The Heart
... 2. blood flows along pressure gradient through any available opening 3. An echocardiogram is a sonogram of the heart and is used to visualize the opening/closing of valves and working of muscles Electrical Event A. electrical events caused by conducting system are recorded as deflection waves transm ...
... 2. blood flows along pressure gradient through any available opening 3. An echocardiogram is a sonogram of the heart and is used to visualize the opening/closing of valves and working of muscles Electrical Event A. electrical events caused by conducting system are recorded as deflection waves transm ...
Heart failure
... remember the arrows would be going backwards to display the backwards progression of CCHF ...
... remember the arrows would be going backwards to display the backwards progression of CCHF ...
Icd 10 code for grade 1 dialostic dysfunction
... failure, a major cause of morbidity and mortality, is defined as symptoms of heart failure in a patient with preserved left ventricular function. It. Dear Sonya, Diastolic dysfunction is an abnormality in the relaxation phase of the heart beat during which the heart is filling with blood in preparat ...
... failure, a major cause of morbidity and mortality, is defined as symptoms of heart failure in a patient with preserved left ventricular function. It. Dear Sonya, Diastolic dysfunction is an abnormality in the relaxation phase of the heart beat during which the heart is filling with blood in preparat ...
Dear Colleagues - Centre for Rare Cardiovascular Diseases
... pulmonary to systemic flow was 2:1). Other findings included mild pulmonary hypertension (mean pulmonary artery pressure, 29 mmHg) increased pulmonary vascular resistance - 203,9 ARU and increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure - 16 mmHg. Discussion, Patients with transannular patch repair of ri ...
... pulmonary to systemic flow was 2:1). Other findings included mild pulmonary hypertension (mean pulmonary artery pressure, 29 mmHg) increased pulmonary vascular resistance - 203,9 ARU and increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure - 16 mmHg. Discussion, Patients with transannular patch repair of ri ...
Medicine and Computers
... Primary care physicians issue approximately 30 renewals per day on average, requiring 80% of nurses' time and costing between five and seven dollars per chart. When using e-prescriptions, physicians save time, and therefore save money ...
... Primary care physicians issue approximately 30 renewals per day on average, requiring 80% of nurses' time and costing between five and seven dollars per chart. When using e-prescriptions, physicians save time, and therefore save money ...
FOCUS ON: ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
... failure), these, too, should be assessed, documented and coded as well. Since many patients with atrial fibrillation are on chronic warfarin therapy, the appropriate “V” code should be used in addition to the code for atrial fibrillation. ...
... failure), these, too, should be assessed, documented and coded as well. Since many patients with atrial fibrillation are on chronic warfarin therapy, the appropriate “V” code should be used in addition to the code for atrial fibrillation. ...
Left ventricular aneurysm - British Heart Foundation
... heart attack. A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries supplying the heart muscle with blood and oxygen becomes blocked, causing part of the heart muscle to die. The affected part area of heart muscle may become weakened, and result in an aneurysm. This is more likely to happen if the ...
... heart attack. A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries supplying the heart muscle with blood and oxygen becomes blocked, causing part of the heart muscle to die. The affected part area of heart muscle may become weakened, and result in an aneurysm. This is more likely to happen if the ...
Beta-blockers for the prevention of sudden cardiac death in heart
... characteristics, study design (including treatment and control arms), follow-up, and outcomes. Pre-specified outcomes of interest included SCD, cardiovascular death (CVD), and all-cause mortality. Outcomes were analyzed according to intention-to-treat. Study quality was formally evaluated using the ...
... characteristics, study design (including treatment and control arms), follow-up, and outcomes. Pre-specified outcomes of interest included SCD, cardiovascular death (CVD), and all-cause mortality. Outcomes were analyzed according to intention-to-treat. Study quality was formally evaluated using the ...
Full Text - Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal
... pericardial disorders. Although, we did not observe statistically significant relationship between severity of clinical symptoms and electrocardiographic changes but 100% of patients with severe symptoms, 35.7% of patients with moderate symptoms and 22.2% patients with mild symptoms had been admitte ...
... pericardial disorders. Although, we did not observe statistically significant relationship between severity of clinical symptoms and electrocardiographic changes but 100% of patients with severe symptoms, 35.7% of patients with moderate symptoms and 22.2% patients with mild symptoms had been admitte ...
