eye
... When the head rotates, movement of the endolymph pushes against the structure and stimulates the hair cells. ...
... When the head rotates, movement of the endolymph pushes against the structure and stimulates the hair cells. ...
Biology
... • set up graded electrical signals in the dendrites of neuron on which synapse impinges ...
... • set up graded electrical signals in the dendrites of neuron on which synapse impinges ...
教案编写基本格式与要求
... The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, digestion and the maintenance of body temperature. The ANS is subdivided into two major sub-divisions; this classification is based on both anatomic and physiologic grounds; the two subdivis ...
... The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, digestion and the maintenance of body temperature. The ANS is subdivided into two major sub-divisions; this classification is based on both anatomic and physiologic grounds; the two subdivis ...
text
... N.Cuneatus. Second order neurons send axons that cross, and continue close to midline as the Medial Lemniscus (ML). Note that at this point information from one side of the body is carried by the ML on the opposite side (crossed). The ML brings sensory information to the thalamus ending up in the ve ...
... N.Cuneatus. Second order neurons send axons that cross, and continue close to midline as the Medial Lemniscus (ML). Note that at this point information from one side of the body is carried by the ML on the opposite side (crossed). The ML brings sensory information to the thalamus ending up in the ve ...
Autonomic Nervous System I and II
... neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sympathetic trunk ganglion and a preverteb ...
... neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sympathetic trunk ganglion and a preverteb ...
The Nervous System
... Movement along axons occurs in two ways Anterograde — toward axonal terminal Retrograde — away from axonal terminal ...
... Movement along axons occurs in two ways Anterograde — toward axonal terminal Retrograde — away from axonal terminal ...
Organic Context of Short-term Behavioral Adaptation
... Cell membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria Lysomes ...
... Cell membrane Endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria Lysomes ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft ...
... Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft ...
Evolution of the Nervous System
... Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft ...
... Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft ...
learning objectives for nervous tissue and nervous system
... function and location of: chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies), neurofibrils, axon hillock, axon collaterals, axon terminals (synaptic end bulbs), and neurotransmitters. 8. What organelle is not found in the axon? What is moved toward the axon terminal? What is kinesin and what does it do? 9. Wha ...
... function and location of: chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies), neurofibrils, axon hillock, axon collaterals, axon terminals (synaptic end bulbs), and neurotransmitters. 8. What organelle is not found in the axon? What is moved toward the axon terminal? What is kinesin and what does it do? 9. Wha ...
The Nervous System
... • Axons are sheathed in a smooth fatty protein called myelin which insulates the axon, prevents the wrong ion channels from opening and considerably increases the speed that nerve impulses travel along the axon. • Without the myelin, the axons would have to be about one hundred times their volume to ...
... • Axons are sheathed in a smooth fatty protein called myelin which insulates the axon, prevents the wrong ion channels from opening and considerably increases the speed that nerve impulses travel along the axon. • Without the myelin, the axons would have to be about one hundred times their volume to ...
Molecular Identification and the Immunolocalization of Purinergic Signaling Receptors in... Mammalian Vomeronasal Organ
... immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry to determine where P2X receptors are expressed and if P2Y receptors are expressed in the mouse VNO. RT-PCR results suggested that there is gene expression of P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y6, P2X1, and P2X3 receptors in the tissue. A selection of the more commonly expre ...
... immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry to determine where P2X receptors are expressed and if P2Y receptors are expressed in the mouse VNO. RT-PCR results suggested that there is gene expression of P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y6, P2X1, and P2X3 receptors in the tissue. A selection of the more commonly expre ...
neocortex-basic neuron types
... Pyramidal Cells (PC; Fig 1A1), the most commonly occurring neocortical neuron (located in layers II-VI), are characterized by a single, prominent, vertically oriented dendrite emerging from the apex of their mainly pyramidal-shaped somata (apical dendrite), several (~4-6) more or less horizontally r ...
... Pyramidal Cells (PC; Fig 1A1), the most commonly occurring neocortical neuron (located in layers II-VI), are characterized by a single, prominent, vertically oriented dendrite emerging from the apex of their mainly pyramidal-shaped somata (apical dendrite), several (~4-6) more or less horizontally r ...
Muscle fiber and motor end plate involvement in the
... animals.11 This alteration of the axonal terminal did not seem to be a significant factor in their extraocular muscles, however. It would seem that alterations of the synaptic vesicles is not a critical modification of the end plate. In this study of extraocular muscle, (1) the reduction of postjunc ...
