New Features of Connectivity in Piriform Cortex Visualized by
... nucleus where dendrites from deep pyramidal and nonpyramidal cells predominate (Haberly, 1998). In layer IIId, long associational axons gave rise to collaterals that ascended to more superficial layers at varying distances from the cell body (Fig. 1 B, arrowheads). Within layer Ib (the deep portion ...
... nucleus where dendrites from deep pyramidal and nonpyramidal cells predominate (Haberly, 1998). In layer IIId, long associational axons gave rise to collaterals that ascended to more superficial layers at varying distances from the cell body (Fig. 1 B, arrowheads). Within layer Ib (the deep portion ...
Morphology of GABAergic Neurons in the Inferior Colliculus of the Cat
... are shown (Fig. 5: 10, 43, 52, 53). Some smaller GADDistribution of GABAergic Cells in the IC positive neurons were included for comparison (Fig. 5: 6, GABAergic neurons were found in every subdivision of 24,55, 71). When the relative sizes of the GABA-positive neurons the IC. The distribution of GA ...
... are shown (Fig. 5: 10, 43, 52, 53). Some smaller GADDistribution of GABAergic Cells in the IC positive neurons were included for comparison (Fig. 5: 6, GABAergic neurons were found in every subdivision of 24,55, 71). When the relative sizes of the GABA-positive neurons the IC. The distribution of GA ...
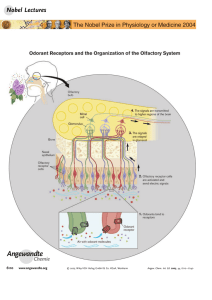
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
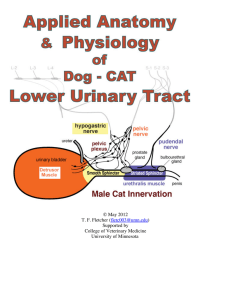
May 2012 TF Fletcher ()
... enable complete emptying of the urinary bladder at appropriate times. Spinal lesions that damage descending tracts from the pons interrupt coordinated detrusorsphincter activity, producing detrusor-sphincter dyssynergy (i.e., loss of synergy = working together). As a consequence of dyssynergy, smoot ...
... enable complete emptying of the urinary bladder at appropriate times. Spinal lesions that damage descending tracts from the pons interrupt coordinated detrusorsphincter activity, producing detrusor-sphincter dyssynergy (i.e., loss of synergy = working together). As a consequence of dyssynergy, smoot ...
PDF Document
... manipulate ionic microdomains, and probe the complex neuronal-extracellular space interactions that regulate neural excitability. The extracellular ionic environment in neural tissue plays a critical role in regulating the resting membrane potential and signaling events such as action potential gene ...
... manipulate ionic microdomains, and probe the complex neuronal-extracellular space interactions that regulate neural excitability. The extracellular ionic environment in neural tissue plays a critical role in regulating the resting membrane potential and signaling events such as action potential gene ...
Plasticity in the developing brain: Implications for
... opens NMDA-type glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic membrane leading to an increase in intracellular calcium and insertion of AMPA type glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. AMPA receptors move into the postsynaptic membrane from a receptor pool located in endosomes within the cytopl ...
... opens NMDA-type glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic membrane leading to an increase in intracellular calcium and insertion of AMPA type glutamate receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. AMPA receptors move into the postsynaptic membrane from a receptor pool located in endosomes within the cytopl ...
An Imperfect Dopaminergic Error Signal Can Drive Temporal
... This is a crucial point, as the phasic dopaminergic firing rate only resembles the error signal of TD learning to a limited extent. The most obvious difference between the two signals is that the low baseline firing rate of the dopamine neurons implies a lower bound for the representation of negativ ...
... This is a crucial point, as the phasic dopaminergic firing rate only resembles the error signal of TD learning to a limited extent. The most obvious difference between the two signals is that the low baseline firing rate of the dopamine neurons implies a lower bound for the representation of negativ ...