Full text
... A normal ECG rarely exists in patients with HF. The presence of anterior Q-waves and a left bundle branch block in patients with ischaemic heart disease are good predictors of a decreased ejection fraction (16) and arrhythmia may be a causative or contributing factor in cases of HF. The significance ...
... A normal ECG rarely exists in patients with HF. The presence of anterior Q-waves and a left bundle branch block in patients with ischaemic heart disease are good predictors of a decreased ejection fraction (16) and arrhythmia may be a causative or contributing factor in cases of HF. The significance ...
Heart Failure - Derby Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
... NT-proBNP <300 ng/L rules out the diagnosis of acute heart failure. Chronic Heart Failure: The following cut-offs are taken from NICE CG108 NT-proBNP (ng/L) ...
... NT-proBNP <300 ng/L rules out the diagnosis of acute heart failure. Chronic Heart Failure: The following cut-offs are taken from NICE CG108 NT-proBNP (ng/L) ...
Chronic valve disease
... left heart (mitral and aortic valves) tends to be more clinically significant due the much higher pressure in the left heart and systemic circulation. This disease is progressive, but the rate of progression is usually slow. The age of onset is typically middle age or later, and the incidence of thi ...
... left heart (mitral and aortic valves) tends to be more clinically significant due the much higher pressure in the left heart and systemic circulation. This disease is progressive, but the rate of progression is usually slow. The age of onset is typically middle age or later, and the incidence of thi ...
دانلود : 19
... pericardial disorders. Although, we did not observe statistically significant relationship between severity of clinical symptoms and electrocardiographic changes but 100% of patients with severe symptoms, 35.7% of patients with moderate symptoms and 22.2% patients with mild symptoms had been admitte ...
... pericardial disorders. Although, we did not observe statistically significant relationship between severity of clinical symptoms and electrocardiographic changes but 100% of patients with severe symptoms, 35.7% of patients with moderate symptoms and 22.2% patients with mild symptoms had been admitte ...
1/Gross and Microscopic Anatomy Of The Human Heart
... y referred to as a functional syncytium, syncytium y y , a single g functional unit. Because cardiac muscle functions as a syncytium, stimulation of an individual muscle cell results in the contraction of all the muscle cells. This is an application of the all-or-nothing principle. Although the prin ...
... y referred to as a functional syncytium, syncytium y y , a single g functional unit. Because cardiac muscle functions as a syncytium, stimulation of an individual muscle cell results in the contraction of all the muscle cells. This is an application of the all-or-nothing principle. Although the prin ...
n–3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Events after Myocardial Infarction
... This combination has an additive effect, with each component targeting a different risk factor for recurrent cardiac events and subsequent complications. An important consideration when discussing secondary prevention therapy with patients is that not only does the prescribed regimen have benefits f ...
... This combination has an additive effect, with each component targeting a different risk factor for recurrent cardiac events and subsequent complications. An important consideration when discussing secondary prevention therapy with patients is that not only does the prescribed regimen have benefits f ...
"Birth defect of Heart, its presentation and treatment"
... In first 3 years of life Fainting spells Abnormal heart beats Child avoids rigorous activities Unable to play with his mates ...
... In first 3 years of life Fainting spells Abnormal heart beats Child avoids rigorous activities Unable to play with his mates ...
九十一年六月分CPC 助猜三軍總醫院小兒科
... The ascites frequently is a component or a complication of hepatic sirrhosis, congestive heart failure, nephrosis, or carcinoma. (transudate) Obstructed venous blood flow from intrahepatic or extrahepatic etiologies can cause splenomegaly. The most common causes include portal vein thrombosis, hepat ...
... The ascites frequently is a component or a complication of hepatic sirrhosis, congestive heart failure, nephrosis, or carcinoma. (transudate) Obstructed venous blood flow from intrahepatic or extrahepatic etiologies can cause splenomegaly. The most common causes include portal vein thrombosis, hepat ...
Left ventricular dysfunction in patients with human
... before death, while wall thickening identified risk population only 18 to 24 months before death. The rapid onset of heart failure has a poor prognosis in both adults and children with HIV infection, since more than half of patients die due to primary heart failure between 6 and 12 months after diag ...
... before death, while wall thickening identified risk population only 18 to 24 months before death. The rapid onset of heart failure has a poor prognosis in both adults and children with HIV infection, since more than half of patients die due to primary heart failure between 6 and 12 months after diag ...
