Natural Causes of Climate Change
... Distribution of Continents Plate Tectonics Mountain Building ...
... Distribution of Continents Plate Tectonics Mountain Building ...
Geology Study Guide
... 2. ___________________________________ is the scientific theory explaining that the lithosphere is divided into moving slabs. It also explains Earth processes, such as volcanic activity and earthquakes. ...
... 2. ___________________________________ is the scientific theory explaining that the lithosphere is divided into moving slabs. It also explains Earth processes, such as volcanic activity and earthquakes. ...
The Physical world
... • Although the earth seems like a solid ball, it is really more like a series of shells that float on one another.—Think of an egg! • Core – solid metallic center made of nickel and iron • Mantle – soft layer of molten rock (magma) • Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface ...
... • Although the earth seems like a solid ball, it is really more like a series of shells that float on one another.—Think of an egg! • Core – solid metallic center made of nickel and iron • Mantle – soft layer of molten rock (magma) • Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface ...
A Living Planet
... Magma flows out of the earth and spreads across and area and cools. Once it reaches the earth’s surface, it is called lava Lava can create a hill or mountain Volcanoes do not erupt on a predictable schedule Ring of Fire- a zone around the rim of the pacific ocean (p. 37) ...
... Magma flows out of the earth and spreads across and area and cools. Once it reaches the earth’s surface, it is called lava Lava can create a hill or mountain Volcanoes do not erupt on a predictable schedule Ring of Fire- a zone around the rim of the pacific ocean (p. 37) ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Minerals
... • Gigantic plates in the Earth’s crust move very slowly atop the planet’s mantle, and wind and water move matter from place to place across the Earth’s surface. • Natural geological hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides can cause ...
... • Gigantic plates in the Earth’s crust move very slowly atop the planet’s mantle, and wind and water move matter from place to place across the Earth’s surface. • Natural geological hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides can cause ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • If you can see rocks on the surface that comes from the interior, you can study them ...
... • If you can see rocks on the surface that comes from the interior, you can study them ...
Assessment Test Spring 2009- Earth Science
... assess the student's knowledge of the three Physical Science Department SLO’s. Preassessment questions have appeared in both exam 1 and 2 throughout the spring 2015 semester. Below is the percentage breakdown of correct responses at the beginning of each semester (ABS) and correct responses recorded ...
... assess the student's knowledge of the three Physical Science Department SLO’s. Preassessment questions have appeared in both exam 1 and 2 throughout the spring 2015 semester. Below is the percentage breakdown of correct responses at the beginning of each semester (ABS) and correct responses recorded ...
Radioactive Decay & Convection Presentation
... terawatts; or about 0.045 W m-2) • Tidal Energy – (0.002%, or about 3 terawatts; or about 0.0059 W m-2). • Waste Heat - (about 0.007%, or about 13 terawatts; or about 0.025 W m-2) ...
... terawatts; or about 0.045 W m-2) • Tidal Energy – (0.002%, or about 3 terawatts; or about 0.0059 W m-2). • Waste Heat - (about 0.007%, or about 13 terawatts; or about 0.025 W m-2) ...
APES Focus/Ch - cynthiaahmed
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
Assessment Test Spring 2009- Earth Science
... assess the student's knowledge of the three Physical Science Department SLO’s. Preassessment questions have appeared in both exam 1,2 and 3 throughout the Fall 2015 semester. Below is the percentage breakdown of correct responses at the beginning of each semester (ABS) and correct responses recorded ...
... assess the student's knowledge of the three Physical Science Department SLO’s. Preassessment questions have appeared in both exam 1,2 and 3 throughout the Fall 2015 semester. Below is the percentage breakdown of correct responses at the beginning of each semester (ABS) and correct responses recorded ...
Chapter 2 Physical Geography: A Living Planet
... rock created by weathering (mud, sand or silt) v. Mechanical Weathering – processes that break rock into smaller pieces (doesn’t change the composition of rock, but the size) example: road construction ...
