Power Point 1 - G. Holmes Braddock
... After fertilization by pollen it later becomes the fruit of the plant ...
... After fertilization by pollen it later becomes the fruit of the plant ...
All in a Flower - Trimble County Schools
... • Ovule: The egg cell of the plant – becomes the seed when fertilized. • Pollen tube: Transfers pollen from stigma to ovule. • Pistil: Female part of flower, composed of three parts – Stigma: Collects pollen ...
... • Ovule: The egg cell of the plant – becomes the seed when fertilized. • Pollen tube: Transfers pollen from stigma to ovule. • Pistil: Female part of flower, composed of three parts – Stigma: Collects pollen ...
Meagan - ayalabme3
... Because it could be a little moister so it can still live a little while longer. Plants need water to grow well. If you give it to much it can drowned. ...
... Because it could be a little moister so it can still live a little while longer. Plants need water to grow well. If you give it to much it can drowned. ...
What is a Plant? - Jordan High School
... • Ancestors of modern plants were waterdwelling organisms similar to algae • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
... • Ancestors of modern plants were waterdwelling organisms similar to algae • Early land plants were centimeters tall – Grew close to the ground to obtain water ...
What are vascular plants?
... • Flowering plants differ from conifers because they grow their seeds inside an ovary, which is embedded in a flower. • Flowers then becomes a fruit containing the seeds. • Examples include most trees, shrubs, vines, flowers, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. ...
... • Flowering plants differ from conifers because they grow their seeds inside an ovary, which is embedded in a flower. • Flowers then becomes a fruit containing the seeds. • Examples include most trees, shrubs, vines, flowers, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. ...
Aim: How do organisms reproduce?
... between asexual and sexual reproduction and describe different types of asexual reproduction DN: Explain the differences between sexual and sexual reproduction ...
... between asexual and sexual reproduction and describe different types of asexual reproduction DN: Explain the differences between sexual and sexual reproduction ...
Chapter 23
... reproduce by releasing spores Seed bearing vascular plants produce seeds and pollen ...
... reproduce by releasing spores Seed bearing vascular plants produce seeds and pollen ...
Plant Diversity Lab 2 Slide Show
... Botanists classify the flowering plants between two major groups: -the DICOTS..................dicotyledonous plants -the MONOCOTS...........monocotyledonous plants the COT in di/cot or mono/cot refers to the term cotyledon. A cotyledon is the embryonic leaf of the seed embryo. Seeds of dicotyledono ...
... Botanists classify the flowering plants between two major groups: -the DICOTS..................dicotyledonous plants -the MONOCOTS...........monocotyledonous plants the COT in di/cot or mono/cot refers to the term cotyledon. A cotyledon is the embryonic leaf of the seed embryo. Seeds of dicotyledono ...
1 - contentextra
... bulk flow, and the removal of sugar at the sink. Sugar is transported into and away from the source and sink sites by active transport. 12 All plants show two different generations in their life cycle: the gametophyte (haploid) and the sporophyte (diploid) generations. These two generations alternat ...
... bulk flow, and the removal of sugar at the sink. Sugar is transported into and away from the source and sink sites by active transport. 12 All plants show two different generations in their life cycle: the gametophyte (haploid) and the sporophyte (diploid) generations. These two generations alternat ...
SEXUAL PROPAGATION Introduction Plant propagation is the
... 5. In the stage of flowering known as full bloom or anthesis, the anthers, the structures containing the pollen, ruptures, and pollen is shed. 6. One of the important events that precedes the fertilization of the egg is the transfer of pollen from the male organ, specifically from the anther, to the ...
... 5. In the stage of flowering known as full bloom or anthesis, the anthers, the structures containing the pollen, ruptures, and pollen is shed. 6. One of the important events that precedes the fertilization of the egg is the transfer of pollen from the male organ, specifically from the anther, to the ...
Bryophytes and Ferns
... A perfect flower has both stamen and carpel present. An imperfect flower doesn’t have both parts present but only one of them- so the flower will either have stamen only- male flower or carpel only- female flower. ...
... A perfect flower has both stamen and carpel present. An imperfect flower doesn’t have both parts present but only one of them- so the flower will either have stamen only- male flower or carpel only- female flower. ...
Bio10Lab7 0609
... make it to the next plant and it is energetically expensive to make. So, most flowering plants use more efficient carriers (animals such as insects, birds, mammals and even reptiles). Most flowers combine male and female parts. The male structure, the stamen (made up of anther & filament) produces t ...