Echo in Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
... Intracellular accumulation & deposition of glycolipids in heart, skin, kidneys First symptoms manifest by age 10 – Peripheral neuropathy, hypohidrosis, skin lesions (angiokeratomas), renal dysfunction ...
... Intracellular accumulation & deposition of glycolipids in heart, skin, kidneys First symptoms manifest by age 10 – Peripheral neuropathy, hypohidrosis, skin lesions (angiokeratomas), renal dysfunction ...
Radiology Packet 1 - University of Prince Edward Island
... lungs centrally, while the periphery (caudal dorsal) is an interstitial infiltrate. Air bronchograms are noted in consolidated regions (Alveolar pattern). ...
... lungs centrally, while the periphery (caudal dorsal) is an interstitial infiltrate. Air bronchograms are noted in consolidated regions (Alveolar pattern). ...
Physiology of Cardiac Hypertrophy in Severely Iron Deficient Rats
... HPLC is a technique used to separate and quantify chemical compounds in a liquid medium Used to determine concentration of norepinephrine in ...
... HPLC is a technique used to separate and quantify chemical compounds in a liquid medium Used to determine concentration of norepinephrine in ...
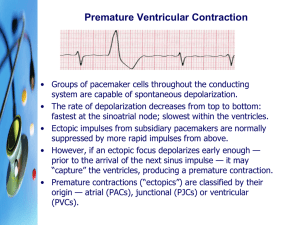
Premature Ventricular Contraction
... system are capable of spontaneous depolarization. • The rate of depolarization decreases from top to bottom: fastest at the sinoatrial node; slowest within the ventricles. • Ectopic impulses from subsidiary pacemakers are normally suppressed by more rapid impulses from above. • However, if an ectopi ...
... system are capable of spontaneous depolarization. • The rate of depolarization decreases from top to bottom: fastest at the sinoatrial node; slowest within the ventricles. • Ectopic impulses from subsidiary pacemakers are normally suppressed by more rapid impulses from above. • However, if an ectopi ...
Heart Failure: Discrepancy Between NYHA Functional Classification
... (HF) exacerbations (1). Large amounts of proBNP can be detected in plasma of healthy subjects and in particular of patients with heart failure. Plasma concentrations of BNP and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are more closely related to measurements of cardiac structure, fu ...
... (HF) exacerbations (1). Large amounts of proBNP can be detected in plasma of healthy subjects and in particular of patients with heart failure. Plasma concentrations of BNP and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are more closely related to measurements of cardiac structure, fu ...
Cardiac contractility modulation
.jpg?width=300)
Cardiac contractility modulation (CCM) is a treatment for patients with moderate to severe left ventricular systolic heart failure (NYHA class II–IV). The short- and long-term use of this therapy enhances both the strength of ventricular contraction and the heart’s pumping capacity. The CCM mechanism is based on stimulation of the cardiac muscle by non-excitatory electrical signals (NES). CCM treatment is delivered by a pacemaker-like device that applies the NES, adjusted to and synchronized with the electrical action in the cardiac cycle.In CCM therapy, electrical stimulation is applied to the cardiac muscle during the absolute refractory period. In this phase of the cardiac cycle, electrical signals cannot trigger new cardiac muscle contractions, hence this type of stimulation is known as a non-excitatory stimulation. However, the electrical CCM signals increase the influx of calcium ions into the cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). In contrast to other electrical stimulation treatments for heart failure, such as pacemaker therapy or implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD), CCM does not affect the cardiac rhythm directly. Rather, the aim is to enhance the heart’s natural contraction (the native cardiac contractility) sustainably over long periods of time. Furthermore, unlike most interventions that increase cardiac contractility, CCM is not associated with an unfavorable increase in oxygen demand by the heart (measured in terms of Myocardial Oxygen Consumption or MVO2). This may be explained by the beneficial effect CCM has in improving cardiac efficiency. A meta-analysis in 2014 and an overview of device-based treatment options in heart failure in 2013 concluded that CCM treatment is safe, that it is generally beneficial to patients and that CCM treatment increases the exercise tolerance (ET) and quality of life (QoL) of patients. Furthermore, preliminary long-term survival data shows that CCM is associated with lower long-term mortality in heart failure patients when compared with expected rates among similar patients not treated with CCM.