Neuron-Binding Human Monoclonal Antibodies Support Central
... CNS tissue and to the surface of neurons in culture. Both monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) overrode the inhibitory effect of CNS mouse myelin on granule cell neurite extension. Neither mAb bound to the surface of mature oligodendrocytes or strictly colocalized with myelin proteins. Sialidase treatment e ...
... CNS tissue and to the surface of neurons in culture. Both monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) overrode the inhibitory effect of CNS mouse myelin on granule cell neurite extension. Neither mAb bound to the surface of mature oligodendrocytes or strictly colocalized with myelin proteins. Sialidase treatment e ...
32 MaxPlanckResearch 3 | 09 Small but mighty: In mice, around ten
... Thus, for better or for worse, he works on the assumption of the “one neuronone receptor hypothesis.” There is, however, some evidence that olfactory sensory neurons can actually produce several receptor types ...
... Thus, for better or for worse, he works on the assumption of the “one neuronone receptor hypothesis.” There is, however, some evidence that olfactory sensory neurons can actually produce several receptor types ...
OPTOGENETIC STUDY OF THE PROJECTIONS FROM THE BED
... cells that project to CeA. In thirteen of these cells, blue light stimuli elicited IPSPs (Fig. 2B1); ...
... cells that project to CeA. In thirteen of these cells, blue light stimuli elicited IPSPs (Fig. 2B1); ...
A monument of inefficiency: The presumed course of the recurrent
... anatomical evidence for vocal ability” in non−avian dino− saurs. In the absence of data, the most that can be said is that if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nerv ...
... anatomical evidence for vocal ability” in non−avian dino− saurs. In the absence of data, the most that can be said is that if sauropods produced or modulated sounds using their la− rynges, those activities were subject to relatively long physi− ological delays. This effect of large body size on nerv ...
Part d
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
Cellular mechanisms underlying network synchrony in the medial
... The entorhinal cortex (EC) forms the main input to the hippocampus and is responsible for the pre-processing (familiarity) of the input signals. On Medial surface, EC approximately maps to areas 28 and 34, at lower left. ...
... The entorhinal cortex (EC) forms the main input to the hippocampus and is responsible for the pre-processing (familiarity) of the input signals. On Medial surface, EC approximately maps to areas 28 and 34, at lower left. ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
... • Muscles atrophy • Death may occur due to paralysis of respiratory muscles or cardiac arrest • Survivors often develop postpolio syndrome many years later, as neurons are lost ...
Cellular Mechanisms in the Amygdala Involved in Memory
... underlying fear memory will enhance our understanding of biological mechanism to enemies, as well as our ability to develop treatments for individual afflicted with anxiety disorders, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The discovery of long-term potentiation (LTP), a phenomenon in which ...
... underlying fear memory will enhance our understanding of biological mechanism to enemies, as well as our ability to develop treatments for individual afflicted with anxiety disorders, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The discovery of long-term potentiation (LTP), a phenomenon in which ...
Axonal morphometry of hippocampal pyramidal neurons semi
... comprehensive understanding of the dynamic mechanisms of hippocampal learning will likely require a quantitative map of the entire axonal arbors originating from different network sub-regions. On the other hand, this same structural complexity renders the 3D digital reconstruction of these axons exc ...
... comprehensive understanding of the dynamic mechanisms of hippocampal learning will likely require a quantitative map of the entire axonal arbors originating from different network sub-regions. On the other hand, this same structural complexity renders the 3D digital reconstruction of these axons exc ...
PAIN
... mechanical stimuli. via A-delta fibers. Polymodal nociceptors: activated by noxious mechanical stimuli, noxious heat, noxious cold, irritant chemicals. slow dull burning pain or aching pain, via nonmyelinated C fibers. Persists long after the stimulus is ...
... mechanical stimuli. via A-delta fibers. Polymodal nociceptors: activated by noxious mechanical stimuli, noxious heat, noxious cold, irritant chemicals. slow dull burning pain or aching pain, via nonmyelinated C fibers. Persists long after the stimulus is ...