... rock created by weathering (mud, sand or silt) v. Mechanical Weathering – processes that break rock into smaller pieces (doesn’t change the composition of rock, but the size) example: road construction ...
Understanding Our Environment
... - Flood control structures have separated floodplains from rivers. Flood Control Governmental air of flooding victims seems to have encouraged building on floodplains. ...
... - Flood control structures have separated floodplains from rivers. Flood Control Governmental air of flooding victims seems to have encouraged building on floodplains. ...
2.3 Land ppt - Maryville City Schools
... • Is the movement of sediment from one locaOon to another • It can wear away or build up landforms • Causes of erosion are wind, ice, and water ...
... • Is the movement of sediment from one locaOon to another • It can wear away or build up landforms • Causes of erosion are wind, ice, and water ...
Erosion - The Agents of Erosion Are Water, Wind, Ice, and Waves
... dirt, and other bits of earth from one place to another by wind and water in various forms. One of the more forceful agents of erosion is running water, which picks up and transports weathered material. This is how sediment finds its way to a river that moves these weathered materials downstream to ...
... dirt, and other bits of earth from one place to another by wind and water in various forms. One of the more forceful agents of erosion is running water, which picks up and transports weathered material. This is how sediment finds its way to a river that moves these weathered materials downstream to ...
Chapter 3 Vocabulary
... erosion a process in which the materials of the Earth's surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported from one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice, or gravity evaporation the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas ...
... erosion a process in which the materials of the Earth's surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported from one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice, or gravity evaporation the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas ...
Introduction to Geomagnetism
... The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfaced within the past 400-700 million years. We must infer tectonic history based ...
... The surface temperature is 740K; most minerals are well above their Curie temperature at 740K – no field imprinted in crustal rocks. What we can say about the surface is that it is very “young” -- completely resurfaced within the past 400-700 million years. We must infer tectonic history based ...
Variables Change Earth Study Guide
... 2) Oceans wash beaches away. 3) Glaciers move rocks and dirt that they have picked up along the way. ...
... 2) Oceans wash beaches away. 3) Glaciers move rocks and dirt that they have picked up along the way. ...
Investigation: Earth Systems
... Develop the ability to work cooperatively, listen to and respect explanations proposed by other students, as well as remain open to new ideas, other’s skepticism and alternative explanations, as scientists do. Understand that energy is a property of many substances, it takes many forms and is tr ...
... Develop the ability to work cooperatively, listen to and respect explanations proposed by other students, as well as remain open to new ideas, other’s skepticism and alternative explanations, as scientists do. Understand that energy is a property of many substances, it takes many forms and is tr ...
Plate Tectonics.common.assessment.studyguide
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
The Earth - Humble ISD
... Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface Continental Drift – __________________ first presented the theory. He claimed that in Earth’s early existence there was only one body of land, ______________. That supercontinent then slowly split and separated into the continents we see today. _________ ...
... Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface Continental Drift – __________________ first presented the theory. He claimed that in Earth’s early existence there was only one body of land, ______________. That supercontinent then slowly split and separated into the continents we see today. _________ ...
Geology Review: Chapter 12
... 8. Although the Earth is thought to be about 4.6 billion years old, no rock that old has ever been found. Refer to the rock cycle (p. 260) and explain why it is unlikely that a rock this old will ever be found. ...
... 8. Although the Earth is thought to be about 4.6 billion years old, no rock that old has ever been found. Refer to the rock cycle (p. 260) and explain why it is unlikely that a rock this old will ever be found. ...
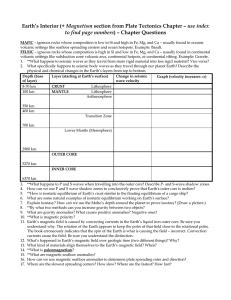
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
... volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in continental volcanic settings like subduction zone volcanic arcs, continental hotpots, or continental rifting. Ex ...
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Greek: γῆ, ge, ""earth""; μορφή, morfé, ""form""; and λόγος, logos, ""study"") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical or chemical processes operating at or near the earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphology is practiced within physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.