Introduction_to_nerv..
... mainly the membranes of Schwann cells • These membranes contain phospholipid molecules that have long fatty acids. • These prevent the movement of charged water soluble ions ...
... mainly the membranes of Schwann cells • These membranes contain phospholipid molecules that have long fatty acids. • These prevent the movement of charged water soluble ions ...
No Slide Title
... Copyright 2000, All Rights Reserved. Material is in logical order: see texts, lab. outline for characteristics To advance to next slide: -click mouse or “page down” To return to the previous slide: - press “page up” ...
... Copyright 2000, All Rights Reserved. Material is in logical order: see texts, lab. outline for characteristics To advance to next slide: -click mouse or “page down” To return to the previous slide: - press “page up” ...
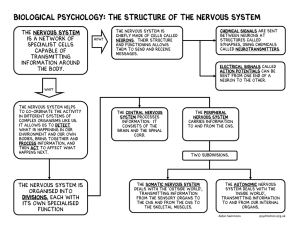
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
CHAPTER EIGHT
... How the pump works - when three sodium ions bind on the inside of the carrier protein and two potassium ions bind on the outside, the ATPase is activated. The molecule of ATP is cleaved, splitting it into ADP + P and liberating a high energy phosphate bond for energy. This energy causes the carrier ...
... How the pump works - when three sodium ions bind on the inside of the carrier protein and two potassium ions bind on the outside, the ATPase is activated. The molecule of ATP is cleaved, splitting it into ADP + P and liberating a high energy phosphate bond for energy. This energy causes the carrier ...
Target-cell-specific concentration of a metabotropic glutamate
... TilE probability of synaptic neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals is regulated by presynaptic receptors responding to transmitters released fro m the same nerve terminal or from terminals of other neurons. The release of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter, is suppressed by pre ...
... TilE probability of synaptic neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals is regulated by presynaptic receptors responding to transmitters released fro m the same nerve terminal or from terminals of other neurons. The release of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter, is suppressed by pre ...
Slide ()
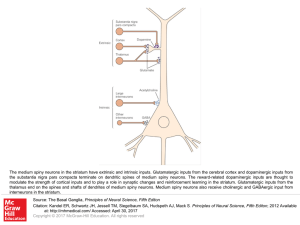
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... D. small molecule neurotransmitter. An action potential just traveled down to the tip of an axon. What will it do next? A. It will "jump" to the target neuron. B. It will travel across the synapse. C. It will trigger the release of neurotransmitters. D. It will gain in strength. Which of the followi ...
... D. small molecule neurotransmitter. An action potential just traveled down to the tip of an axon. What will it do next? A. It will "jump" to the target neuron. B. It will travel across the synapse. C. It will trigger the release of neurotransmitters. D. It will gain in strength. Which of the followi ...
Objectives included for the test File
... D-Neurotransmitters and synapses State that some presynaptic neurons excite postsynaptic transmission and others inhibit postsynaptic transmission. Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synap ...
... D-Neurotransmitters and synapses State that some presynaptic neurons excite postsynaptic transmission and others inhibit postsynaptic transmission. Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synap ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... Hebb was fascinated by the way people learned and the way they retained information. In 1949, he suggested that the nervous system was encoding information by strengthening activated neuronal connections. ...
... Hebb was fascinated by the way people learned and the way they retained information. In 1949, he suggested that the nervous system was encoding information by strengthening activated neuronal connections. ...
Neuro Quiz 4 – Notes from April 9 to April 16 First order neurons
... 77. T or F: Interneurons have many interconnections amongst themselves, but have little to do with the anterior motor neurons. 78. Most incoming signals are transmitted first through _______ , where they are appropriately processed. These neurons integrate all the incoming and outgoing information. ...
... 77. T or F: Interneurons have many interconnections amongst themselves, but have little to do with the anterior motor neurons. 78. Most incoming signals are transmitted first through _______ , where they are appropriately processed. These neurons integrate all the incoming and outgoing information. ...
Nervous System
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives ...
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives ...
BOX 11.1 NEURONAL CABLE THEORY AND COMPUTATIONAL
... Rushton, 1946), but Rall extended its application to dendrites. Although much of Rall’s work used this equation to analyze voltage changes in simple linear cables, he also applied it to branching cables and showed that it could be used to analyze dendrites with arbitrary branching geometries. Indeed ...
... Rushton, 1946), but Rall extended its application to dendrites. Although much of Rall’s work used this equation to analyze voltage changes in simple linear cables, he also applied it to branching cables and showed that it could be used to analyze dendrites with arbitrary branching geometries. Indeed ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
... 9. Close examination of an effector organ shows that it receives innervation by way of two neurons. The first is located in the spinal cord and synapses with a second in a chain ganglion. Chemical analysis indicates that the postsynaptic neuron releases acetylcholine and that the effector has many ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
Technical Definitions
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
... that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an article by German anatomist Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer in 1891. Waldeyer proposed neurons to be spec ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neuron that receives information. d. Axon – Long fiber that transmits information away to other neurons, muscles, or glands. e. Myelin Sheath – Insulating Material that encases some Axons. i. It speeds up to transmission of information. f. Terminal Button – Small knobs where ...
... c. Dendrite – Parts of a Neuron that receives information. d. Axon – Long fiber that transmits information away to other neurons, muscles, or glands. e. Myelin Sheath – Insulating Material that encases some Axons. i. It speeds up to transmission of information. f. Terminal Button – Small knobs where ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... • A synapse is the junction between: • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
... • A synapse is the junction between: • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
Synapse formation in developing neural circuits.
... components (Cowan and Kandel, 2001; De Camilli et al., 2001). There are two general categories of synapses: electrical synapses and chemical synapses. Physiologists and neuropharmacologists functionally defined these two categories of synapses well before they were visualized by cell biologists (Cow ...
... components (Cowan and Kandel, 2001; De Camilli et al., 2001). There are two general categories of synapses: electrical synapses and chemical synapses. Physiologists and neuropharmacologists functionally defined these two categories of synapses well before they were visualized by cell biologists (Cow ...
Wallin_Back_to_School_with_the_Thinking_Maps
... reference (perspective), which leads to less confusion and better communication • allow students to SHOW their THINKING ...
... reference (perspective), which leads to less confusion and better communication • allow students to SHOW their THINKING ...
Psychology 210
... Graded Potentials Action Potentials are referred to as “________________________________” Either get an action potential or not Inputs that don’t reach threshold: Graded Potentials Can add up across synapses/inputs to reach threshold Saltatory Conduction ________________________________is not perfe ...
... Graded Potentials Action Potentials are referred to as “________________________________” Either get an action potential or not Inputs that don’t reach threshold: Graded Potentials Can add up across synapses/inputs to reach threshold Saltatory Conduction ________________________________is not perfe ...
Brain Neurotransmitters
... Alcohol acts at many sites, including the reticular formation, spinal cord, cerebellum and cerebral cortex, and on many neurotransmitter systems. ...
... Alcohol acts at many sites, including the reticular formation, spinal cord, cerebellum and cerebral cortex, and on many neurotransmitter systems. ...