Integrating Optogenetic and Pharmacological Approaches to Study
... manipulation. We also discuss recent advances that allow for the selective modulation of cellular function and gene expression with light. In addition, we outline ...
... manipulation. We also discuss recent advances that allow for the selective modulation of cellular function and gene expression with light. In addition, we outline ...
ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels in the Brain: Sensors of
... min of hypoxic challenge (15), and hypoxia-induced hyperpolarization is depressed by the sulfonylureas glibenclamide and tolbutamide in some CA1 neurons (19). However, in other CA1 neurons (for review, see Ref. 19) that are insensitive to KATP channel blockers, a rise in the intracellular Ca2+ conce ...
... min of hypoxic challenge (15), and hypoxia-induced hyperpolarization is depressed by the sulfonylureas glibenclamide and tolbutamide in some CA1 neurons (19). However, in other CA1 neurons (for review, see Ref. 19) that are insensitive to KATP channel blockers, a rise in the intracellular Ca2+ conce ...
Peripheral Nerve Diseases
... All ventral rami except T2-T12 form interlacing nerve networks called plexuses Plexuses are found in the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve Dam ...
... All ventral rami except T2-T12 form interlacing nerve networks called plexuses Plexuses are found in the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral regions Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve Dam ...
Effects of excess vitamin B6 intake on cerebral cortex neurons in rat
... rats have demonstrated that dietary deficiency of vitamin B6 causes very important morphological changes such as dendrite loss, perikaryonal swelling, vacuolization of dendrites, neuropil degeneration in cortical layers, glial proliferation in the area of neuronal loss [35], and decreased number of ...
... rats have demonstrated that dietary deficiency of vitamin B6 causes very important morphological changes such as dendrite loss, perikaryonal swelling, vacuolization of dendrites, neuropil degeneration in cortical layers, glial proliferation in the area of neuronal loss [35], and decreased number of ...
Use of an Amino-Cupric-Silver Technique for the Detection of Early
... been obtained in sections that have been postfixed for only 25 h or at the other extreme for 2-3 months in a refrigerator (4°C). The postfixation eventually suppresses normal fiber staining; at 24 h some normal fibers will be stained, while with extended postfixation, impregnation of degenerating ne ...
... been obtained in sections that have been postfixed for only 25 h or at the other extreme for 2-3 months in a refrigerator (4°C). The postfixation eventually suppresses normal fiber staining; at 24 h some normal fibers will be stained, while with extended postfixation, impregnation of degenerating ne ...
The Central Nervous System
... Information travels within the nervous system primarily in the form of propagated electrical signals known as action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated axons. ...
... Information travels within the nervous system primarily in the form of propagated electrical signals known as action potentials. The most important information (e.g., vision, balance, movement), is carried by myelinated axons. ...
Document
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
Figure 15.9
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
Technologies émergentes de mémoire résistive pour les systèmes
... (CBRAM) and Metal-Oxide based Memory (OXRAM) can play in dedicated neuromorphic hardware. We focus on the emulation of synaptic plasticity effects such as long-term potentiation (LTP), long term depression (LTD) and spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP) with RRAM synapses. We developed novel low- ...
... (CBRAM) and Metal-Oxide based Memory (OXRAM) can play in dedicated neuromorphic hardware. We focus on the emulation of synaptic plasticity effects such as long-term potentiation (LTP), long term depression (LTD) and spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP) with RRAM synapses. We developed novel low- ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... is that ion transporters are as important as channels in the generation of electrical signals. During the recent years, there has been a sharp increase in the interest of neurobiologists in plasmalemmal ion-transport mechanisms, especially in cation chloride cotransporters (CCCs). Initially, CCCs we ...
... is that ion transporters are as important as channels in the generation of electrical signals. During the recent years, there has been a sharp increase in the interest of neurobiologists in plasmalemmal ion-transport mechanisms, especially in cation chloride cotransporters (CCCs). Initially, CCCs we ...
Autonomic NS
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
serotonergic modulation of swimming speed in the pteropod mollusc
... swimming system of Clione limacina (Satterlie, 1995). Since *Address for correspondence. ...
... swimming system of Clione limacina (Satterlie, 1995). Since *Address for correspondence. ...
Functional Motifs Composed of Morphologically Homologous
... Whitney U test). The shortest latency of the M-cells among recorded RSNs demonstrated markedly fast conduction velocity in the M-cell axon (Table 1) and corresponded to the exceptionally large diameter of the myelinated M-axon. Morphology of RSNs in r4 –r6 In the present study, single intracellular ...
... Whitney U test). The shortest latency of the M-cells among recorded RSNs demonstrated markedly fast conduction velocity in the M-cell axon (Table 1) and corresponded to the exceptionally large diameter of the myelinated M-axon. Morphology of RSNs in r4 –r6 In the present study, single intracellular ...
Structure and Function in the Inferior Olivary Nucleus
... The inferior olivary nucleus is the source of the climbing fibres, one of the two major afferent pathways into the cerebellum. This thesis is concerned with aspects of the cellular anat ...
... The inferior olivary nucleus is the source of the climbing fibres, one of the two major afferent pathways into the cerebellum. This thesis is concerned with aspects of the cellular anat ...
neuronal types and their specification dynamics in
... target tissues receive some input at all time. It is this complementary interaction between the two autonomic divisions that maintains body homeostasis. Despite their general similarities, there are crucial differences regarding the location of the sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons and the neu ...
