Appendix A. Survey text. Please provide the following information
... □ No cardiac catheterization lab □ Diagnostic catheterization lab only □ Interventional catheterization lab with limited hours □ 24/7 Interventional catheterization lab ...
... □ No cardiac catheterization lab □ Diagnostic catheterization lab only □ Interventional catheterization lab with limited hours □ 24/7 Interventional catheterization lab ...
Folie 1
... sudden death and long-term disability. • The prognosis of an AMI depends on the ability to manage acute complications such as life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and, in the long term, reducing the infarct size. Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are the only possible way to save the life of ...
... sudden death and long-term disability. • The prognosis of an AMI depends on the ability to manage acute complications such as life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias and, in the long term, reducing the infarct size. Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) are the only possible way to save the life of ...
12chuyendao_ECG_2 - maritime advance life
... Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can’t conduct the impulse Most common cause: ischemic heart disease ...
... Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can’t conduct the impulse Most common cause: ischemic heart disease ...
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of
... Consider anticoagulation for patients with chronic HF who have Afib and NO additional cardioembolic risk factors. (IIa,B) ...
... Consider anticoagulation for patients with chronic HF who have Afib and NO additional cardioembolic risk factors. (IIa,B) ...
Gabie Gomez - Labmongers2
... flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conduction through the (SA) node and (AV) nodes is slowed and the refractory period i ...
... flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conduction through the (SA) node and (AV) nodes is slowed and the refractory period i ...
Just Move It
... heart rate, conversational pace Vigorous PA: breathing and heart rate, only words or short sentences possible ...
... heart rate, conversational pace Vigorous PA: breathing and heart rate, only words or short sentences possible ...
VAD Strategies and Outcomes in Congenital Heart Disease
... setting of progressive heart failure, usually after previous cardiac surgery. Rarely, long term “Destination” therapy ...
... setting of progressive heart failure, usually after previous cardiac surgery. Rarely, long term “Destination” therapy ...
kbems-pp10
... List and describe the assessment parameters to be evaluated in a patient with a suspected myocardial infarction. 10 Identify the anticipated clinical presentation of a patient with a suspected acute myocardial infarction. 11 Describe the time window as it pertains to reperfusion of a myocardial inju ...
... List and describe the assessment parameters to be evaluated in a patient with a suspected myocardial infarction. 10 Identify the anticipated clinical presentation of a patient with a suspected acute myocardial infarction. 11 Describe the time window as it pertains to reperfusion of a myocardial inju ...
Understanding cardiomyopathy
... reached an advanced stage and some 50% of these patients will die within two years.2 For these individuals, heart transplantation offers the only hope of long-term survival and is considered for patients who are unresponsive to medical therapy. Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) Peripartum cardiomyopa ...
... reached an advanced stage and some 50% of these patients will die within two years.2 For these individuals, heart transplantation offers the only hope of long-term survival and is considered for patients who are unresponsive to medical therapy. Peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) Peripartum cardiomyopa ...
Goals and Objectives Interventional Cardiology
... requirements for cardiology training by major disease process. There is considerable overlap in different areas of training – especially in the areas of coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease and congestive heart failure as well as other niche areas. The guidelines below highlight the speci ...
... requirements for cardiology training by major disease process. There is considerable overlap in different areas of training – especially in the areas of coronary artery disease, valvular heart disease and congestive heart failure as well as other niche areas. The guidelines below highlight the speci ...
Lesson Four - CatsTCMNotes
... strength results in recruitment of a second motor unit. In this example, it is 12 Hz, the reciprocal of the recruitment interval, which is 85 ms. (C) With further increase in muscle strength, a third motor unit is recruited. ...
... strength results in recruitment of a second motor unit. In this example, it is 12 Hz, the reciprocal of the recruitment interval, which is 85 ms. (C) With further increase in muscle strength, a third motor unit is recruited. ...
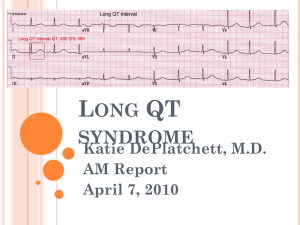
Long QT Syndrome
... LQT1 = exercise-related LQT2 = auditory stimuli LQT3 = at rest or sleep; no benefit from BB Most cases discovered after syncope or arrest ...
... LQT1 = exercise-related LQT2 = auditory stimuli LQT3 = at rest or sleep; no benefit from BB Most cases discovered after syncope or arrest ...
Referring Patients for Advanced Heart Failure Therapies
... for evaluation for advanced HF therapies, including heart transplantation and left ventricular assist device (LVAD). To guide the appropriate recognition and timely referral or these patients, the 2013 ACCF/AHA Heart Failure Guidelines have outlined clinical events and findings useful for identifyin ...
... for evaluation for advanced HF therapies, including heart transplantation and left ventricular assist device (LVAD). To guide the appropriate recognition and timely referral or these patients, the 2013 ACCF/AHA Heart Failure Guidelines have outlined clinical events and findings useful for identifyin ...
When Is it Appropriate to Withdraw Cardiac Resynchronization
... suggested a worse outcome among patients with right ...
... suggested a worse outcome among patients with right ...
Drugs for Heart Failure
... a. Negative inotropic effects b. May have a beneficial effect on mortality with non-ischemic heart failurepraise trial c. May be beneficial for isolated diastolic dysfunction Amiodarone a. Because sudden cardiac death due to arrhythmias can cause 40% of heart failure deaths so, the drug can be somet ...
... a. Negative inotropic effects b. May have a beneficial effect on mortality with non-ischemic heart failurepraise trial c. May be beneficial for isolated diastolic dysfunction Amiodarone a. Because sudden cardiac death due to arrhythmias can cause 40% of heart failure deaths so, the drug can be somet ...
