Slide ()
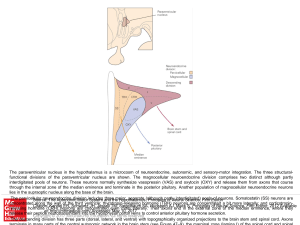
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
The Nervous System
... Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
... Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
CHAPTER 3
... biological psychologists examine the cells and chemicals that make up the structure and functioning of the nervous system. a) Neurons, or nerve cells, are the basic cells that make up the nervous system. Neurons receive information and transmit it to other cells by conducting electrochemical impulse ...
... biological psychologists examine the cells and chemicals that make up the structure and functioning of the nervous system. a) Neurons, or nerve cells, are the basic cells that make up the nervous system. Neurons receive information and transmit it to other cells by conducting electrochemical impulse ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... coming from body wall - skin, muscles and joints; Visceral Sensroy = coming from internal organs - viscera Motor neurons take information from CNS to effectors like muscles or glands. Motor = Effrent. Somatic Motor – going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. ...
... coming from body wall - skin, muscles and joints; Visceral Sensroy = coming from internal organs - viscera Motor neurons take information from CNS to effectors like muscles or glands. Motor = Effrent. Somatic Motor – going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. ...
background information - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... There are millions of nerve cells in the body. Nerve cells are called neurons and they have a very different shape than most other cells in the body. The cell body contains structures found in other body cells (such as the nucleus and mitochondria). A nerve cell body has dendrites that reach out int ...
... There are millions of nerve cells in the body. Nerve cells are called neurons and they have a very different shape than most other cells in the body. The cell body contains structures found in other body cells (such as the nucleus and mitochondria). A nerve cell body has dendrites that reach out int ...
16. Taste, smell
... (cyclic AMP) opens sodium channels causing depolarization; resting membrane potential (-55 mv.) causes background tonic signal (slow volley of action potentials) – receptor excitation results in increased signal strength (more rapid volley of APs) - pathways: receptor axons traverse cribriform plate ...
... (cyclic AMP) opens sodium channels causing depolarization; resting membrane potential (-55 mv.) causes background tonic signal (slow volley of action potentials) – receptor excitation results in increased signal strength (more rapid volley of APs) - pathways: receptor axons traverse cribriform plate ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... ▪ Neurons vary with respect to their function: Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glan ...
... ▪ Neurons vary with respect to their function: Sensory neurons: (Afferent) Carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) toward the central nervous system. Motor neurons: (motoneurons) (Efferent) Carry signals away from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glan ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... cleft. That region or junction is called synapses. – This is where neurons communicate – The signaling activity of the nervous system is made up of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons. • These synapses do not communicate by touch, but by releasing chemicals, or neuro ...
... cleft. That region or junction is called synapses. – This is where neurons communicate – The signaling activity of the nervous system is made up of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons. • These synapses do not communicate by touch, but by releasing chemicals, or neuro ...
P.1.a.016 Emotionally painful stress causes changes in L1 insertion
... 6 for schizophrenia. Kinesin family member 13A (KIF13A) gene located at chromosome 6p23, encodes a member of the kinesin family of microtubule-based motor proteins that function in the positioning of endosomes. This family member can direct mannose-6-phosphate receptor-containing vesicles from the t ...
... 6 for schizophrenia. Kinesin family member 13A (KIF13A) gene located at chromosome 6p23, encodes a member of the kinesin family of microtubule-based motor proteins that function in the positioning of endosomes. This family member can direct mannose-6-phosphate receptor-containing vesicles from the t ...
Ling 8700: Lecture Notes 1 A Model of Neural Activation
... 1. start with more K+ but much fewer Na+ ions than outside, creating membrane potential; 2. receptors receive neurotransmitters, open ligand-gated channels; 3. ligand-gated channels let Ca++ /Cl− in or K+ out, changing potential (this is a linear function on the sum of pos/neg ions in the neuron); 4 ...
... 1. start with more K+ but much fewer Na+ ions than outside, creating membrane potential; 2. receptors receive neurotransmitters, open ligand-gated channels; 3. ligand-gated channels let Ca++ /Cl− in or K+ out, changing potential (this is a linear function on the sum of pos/neg ions in the neuron); 4 ...
and by climbing fibers
... Excitatory inputs to the cerebellum are provided by mossy fibers and climbing fibers. The mossy fibers originate in the spinocerebellar tract and in brain stem nuclei; they excite granule cells. The climbing fibers originate in the medulla (the inferior olive); they make synapses on Purkinje cells. ...
... Excitatory inputs to the cerebellum are provided by mossy fibers and climbing fibers. The mossy fibers originate in the spinocerebellar tract and in brain stem nuclei; they excite granule cells. The climbing fibers originate in the medulla (the inferior olive); they make synapses on Purkinje cells. ...
