – first regions to receive and process sensory input • Association areas integrate different typ ...
Evidence of a Specific Spinal Pathway for the Sense of Warmth in
... Using a CO2 laser stimulator (Neurolas, Electronic Engineering, Florence, Italy) we delivered brief pulses (wavelength: 10.6 m) to the skin overlying C5, T2, T6, and T10 vertebral spinous processes (four subjects) or C5 and T10 (15 subjects). To avoid habituation, sensitization, and tissue damage, ...
... Using a CO2 laser stimulator (Neurolas, Electronic Engineering, Florence, Italy) we delivered brief pulses (wavelength: 10.6 m) to the skin overlying C5, T2, T6, and T10 vertebral spinous processes (four subjects) or C5 and T10 (15 subjects). To avoid habituation, sensitization, and tissue damage, ...
Evidence of a Specific Spinal Pathway for the
... Using a CO2 laser stimulator (Neurolas, Electronic Engineering, Florence, Italy) we delivered brief pulses (wavelength: 10.6 m) to the skin overlying C5, T2, T6, and T10 vertebral spinous processes (four subjects) or C5 and T10 (15 subjects). To avoid habituation, sensitization, and tissue damage, ...
... Using a CO2 laser stimulator (Neurolas, Electronic Engineering, Florence, Italy) we delivered brief pulses (wavelength: 10.6 m) to the skin overlying C5, T2, T6, and T10 vertebral spinous processes (four subjects) or C5 and T10 (15 subjects). To avoid habituation, sensitization, and tissue damage, ...
15. Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
... with bodies located in the brain or spinal cord and axons that extend through cranial or spinal nerves. The axons of somatic motor neurons synapse with skeletal muscles. All somatic motor neurons release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) from their synaptic knobs. ACh is always excitatory at ...
... with bodies located in the brain or spinal cord and axons that extend through cranial or spinal nerves. The axons of somatic motor neurons synapse with skeletal muscles. All somatic motor neurons release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) from their synaptic knobs. ACh is always excitatory at ...
Powerpoint Slides
... Single-Neuron Recording • Stick a thin electrode into an animal’s brain (rat, cat, monkey) • record action potentials from a single neuron • measure neuronal firing under a range of conditions ...
... Single-Neuron Recording • Stick a thin electrode into an animal’s brain (rat, cat, monkey) • record action potentials from a single neuron • measure neuronal firing under a range of conditions ...
Location and connectivity determine GABAergic interneuron survival in the brains... South Hampshire sheep with CLN6 neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis
... distinctive pattern of change for each calcium binding protein. Loss of neurons positive to parvalbumin from the affected cortex became apparent at four months of age and had become profound by 19 months. The extent of loss varied markedly between regions, as to a lesser extent did the loss of somat ...
... distinctive pattern of change for each calcium binding protein. Loss of neurons positive to parvalbumin from the affected cortex became apparent at four months of age and had become profound by 19 months. The extent of loss varied markedly between regions, as to a lesser extent did the loss of somat ...
Understanding Adolescent Brain Development and Its Implications
... CHANGES IN THE FRONTAL LOBES DURING ADOLESCENCE Some of the most intriguing changes in the brain during adolescence take place in the frontal lobes. These brain areas, located just behind the forehead, play critical roles in memory, intentional movement, controlling emotional urges, making decisions ...
... CHANGES IN THE FRONTAL LOBES DURING ADOLESCENCE Some of the most intriguing changes in the brain during adolescence take place in the frontal lobes. These brain areas, located just behind the forehead, play critical roles in memory, intentional movement, controlling emotional urges, making decisions ...
Canonical computations of cerebral cortex
... species, the selectivity of neuronal responses (the relative response strength across different stimuli) is primarily established by the pattern of feedforward connections the neurons receive (thalamic input and perhaps thalamicdriven inhibition). Intracortical recurrent input primarily determines t ...
... species, the selectivity of neuronal responses (the relative response strength across different stimuli) is primarily established by the pattern of feedforward connections the neurons receive (thalamic input and perhaps thalamicdriven inhibition). Intracortical recurrent input primarily determines t ...
Habit formation
... causally controls the habitual behaviors, which remains to be tested, habits may be encoded in the DLS by signals that help link the actions together into a chunk, with salient features being its initiation and termination 28,29, just as working memory processes can involve a chunking together infor ...
... causally controls the habitual behaviors, which remains to be tested, habits may be encoded in the DLS by signals that help link the actions together into a chunk, with salient features being its initiation and termination 28,29, just as working memory processes can involve a chunking together infor ...
Brain Matters: Brain Anatomy
... Parahippocampal gyrus: The parahippocampal gyrus is a brain structure that surrounds the hippocampus. It is important to memory formation and retrieval and plays a particularly important role in both spatial memory and episodic (declarative) memory. The parahippocampal gyrus is also involved in face ...
... Parahippocampal gyrus: The parahippocampal gyrus is a brain structure that surrounds the hippocampus. It is important to memory formation and retrieval and plays a particularly important role in both spatial memory and episodic (declarative) memory. The parahippocampal gyrus is also involved in face ...
Lateral Zone
... intended plan of movement with actually performed movement, especially of distal parts of limbs. So it acts as a comparator. • If there is any discrepancy from the intended plan of movement, corrective signals are sent to motor cortex to correct it. ...
... intended plan of movement with actually performed movement, especially of distal parts of limbs. So it acts as a comparator. • If there is any discrepancy from the intended plan of movement, corrective signals are sent to motor cortex to correct it. ...
Zola-Morgan et al. 1986
... fasciculation and shivering. During that period he was generally unresponsive, presumably because of the neuromuscular blockade, but there were times between drug administrations when he appeared to understand verbal stimuli and opened his eyes on request. Postoperative course. On September 20, R.B. ...
... fasciculation and shivering. During that period he was generally unresponsive, presumably because of the neuromuscular blockade, but there were times between drug administrations when he appeared to understand verbal stimuli and opened his eyes on request. Postoperative course. On September 20, R.B. ...