... make it to the next plant and it is energetically expensive to make. So, most flowering plants use more efficient carriers (animals such as insects, birds, mammals and even reptiles). Most flowers combine male and female parts. The male structure, the stamen (made up of anther & filament) produces t ...
Cell Respiration Study Guide
... Know the basic structure of seeds, leaves, the flowers, roots and stems - the function of the most predominant parts. Review the basics behind photosynthesis in respect to plant nutrition Understand the way that water potential works in relations to water movement into and around plants – it w ...
... Know the basic structure of seeds, leaves, the flowers, roots and stems - the function of the most predominant parts. Review the basics behind photosynthesis in respect to plant nutrition Understand the way that water potential works in relations to water movement into and around plants – it w ...
Chapter 5: Seed Plants
... -Pollen grains containing sperm cells are carried from ___________ to __________ (__________________). -A _______________ grows from the pollen grain to the ovule. Sperm swim down the pollen tube and fertilize the egg cells. (__________________). -__________ develop into seeds and the __________ bec ...
... -Pollen grains containing sperm cells are carried from ___________ to __________ (__________________). -A _______________ grows from the pollen grain to the ovule. Sperm swim down the pollen tube and fertilize the egg cells. (__________________). -__________ develop into seeds and the __________ bec ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. In angiosperms, pollen grains are produced in a. anthers. b. carpels. c. ovules. d. sepals. _____ 2. Which of the following is NOT part of the female structure of a flower? a. filament b. style ...
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. In angiosperms, pollen grains are produced in a. anthers. b. carpels. c. ovules. d. sepals. _____ 2. Which of the following is NOT part of the female structure of a flower? a. filament b. style ...
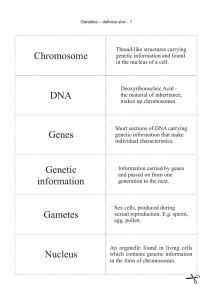
Chromosome DNA Genes Genetic information
... which contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes. ...
... which contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes. ...
Multiple Choice Unit 7 Plants Unit Test A
... the line provided. ____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of plants? a. unicellular b. contain cell walls made of cellulose c. make their own food d. eukaryotes ____ 2. Plants that lack vascular tissue and depend on water for reproduction are classified as a. bryophytes. b. ferns. c. ...
... the line provided. ____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of plants? a. unicellular b. contain cell walls made of cellulose c. make their own food d. eukaryotes ____ 2. Plants that lack vascular tissue and depend on water for reproduction are classified as a. bryophytes. b. ferns. c. ...
Fungi and plants practice
... A. parasitic interactions between a fungus and an alga. B. only found growing on living matter. C. symbiotic associations between a fungus and an alga. D. capable of causing some obscure diseases. E. insensitive to changes in the environment. ...
... A. parasitic interactions between a fungus and an alga. B. only found growing on living matter. C. symbiotic associations between a fungus and an alga. D. capable of causing some obscure diseases. E. insensitive to changes in the environment. ...
The-plant-kingdom - english for biology
... with an anther at the tip. The pistil of most flowers has three parts – the stigma, style and ovary. How do plants reproduce? Flowering plants reproduce themselves from seeds which form inside the ovary of the flower after fertilization. Flowers produce a fine dust called pollen (known as pollen gra ...
... with an anther at the tip. The pistil of most flowers has three parts – the stigma, style and ovary. How do plants reproduce? Flowering plants reproduce themselves from seeds which form inside the ovary of the flower after fertilization. Flowers produce a fine dust called pollen (known as pollen gra ...
Angiosperm Reproduction
... • In some species the root system of a single parent gives rise to many adventitious shoots that become separate shoot systems Photo shows groups of aspen trees that have descended by asexual reproduction from root system of parent trees. Separate groves derived from the root systems of different pa ...
... • In some species the root system of a single parent gives rise to many adventitious shoots that become separate shoot systems Photo shows groups of aspen trees that have descended by asexual reproduction from root system of parent trees. Separate groves derived from the root systems of different pa ...
Plant Kingdom
... Conifers—pine trees 24. How do gymnosperms reproduce? (pg. 274—and figure 19 on pg. 275) First, pollen falls from a male cone onto a female cone. In time, a sperm cell and an egg cell join together in an ovule on the female cone. After fertilization occurs, the seed develops on the scale of the fema ...
... Conifers—pine trees 24. How do gymnosperms reproduce? (pg. 274—and figure 19 on pg. 275) First, pollen falls from a male cone onto a female cone. In time, a sperm cell and an egg cell join together in an ovule on the female cone. After fertilization occurs, the seed develops on the scale of the fema ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.