molecular mechanisms of axonal regeneration in the central
... myelinating axons.11 Many techniques have produced at least some degree of success in improving neuronal survival and function after CNS injury. Benefits observed to date, however, have been relatively limited. Due to the large number of molecular mediators of axonal growth and the many different ta ...
... myelinating axons.11 Many techniques have produced at least some degree of success in improving neuronal survival and function after CNS injury. Benefits observed to date, however, have been relatively limited. Due to the large number of molecular mediators of axonal growth and the many different ta ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
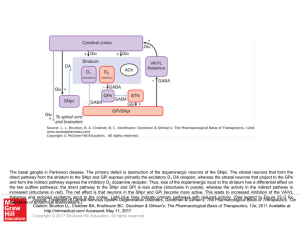
... The basal ganglia in Parkinson disease. The primary defect is destruction of the dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc. The striatal neurons that form the direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the ...
... The basal ganglia in Parkinson disease. The primary defect is destruction of the dopaminergic neurons of the SNpc. The striatal neurons that form the direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
The Nervous System
... • The myelin sheath is made by ________ in the CNS and by _________ in the PNS. • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. • In the PNS, the exterior of the Schwann cell surrounding an axon is the neurilemma ...
... • The myelin sheath is made by ________ in the CNS and by _________ in the PNS. • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. • In the PNS, the exterior of the Schwann cell surrounding an axon is the neurilemma ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
13.1- neurons
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
... When myelin is damaged, dense, scar-like tissue forms around nerve fibers throughout the brain and spinal cord. These scars, sometimes referred to as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spina ...
the nervous system - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... pertaining to the control of skeletal muscle (somatic motor) activity or sensory information from skeletal muscles, tendons, and joints (somatic sensory) pertaining to the control of functions, such as digestion, circulation, etc. (visceral motor) or sensory information from visceral organs (viscera ...
... pertaining to the control of skeletal muscle (somatic motor) activity or sensory information from skeletal muscles, tendons, and joints (somatic sensory) pertaining to the control of functions, such as digestion, circulation, etc. (visceral motor) or sensory information from visceral organs (viscera ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain B) Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
... impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain B) Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain ...
Chapter 3 Notes (part 1) 1. Basic Elements of the Nervous System (a
... of the cell) B. Cell Membrane/Cytoplasmic Membrane selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which ca ...
... of the cell) B. Cell Membrane/Cytoplasmic Membrane selectively-permeable membrane which separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular matrix contains ion channels and protein pumps which manage the flow of ions (charged particles) into and out of the cell C. Axon The part of the cell which ca ...
Neurons Short Version
... Most of the surface and outer few millimeters is gray matter, while most of the inner tracts are composed of white matter (myelinated neurons). Remember in the brain the outer layers are gray matter and the inner is white matter while in the spinal cord the outer layer is white matter and the inne ...
... Most of the surface and outer few millimeters is gray matter, while most of the inner tracts are composed of white matter (myelinated neurons). Remember in the brain the outer layers are gray matter and the inner is white matter while in the spinal cord the outer layer is white matter and the inne ...
Structural arrangement of the nervous sytem. Blood-brain
... transport of trophic and other signalling molecules from the periphery to the neuronal body some neurotropic viruses such as poliomyelitis, herpes, and rabies and neurotoxins enter peripheral nerve endings and ascend to infect the cell body via retrograde transport ...
... transport of trophic and other signalling molecules from the periphery to the neuronal body some neurotropic viruses such as poliomyelitis, herpes, and rabies and neurotoxins enter peripheral nerve endings and ascend to infect the cell body via retrograde transport ...
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
file - Athens Academy
... 14. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stim ...
... 14. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stim ...
Types of neurons
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
Types of neurons
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
... carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord. ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... Sensory neuron-specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation Local neuron-small neuron with no axon or a very short one Efferent axon-carries information away from the structure Afferent axon-brings information into a structure Intrinsic/interneuron-the cell’s den ...
... Sensory neuron-specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation Local neuron-small neuron with no axon or a very short one Efferent axon-carries information away from the structure Afferent axon-brings information into a structure Intrinsic/interneuron-the cell’s den ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... polarized. These changes in the electrical potential of the membrane of the nerve cell results into generation of nerve impulse. It begins with change in the permeability of the membrane and give rise to electrochemical events. These are known as nerve impulses. Normally these impulses start off in ...
... polarized. These changes in the electrical potential of the membrane of the nerve cell results into generation of nerve impulse. It begins with change in the permeability of the membrane and give rise to electrochemical events. These are known as nerve impulses. Normally these impulses start off in ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • long-term memory - involves structural changes in neural connections ...
... • long-term memory - involves structural changes in neural connections ...