... target tissues receive some input at all time. It is this complementary interaction between the two autonomic divisions that maintains body homeostasis. Despite their general similarities, there are crucial differences regarding the location of the sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons and the neu ...
Tyrosine Hydroxylase in the Rat Parabrachial Region: Ultrastructural
... ribosomes, and microtubules. The labeled dendrites were most often postsynaptic to 1 unlabeled terminal seen in a single plane of section (Fig. 2A). The unlabeled terminals measured 0.4-1.2 pm, contained mitochondria and numerous flattened or oval s&s, and appeared to form primarily asymmetric densi ...
... ribosomes, and microtubules. The labeled dendrites were most often postsynaptic to 1 unlabeled terminal seen in a single plane of section (Fig. 2A). The unlabeled terminals measured 0.4-1.2 pm, contained mitochondria and numerous flattened or oval s&s, and appeared to form primarily asymmetric densi ...
BRAINSTEM
... higher order sensory cortical areas and primary motor cortex. Callosal neurons arise in layers 2 and 3 and project to the contralateral somatic sensory cortex via the body of the corpus callosum. Descending projection neurons descend to the striatum, VP nuclei, brain stem (esp. dorsal column nuclei) ...
... higher order sensory cortical areas and primary motor cortex. Callosal neurons arise in layers 2 and 3 and project to the contralateral somatic sensory cortex via the body of the corpus callosum. Descending projection neurons descend to the striatum, VP nuclei, brain stem (esp. dorsal column nuclei) ...
Nervous System - Lakeridge Health
... a relay station which receives sensory impressions from lower regions in the body and projects them onto the cerebral cortex for interpretation. It is possible that certain types of pain may reach consciousness in this area as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... a relay station which receives sensory impressions from lower regions in the body and projects them onto the cerebral cortex for interpretation. It is possible that certain types of pain may reach consciousness in this area as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
CNS - Algonquin College
... a relay station which receives sensory impressions from lower regions in the body and projects them onto the cerebral cortex for interpretation. It is possible that certain types of pain may reach consciousness in this area as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... a relay station which receives sensory impressions from lower regions in the body and projects them onto the cerebral cortex for interpretation. It is possible that certain types of pain may reach consciousness in this area as well. ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Nogo Receptor mRNA Expression in Intact and Regenerating CNS
... IN-1. Nogo-A is found in CNS myelin and is highly expressed by oligodendrocytes but not by Schwann cells. A 66-residue putative extracellular domain sequence (Nogo-66), common to all three forms, inhibits axonal extension and induces the collapse of growth cones. It is now clear, however, that sever ...
... IN-1. Nogo-A is found in CNS myelin and is highly expressed by oligodendrocytes but not by Schwann cells. A 66-residue putative extracellular domain sequence (Nogo-66), common to all three forms, inhibits axonal extension and induces the collapse of growth cones. It is now clear, however, that sever ...
Chapter 11 Fundamentals of Nervous System
... Repolarization – the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential Hyperpolarization – the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential ...
... Repolarization – the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential Hyperpolarization – the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential ...
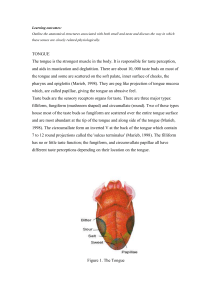
The bit used for relationship between smell and taste
... sourness. If students are patient, some may notice that as the candy dissolves they can identify the specific taste. This is due to some scent molecules travel up to the olfactory organ through the oropharynx, the passage at the back of the throat and to the nose. Since we can only taste four differ ...
... sourness. If students are patient, some may notice that as the candy dissolves they can identify the specific taste. This is due to some scent molecules travel up to the olfactory organ through the oropharynx, the passage at the back of the throat and to the nose. Since we can only taste four differ ...
Planar cell polarity signaling in neural development
... The consensus view is that PCP is mediated by transient asymmetric expression of surface membrane complexes in different sectors of the adherens junction (AJ) belt (Figure 1). In the wing, Flamingo is present symmetrically, whereas Frizzled and Van Gogh are targeted to opposing junctional domains, F ...
... The consensus view is that PCP is mediated by transient asymmetric expression of surface membrane complexes in different sectors of the adherens junction (AJ) belt (Figure 1). In the wing, Flamingo is present symmetrically, whereas Frizzled and Van Gogh are targeted to opposing junctional domains, F ...
Cautionary Observations on Preparing and Interpreting Brain
... cells. But this is often not the case. For example, the anti-Fas II antibody, which recognizes cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin II (Drosophila homologue of NCAM; Grenningloh et al., 1991), nicely labels neural fibers of specific cells but not their cell bodies, making it impossible to trace the orig ...
... cells. But this is often not the case. For example, the anti-Fas II antibody, which recognizes cell adhesion molecule Fasciclin II (Drosophila homologue of NCAM; Grenningloh et al., 1991), nicely labels neural fibers of specific cells but not their cell bodies, making it impossible to trace the orig ...
Motor Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum
... 1. Projects to primary motor cortex and brain stem (particularly descending reticular formation) 2. Associated with assembling movements into coordinated actions. Lesions impair ability to develop appropriate sequences of muscle contractions 3. Participates in movements that involve several joints a ...
... 1. Projects to primary motor cortex and brain stem (particularly descending reticular formation) 2. Associated with assembling movements into coordinated actions. Lesions impair ability to develop appropriate sequences of muscle contractions 3. Participates in movements that involve several joints a ...