Impact of Aortic Valve Design, component materials and
... 1. Bouma B J et al. To operate or not on elderly patients with aortic stenosis: the decision and its consequences. Heart 1999;82:143-148 2. Iung B et al. A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: The Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease. European Heart Journal 20 ...
... 1. Bouma B J et al. To operate or not on elderly patients with aortic stenosis: the decision and its consequences. Heart 1999;82:143-148 2. Iung B et al. A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: The Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease. European Heart Journal 20 ...
Approach to Congestive Heart Failure and Vascular Emergencies
... Aortic Dissection May occur anywhere along the aorta Most common site is in the chest just past the origin of the left subclavian artery Occurs when a tear in the lining of the aorta allows blood to get in between layers of the vessel ...
... Aortic Dissection May occur anywhere along the aorta Most common site is in the chest just past the origin of the left subclavian artery Occurs when a tear in the lining of the aorta allows blood to get in between layers of the vessel ...
ARRHYTHMIAS in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
... Cardiology Clinical Nurse Specialist Stanford Hospital and Clinics Palo Alto, California INTRODUCTION Symptomatic arrhythmias occur with increasing frequency for adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) as they move through adolescence and into adulthood. Arrhythmias are associated with increased hospi ...
... Cardiology Clinical Nurse Specialist Stanford Hospital and Clinics Palo Alto, California INTRODUCTION Symptomatic arrhythmias occur with increasing frequency for adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) as they move through adolescence and into adulthood. Arrhythmias are associated with increased hospi ...
Cardiomyopathy
... Heart tissue problem from previous heart attack Pregnancy Nutritional deficiencies. Abuse of cocaine or anti-depressants Excessive use of alcohol ...
... Heart tissue problem from previous heart attack Pregnancy Nutritional deficiencies. Abuse of cocaine or anti-depressants Excessive use of alcohol ...
Caring For Patients With Cardiomyopathy
... with disproportional septum enlargement as compared to free wall decreased LV cavity creates diastolic stiffness impairing filling thickened, elongated MV leaflets are displaced and may obstruct LV outflow tract LVSDP atrial and pulmonary pressure ...
... with disproportional septum enlargement as compared to free wall decreased LV cavity creates diastolic stiffness impairing filling thickened, elongated MV leaflets are displaced and may obstruct LV outflow tract LVSDP atrial and pulmonary pressure ...
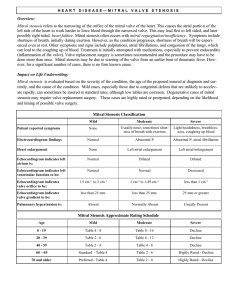
Mitral stenosis
... left side of the heart to work harder to force blood through the narrowed valve. This may lead first to left sided, and later possibly right sided, heart failure . Mitral stenosis often occurs with mitral regurgitation/insufficiency . Symptoms include shortness of breath, initially during exertion. ...
... left side of the heart to work harder to force blood through the narrowed valve. This may lead first to left sided, and later possibly right sided, heart failure . Mitral stenosis often occurs with mitral regurgitation/insufficiency . Symptoms include shortness of breath, initially during exertion. ...
CME Credit Application Form (1 CME credit)
... It has a low prevalence and is an indicator of poor survival. It has a low prevalence and has no relationship with mortality. It has a high prevalence and is an indicator of poor survival. It has a high prevalence and has no relationship with mortality. 2. Which of the following statements i ...
... It has a low prevalence and is an indicator of poor survival. It has a low prevalence and has no relationship with mortality. It has a high prevalence and is an indicator of poor survival. It has a high prevalence and has no relationship with mortality. 2. Which of the following statements i ...
Chapter 20 - FacultyWeb
... Contraction of the ventricles Closure of the semilunar valves Tightening of chordae tendineae and contraction of papillary muscles ...
... Contraction of the ventricles Closure of the semilunar valves Tightening of chordae tendineae and contraction of papillary muscles ...
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function in
... Systolic and diastolic functions of the left ventricle were normal in both groups, although stroke volume was high the obese one. The right ventricle tissue Doppler parameters were similar in both groups. However, S wave of septal/lateral tricuspid valve annulus was reduced in the obese group, but n ...
... Systolic and diastolic functions of the left ventricle were normal in both groups, although stroke volume was high the obese one. The right ventricle tissue Doppler parameters were similar in both groups. However, S wave of septal/lateral tricuspid valve annulus was reduced in the obese group, but n ...
Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits Path of Blood Flow Heart Anatomy
... • HR – (+) - chronotropic factors: HR – (-) - chronotropic factors: HR © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • HR – (+) - chronotropic factors: HR – (-) - chronotropic factors: HR © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Images and Case Reports in Heart Failure
... he use of left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) in the management of advanced heart failure has grown substantially in recent years, with implantation of these devices increasing 10-fold since the approval of a continuous-flow device for destination therapy in January 2010. With the significant in ...