... animals.11 This alteration of the axonal terminal did not seem to be a significant factor in their extraocular muscles, however. It would seem that alterations of the synaptic vesicles is not a critical modification of the end plate. In this study of extraocular muscle, (1) the reduction of postjunc ...
neural progenitor cells
... neurogenetics, neural excitability, nervous system disorders, neurotransmitters and screening therapeutics: • Normal CD34+ iPSC-derived NPCs • Gene-edited, lineage-specific reporter NPCs ...
... neurogenetics, neural excitability, nervous system disorders, neurotransmitters and screening therapeutics: • Normal CD34+ iPSC-derived NPCs • Gene-edited, lineage-specific reporter NPCs ...
Contacts among non-sister dendritic branches at
... NR1 (A–C) or GluR2 (D) in red shows the highest concentration of these glutamate receptors at BDIs compared to other regions along the dendrites. (E) The fluorescence, per number of dendritic segments, measured within a 3.75 μm radius from the structure center, (mean ± STD, (p < 0.001 for NR1, p = 0 ...
... NR1 (A–C) or GluR2 (D) in red shows the highest concentration of these glutamate receptors at BDIs compared to other regions along the dendrites. (E) The fluorescence, per number of dendritic segments, measured within a 3.75 μm radius from the structure center, (mean ± STD, (p < 0.001 for NR1, p = 0 ...
Ch48(2) - ISpatula
... B) the motor neuron is considered the postsynaptic cell and the skeletal muscle is the presynaptic cell. C) action potentials are possible on the motor neuron but not the skeletal muscle. D) action potentials are possible on the skeletal muscle but not the motor neuron. E) the motor neuron fires act ...
... B) the motor neuron is considered the postsynaptic cell and the skeletal muscle is the presynaptic cell. C) action potentials are possible on the motor neuron but not the skeletal muscle. D) action potentials are possible on the skeletal muscle but not the motor neuron. E) the motor neuron fires act ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations simultaneously. • At the end of the axon, specializations called terminal buttons occur. • Here information is transferred to the dendrites of other neurones. Prof. ...
... and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations simultaneously. • At the end of the axon, specializations called terminal buttons occur. • Here information is transferred to the dendrites of other neurones. Prof. ...
Biology - Chpt 14- The Nervous System
... Autonomic or ANS which is associated with the involuntary control of body movements such as reflex and controls such things as heart rate, body temperature, digestion etc. The ANS is further divided into • Parasympathetic nervous system works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and ...
... Autonomic or ANS which is associated with the involuntary control of body movements such as reflex and controls such things as heart rate, body temperature, digestion etc. The ANS is further divided into • Parasympathetic nervous system works in actions that do not require a fast response (rest and ...
Essentials of Human Anatomy 12
... • Optic disc lacks photoreceptors. • Called the blind spot because no image forms there. • Just lateral to the optic disc is a rounded, yellowish region of the retina called the macula lutea containing a pit called the fovea centralis (the area of sharpest vision). – contains the highest proportion ...
... • Optic disc lacks photoreceptors. • Called the blind spot because no image forms there. • Just lateral to the optic disc is a rounded, yellowish region of the retina called the macula lutea containing a pit called the fovea centralis (the area of sharpest vision). – contains the highest proportion ...
Neural tube formation in the chick embryo - CSE IITK
... 2. Shaping of the neural plate 3. Bending of the neural plate to form the groove 4. Closure of the neural groove to form the neural tube. http://www.mun.ca/biology/desmid/brian/BIOL3530/DEVO_12/ch12f19.jpg http://briebuzz.blogspot.in/ ...
... 2. Shaping of the neural plate 3. Bending of the neural plate to form the groove 4. Closure of the neural groove to form the neural tube. http://www.mun.ca/biology/desmid/brian/BIOL3530/DEVO_12/ch12f19.jpg http://briebuzz.blogspot.in/ ...
Biology and Behavior
... 1.The 4 major parts of the neuron are ____, ____, ____, _____. (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action pote ...
... 1.The 4 major parts of the neuron are ____, ____, ____, _____. (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action pote ...
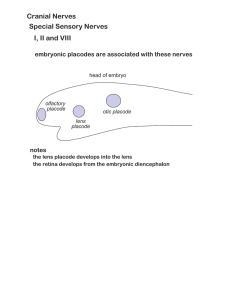
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...
... Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII embryonic placodes are associated with these nerves ...