Components of Decision-Making
... μ+ = excitatory mu-opioid receptor; μ- = inhibitory mu-opioid receptor; LH = lateral hypothalamus; Orx1 = orexin type 1 receptor; DA = dopamine; VTA = ventral tegmental area; NAc = nucleus accumbens; NIH = novelty-induced hypophagia; NE = norepinephrine; LC = locus ceruleus; BPN = buprenorphine ; Dy ...
... μ+ = excitatory mu-opioid receptor; μ- = inhibitory mu-opioid receptor; LH = lateral hypothalamus; Orx1 = orexin type 1 receptor; DA = dopamine; VTA = ventral tegmental area; NAc = nucleus accumbens; NIH = novelty-induced hypophagia; NE = norepinephrine; LC = locus ceruleus; BPN = buprenorphine ; Dy ...
The neural milieu of the developing choroid plexus: neural stem
... 1978a,b,c; Edvinsson and Lindvall, 1978), but there is only one study where this issue was specifically addressed and that suggests that the CP becomes innervated postnatally (Lindvall and Owman, 1978). This seems peculiar, as innervation tends to occur at early stages of organ development, before a ...
... 1978a,b,c; Edvinsson and Lindvall, 1978), but there is only one study where this issue was specifically addressed and that suggests that the CP becomes innervated postnatally (Lindvall and Owman, 1978). This seems peculiar, as innervation tends to occur at early stages of organ development, before a ...
Some insights into computational models of (patho)physiological
... understand how the brain works it is not enough to accumulate continuously more and more facts. In order to acquire a coherent view of the mechanisms through which the nervous system mediates behavior, the experimental facts have to be related to each other. The interactions between neural component ...
... understand how the brain works it is not enough to accumulate continuously more and more facts. In order to acquire a coherent view of the mechanisms through which the nervous system mediates behavior, the experimental facts have to be related to each other. The interactions between neural component ...
Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase-like
... neurons in the metamorphosing nervous system (for review see Truman, 1996). Most nerve cells of the adult brain that differentiate during metamorphosis arise from neuroblasts that have been arrested during early larval stages and that start a second phase of proliferation in late larval stages. Amon ...
... neurons in the metamorphosing nervous system (for review see Truman, 1996). Most nerve cells of the adult brain that differentiate during metamorphosis arise from neuroblasts that have been arrested during early larval stages and that start a second phase of proliferation in late larval stages. Amon ...
The Nervous System
... Dorsal (posterior) horns Ventral (anterior)horns Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) ...
... Dorsal (posterior) horns Ventral (anterior)horns Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) ...
Long-term potentiation in the anterior cingulate cortex and chronic
... cyclases (ACs), mainly AC1 and Ca2þ/CaM-dependent protein kinases. The trafficking of postsynaptic GluA1 containing AMPA receptor contributes to enhanced synaptic responses. An NMDA receptor independent form of LTP can be also induced. Activation of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels (L-VGCCs) is ...
... cyclases (ACs), mainly AC1 and Ca2þ/CaM-dependent protein kinases. The trafficking of postsynaptic GluA1 containing AMPA receptor contributes to enhanced synaptic responses. An NMDA receptor independent form of LTP can be also induced. Activation of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels (L-VGCCs) is ...
Drosophila GABA, short neuropeptide F and their receptors
... and learning behavior [see (Davis, 1996)]. 1.2. Neurotransmitters and neuropeptides Neurons are communicating with each other by chemical and occasionally electrical signalling. The chemical transmission is based on various types of substances such as neuropeptides or different kinds of neurotransmi ...
... and learning behavior [see (Davis, 1996)]. 1.2. Neurotransmitters and neuropeptides Neurons are communicating with each other by chemical and occasionally electrical signalling. The chemical transmission is based on various types of substances such as neuropeptides or different kinds of neurotransmi ...
Glia–Neuron Interactions in Nervous System Function
... Although these approaches have proven quite informative, it is yet unclear how relevant these studies are to the functioning of the nervous system in vivo. Glial alterations leading to obvious organismal consequences have been described. Demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Dejerine‐S ...
... Although these approaches have proven quite informative, it is yet unclear how relevant these studies are to the functioning of the nervous system in vivo. Glial alterations leading to obvious organismal consequences have been described. Demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Dejerine‐S ...