... he use of left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) in the management of advanced heart failure has grown substantially in recent years, with implantation of these devices increasing 10-fold since the approval of a continuous-flow device for destination therapy in January 2010. With the significant in ...
Isolated Non-Compacted Right Ventricular Myocardium
... of embryonic ventricular sinusoids results in non compaction.7 However the exact etiology still remains unknown. Morbidity and mortality is substantial at an early age with five year survival less than 50%. The main complications are heart failure, arrhythmias and embolism. Endomyocardial morphology ...
... of embryonic ventricular sinusoids results in non compaction.7 However the exact etiology still remains unknown. Morbidity and mortality is substantial at an early age with five year survival less than 50%. The main complications are heart failure, arrhythmias and embolism. Endomyocardial morphology ...
New guidelines from the American Heart Association Antibiotics and
... them include people with: ...
... them include people with: ...
S0735109716344436_mmc1
... had failed at least 1 class Ic or III AAD, were 18 to 80 years old, and had a life expectancy ≥2 years. Exclusion criteria were: unable or unwilling to take AADs; catheter ablation for AF within the preceding 4 months; myocardial infarction within the preceding 2 months; cerebrovascular accident (an ...
... had failed at least 1 class Ic or III AAD, were 18 to 80 years old, and had a life expectancy ≥2 years. Exclusion criteria were: unable or unwilling to take AADs; catheter ablation for AF within the preceding 4 months; myocardial infarction within the preceding 2 months; cerebrovascular accident (an ...
Congestive Heart Failure
... 3. In venous, results in a net increase in blood flow into the arterial system, increasing preload, and subsequently workload on the heart Diastolic Heart Failure a. In this form of heart failure (30-40% of heart failure), there is preserved contractility of the myocytes, but decreased ventricular r ...
... 3. In venous, results in a net increase in blood flow into the arterial system, increasing preload, and subsequently workload on the heart Diastolic Heart Failure a. In this form of heart failure (30-40% of heart failure), there is preserved contractility of the myocytes, but decreased ventricular r ...
Pathologies cardiaques à risque chez le jeune sportif
... – 70 % causes can be identified by PP screening… • Maron. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10:374-7. –2 M high school (12-18Y) athlete population (1986-2011), 13 SD (autopsy). •risk of cardiovascular SD: 1:150,000 participants/year •30% detectable (include ECG)… ...
... – 70 % causes can be identified by PP screening… • Maron. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10:374-7. –2 M high school (12-18Y) athlete population (1986-2011), 13 SD (autopsy). •risk of cardiovascular SD: 1:150,000 participants/year •30% detectable (include ECG)… ...
Part I - The Heart - Ms. Lynch`s Lessons
... ● Highest point of blood pressure in the systemic circuit ○ Right Coronary Artery ■ follows coronary sulcus ■ supplies RA, R & LV, & the nodes ■ branches into the posterior interventricular artery ○ Left Coronary Artery ■ supplies LA, LV, & interventricular septum ■ branches into the circumflex arte ...
... ● Highest point of blood pressure in the systemic circuit ○ Right Coronary Artery ■ follows coronary sulcus ■ supplies RA, R & LV, & the nodes ■ branches into the posterior interventricular artery ○ Left Coronary Artery ■ supplies LA, LV, & interventricular septum ■ branches into the circumflex arte ...
ARVD Program Brochure
... Drs. Frank Marcus and Guy Fontaine first described the clinical features of ARVD in 1982. This condition is now often referred to as Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC). ARVD/C is a leading cause of sudden death among young athletes, although people within a broad range of ages an ...
... Drs. Frank Marcus and Guy Fontaine first described the clinical features of ARVD in 1982. This condition is now often referred to as Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC). ARVD/C is a leading cause of sudden death among young athletes, although people within a broad range of ages an ...
The Heart and its Function - School of Medicine
... Aortic stenosis – narrowing of valve opening – high pressure gradient increases systolic pressure and increases ventricular work. ...
... Aortic stenosis – narrowing of valve opening – high pressure gradient increases systolic pressure and increases ventricular work. ...
Cardiac Assessment Outline
... • Determines size, shape and motion of cardiac structures • Sometimes done with stress test, obtaining images while resting and while stressed • Ventricular wall motion during stress but not during rest result in a positive result • Can help detect mitral valve stenosis and regurgitation, mitral val ...
... • Determines size, shape and motion of cardiac structures • Sometimes done with stress test, obtaining images while resting and while stressed • Ventricular wall motion during stress but not during rest result in a positive result • Can help detect mitral valve stenosis and regurgitation, mitral val ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.