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
... Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) is a rare condition that affects the heart of otherwise fit and healthy people. It causes the heart to beat abnormally fast (ventricular tachycardia), usually at times of exercise (particularly swimming) or high emotion. It can result in d ...
... Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) is a rare condition that affects the heart of otherwise fit and healthy people. It causes the heart to beat abnormally fast (ventricular tachycardia), usually at times of exercise (particularly swimming) or high emotion. It can result in d ...
EP show 2
... to get adequate LV pacing down far enough off the AV groove is also an issue. This technology still needs refinement so that these leads can be implanted widely and safely. ...
... to get adequate LV pacing down far enough off the AV groove is also an issue. This technology still needs refinement so that these leads can be implanted widely and safely. ...
Facts About Sudden Cardiac Arrest
... the heart could turn an abnormally rapid rhythm into a normal one. Later, it also became clear that cardiac arrest could be reversed outside the hospital if specially trained emergency rescue teams reached the person quickly Chances of survival are reduced by 7-10 percent with every passing minute. ...
... the heart could turn an abnormally rapid rhythm into a normal one. Later, it also became clear that cardiac arrest could be reversed outside the hospital if specially trained emergency rescue teams reached the person quickly Chances of survival are reduced by 7-10 percent with every passing minute. ...
Heart Failure and Treatment Options
... Between 2,000 and 2,500 Americans receive a heart transplant each year, while another 25,000-50,000 Americans die waiting for a donor heart to become available. Recent guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the AHA recommend that physicians consider ventricular assist devices ( ...
... Between 2,000 and 2,500 Americans receive a heart transplant each year, while another 25,000-50,000 Americans die waiting for a donor heart to become available. Recent guidelines from the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the AHA recommend that physicians consider ventricular assist devices ( ...
Slide ()
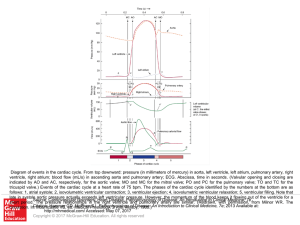
... tricuspid valve.) Events of the cardiac cycle at a heart rate of 75 bpm. The phases of the cardiac cycle identified by the numbers at the bottom are as follows: 1, atrial systole; 2, isovolumetric ventricular contraction; 3, ventricular ejection; 4, isovolumetric ventricular relaxation; 5, ventricul ...
... tricuspid valve.) Events of the cardiac cycle at a heart rate of 75 bpm. The phases of the cardiac cycle identified by the numbers at the bottom are as follows: 1, atrial systole; 2, isovolumetric ventricular contraction; 3, ventricular ejection; 4, isovolumetric ventricular relaxation; 5, ventricul ...
Heart Failure
... Clinical presentation How to treat ◦ Acute cardiac failure ◦ Chronic cardiac failure ...
... Clinical presentation How to treat ◦ Acute cardiac failure ◦ Chronic cardiac failure ...
Sudden Cardiac Death - LeadER Animal Specialty Hospital
... occur suddenly within the pericardial sac. If too much blood accumulates rapidly within the pericardial sac, the right side of the heart is unable to fill up properly with blood, leading to less blood getting into the lungs and oxygen depletion in the body tissues. This can lead to a rapid death. Di ...
... occur suddenly within the pericardial sac. If too much blood accumulates rapidly within the pericardial sac, the right side of the heart is unable to fill up properly with blood, leading to less blood getting into the lungs and oxygen depletion in the body tissues. This can lead to a rapid death. Di ...
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
... (at the level of the xyphoid process) sensing electrodes of the lead system that has been tunneled subcutaneously with a non-traumatic tool to position the coil parallel to, and 1–2 cm to the left of, the sternum (Fig. 6). The pin connector end of the lead is tunneled to the pocket created in the le ...
... (at the level of the xyphoid process) sensing electrodes of the lead system that has been tunneled subcutaneously with a non-traumatic tool to position the coil parallel to, and 1–2 cm to the left of, the sternum (Fig. 6). The pin connector end of the lead is tunneled to the pocket created in the le ...
Cardiac contractility modulation
.jpg?width=300)
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) is a treatment for patients with moderate to severe left ventricular systolic heart failure (NYHA class II–IV). The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances both the strength of ventricular contraction and the heart’s pumping capacity. The CCM mechanism is based on stimulation of the cardiac muscle by non-excitatory electrical signals (NES). CCM treatment is delivered by a pacemaker-like device that applies the NES, adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.In CCM therapy, electrical stimulation is applied to the cardiac muscle during the absolute refractory period. In this phase of the cardiac cycle, electrical signals cannot trigger new cardiac muscle contractions, hence this type of stimulation is known as a non-excitatory stimulation. However, the electrical CCM signals increase the influx of calcium ions into the cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). In contrast to other electrical stimulation treatments for heart failure, such as pacemaker therapy or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), CCM does not affect the cardiac rhythm directly. Rather, the aim is to enhance the heart’s natural contraction (the native cardiac contractility) sustainably over long periods of time. Furthermore, unlike most interventions that increase cardiac contractility, CCM is not associated with an unfavorable increase in oxygen demand by the heart (measured in terms of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption or MVO2). This may be explained by the beneficial effect CCM has in improving cardiac efficiency. A meta-analysis in 2014 and an overview of device-based treatment options in heart failure in 2013 concluded that CCM treatment is safe, that it is generally beneficial to patients and that CCM treatment increases the exercise tolerance (ET) and quality of life (QoL) of patients. Furthermore, preliminary long-term survival data shows that CCM is associated with lower long-term mortality in heart failure patients when compared with expected rates among similar patients not treated with CCM.