Endocrine System PowerPoint
... Hormones are released directly into the bloodstream They are transported by the bloodstream to all parts of the body with the flow of blood ...
... Hormones are released directly into the bloodstream They are transported by the bloodstream to all parts of the body with the flow of blood ...
Ch6 - Unit3Biology
... These neurohormones are released into the blood, which then travel to the target organ which receives the signal thus resulting in a response from the receptor cell. For example, the hypothalamus of the brain has several different kinds of neurons each producing a different kind of neurohormone. The ...
... These neurohormones are released into the blood, which then travel to the target organ which receives the signal thus resulting in a response from the receptor cell. For example, the hypothalamus of the brain has several different kinds of neurons each producing a different kind of neurohormone. The ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System, Part 2
... • Repeated use increases the efficiency of neurotransmission • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron – Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry – Ca2+ activates k ...
... • Repeated use increases the efficiency of neurotransmission • Ca2+ concentration increases in presynaptic terminal and ostsynaptic neuron • Brief high-frequency stimulation partially depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron – Chemically gated channels (NMDA receptors) allow Ca2+ entry – Ca2+ activates k ...
Dr. Begay`s Notes from Pharm I
... binding of DA or NE trigger a sequence of chemical events within the postsynaptic cell membrane affecting ion channels and intracelluar metabolic activity. Termination of transmitter action by presynapse reuptake mechanism and MAO enzyme degradation within axon terminal. ...
... binding of DA or NE trigger a sequence of chemical events within the postsynaptic cell membrane affecting ion channels and intracelluar metabolic activity. Termination of transmitter action by presynapse reuptake mechanism and MAO enzyme degradation within axon terminal. ...
Biological Psychology A branch of psychology concerned with links
... A neural impulse (a brief electrical charge) that travels down an axon; The action potential is generated by movement of positively charged atoms through channels in the axon's membrane ...
... A neural impulse (a brief electrical charge) that travels down an axon; The action potential is generated by movement of positively charged atoms through channels in the axon's membrane ...
Outline: Muscular System
... Body mass index (BMI): an indirect measurement of body density (The leaner you are, the more muscle mass you have; a degree of leanness reduces heart disease & metabolic disorders). ...
... Body mass index (BMI): an indirect measurement of body density (The leaner you are, the more muscle mass you have; a degree of leanness reduces heart disease & metabolic disorders). ...
Andrew Rosen - Chapter 3: The Brain and Nervous System Intro
... o Axon terminals – Location of actual transmission process in presynaptic neurons o Synaptic vesicles – Located in axon terminals that are filled with neurotransmitters that will influence other neurons When a presynaptic neuron fires, some vesicles burst and release chemicals into the gap Postsynap ...
... o Axon terminals – Location of actual transmission process in presynaptic neurons o Synaptic vesicles – Located in axon terminals that are filled with neurotransmitters that will influence other neurons When a presynaptic neuron fires, some vesicles burst and release chemicals into the gap Postsynap ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... equilibrium and b_____; muscle tone; only 10% of brain but contains more _____ than the rest of the brain combined; _____ working part of the brain; capable of making _____ based on previous experiences; enables rest of brain to work more _____ because it can carry out tasks _____ without conscious ...
... equilibrium and b_____; muscle tone; only 10% of brain but contains more _____ than the rest of the brain combined; _____ working part of the brain; capable of making _____ based on previous experiences; enables rest of brain to work more _____ because it can carry out tasks _____ without conscious ...
Symptoms: visual disturbances, ______, loss of
... 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron to the next iii. Transmission across the sy ...
... 1. ________ terminal of the presynaptic neuron 2. ___________ region on the postsynaptic neuron g. Synaptic cleft i. Fluid-filled space separating the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons ii. Prevents nerve impulses from ___________ passing from one neuron to the next iii. Transmission across the sy ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... GOLGI TENDON Sensitive to muscle tension and active ORGAN contraction Protect muscle from excess contraction force Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… …Agonist muscle causing it to relax ...
... GOLGI TENDON Sensitive to muscle tension and active ORGAN contraction Protect muscle from excess contraction force Stimulation of GTO an afferent impulse is sent to the central nervous system In turn, efferent impulses are sent to the… …Agonist muscle causing it to relax ...
MS Word Version
... 1. (Page 3.) Label the diagram on page 3. 2. (Page 3, 4.) Put these statements into the correct order for synaptic transmission: a. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. b. The presence of calcium inside the cell causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane. c. Most often, t ...
... 1. (Page 3.) Label the diagram on page 3. 2. (Page 3, 4.) Put these statements into the correct order for synaptic transmission: a. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft. b. The presence of calcium inside the cell causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane. c. Most often, t ...
a14b NeuroPhysII
... • Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters • Typically composed of two parts o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... • Specialized for the release and reception of neurotransmitters • Typically composed of two parts o Axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, which contains synaptic vesicles o Receptor region on the postsynaptic neuron ...