Mass Extinctions
... • Rapid movement of tectonic plates in the Mesozoic Era and the collisions and subduction produced extensive Volcanic activity around plate boundaries • Plate boundaries are still the location of much of Earth’s volcanic activity ...
... • Rapid movement of tectonic plates in the Mesozoic Era and the collisions and subduction produced extensive Volcanic activity around plate boundaries • Plate boundaries are still the location of much of Earth’s volcanic activity ...
Rock Cycle Weathering Vocab
... f. Explain the effects of physical processes (erosion, deposition, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). h: Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material. i: Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the ea ...
... f. Explain the effects of physical processes (erosion, deposition, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). h: Describe soil as consisting of weathered rocks and decomposed organic material. i: Explain the effects of human activity on the erosion of the ea ...
Lesson 13: The Rock Cycle 9/20/13 Essential Questions:
... the series of processes that continually change one rock type to another ...
... the series of processes that continually change one rock type to another ...
Solutions
... 8. Why is the Moon so much more heavily cratered than Earth? Explain how crater counts tell us the age of a surface? The fact that the Moon is much more heavily cratered than the Earth tells us that the Moon’s surface is much older. This is because the Moon is long dead geologically, except for i ...
... 8. Why is the Moon so much more heavily cratered than Earth? Explain how crater counts tell us the age of a surface? The fact that the Moon is much more heavily cratered than the Earth tells us that the Moon’s surface is much older. This is because the Moon is long dead geologically, except for i ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface
... of sediment by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Runoff, creeks, streams, and rivers pick up and carry sediment away. This can weather the landscape in dramatic ways. ...
... of sediment by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Runoff, creeks, streams, and rivers pick up and carry sediment away. This can weather the landscape in dramatic ways. ...
B3a Worksheet 3: DNA
... spots in the crust. Explain why magma can reach the surface in this way. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is a tectonic plate? ______________________________________________ ...
... spots in the crust. Explain why magma can reach the surface in this way. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. What is a tectonic plate? ______________________________________________ ...
CHAPTER 1: Basic Concepts
... 11. Density – (p.32) The frequency with which something exists with a given unit of area. 12. Diffusion – (p.36) The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time. 13. Distance Decay – (p.36) The diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with ...
... 11. Density – (p.32) The frequency with which something exists with a given unit of area. 12. Diffusion – (p.36) The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time. 13. Distance Decay – (p.36) The diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with ...
GLS100Lab_FR_Geology
... Goals: Students will develop a model of landform development based on field observations and data from the literature. ...
... Goals: Students will develop a model of landform development based on field observations and data from the literature. ...
Effects of Glaciers - Salem State University
... Goals: Students will develop a model of landform development based on field observations and data from the literature. ...
... Goals: Students will develop a model of landform development based on field observations and data from the literature. ...
Lesson 3.3 - Earth`s Spheres
... Why is Earth’s biosphere called “the living Earth”? The living things (and the non-living things with which they interact) live only in this sphere, the biosphere. ...
... Why is Earth’s biosphere called “the living Earth”? The living things (and the non-living things with which they interact) live only in this sphere, the biosphere. ...
Weathering and Erosion
... bedrock of the river and create deeper valleys, materials are then deposited at the mouth, or end of the river, usually to form a delta. • Waves erosion - storm waves can strike rock cliffs with a force of thousands of kilograms per square meter, bedrock can be split by water forced into cracks and ...
... bedrock of the river and create deeper valleys, materials are then deposited at the mouth, or end of the river, usually to form a delta. • Waves erosion - storm waves can strike rock cliffs with a force of thousands of kilograms per square meter, bedrock can be split by water forced into cracks and ...
Abstract template - Institute for Planetary Materials
... subduction zone phenomena, e.g., magmatism, seismicity, crustal deformation, metamorphism, hot springs activity and ore formation, etc. In order to understand the nature and dynamics of these fluids and clarify their roles in the subduction zone processes, we organized a research team consisting of ...
... subduction zone phenomena, e.g., magmatism, seismicity, crustal deformation, metamorphism, hot springs activity and ore formation, etc. In order to understand the nature and dynamics of these fluids and clarify their roles in the subduction zone processes, we organized a research team consisting of ...
chapt03_lecture Getis 13e
... After weathering processes decompose rock, the force of gravity and the erosional agents of running water, wind and moving ice carry the weathered material to new locations. ...
... After weathering processes decompose rock, the force of gravity and the erosional agents of running water, wind and moving ice carry the weathered material to new locations. ...
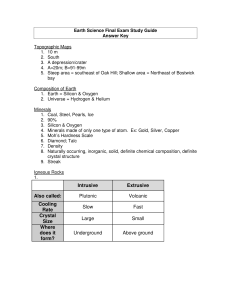
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 4. What do minerals in the sulfate group contain (sulfur) 5. What mineral reacts with acid? (calcite) 6. What does inorganic mean? (not living) 7. Why is coal not a mineral? (it came from living things) 8. What determines a rocks texture? (arrangement, size, and shape of a rocks grains or crystals) ...
... 4. What do minerals in the sulfate group contain (sulfur) 5. What mineral reacts with acid? (calcite) 6. What does inorganic mean? (not living) 7. Why is coal not a mineral? (it came from living things) 8. What determines a rocks texture? (arrangement, size, and shape of a rocks grains or crystals) ...
GEOFLUID PROCESSES IN SUBDUCTION ZONES AND MANTLE
... in various subduction zone phenomena, e.g., magmatism, seismicity, crustal deformation, metamorphism, hot springs activity and ore formation, etc. In order to understand the nature and dynamics of these fluids and clarify their roles in the subduction zone processes, we organized a research team con ...
... in various subduction zone phenomena, e.g., magmatism, seismicity, crustal deformation, metamorphism, hot springs activity and ore formation, etc. In order to understand the nature and dynamics of these fluids and clarify their roles in the subduction zone processes, we organized a research team con ...
5 Themes of Geography
... Weathering • Breakdown of rock at or near the earth’s surface • 2 types of weathering – Mechanical – Chemical ...
... Weathering • Breakdown of rock at or near the earth’s surface • 2 types of weathering – Mechanical – Chemical ...
Q2 Environmental Science Study Guide
... 34. What percent of the worlds water is saltwater? ___________________ 35. The measurement of the amount of salt in the ocean is called ___________________ 36. Continuous moving streams of water in the ocean are called ____________________ 37. Of each of the following pairs, circle the one that is m ...
... 34. What percent of the worlds water is saltwater? ___________________ 35. The measurement of the amount of salt in the ocean is called ___________________ 36. Continuous moving streams of water in the ocean are called ____________________ 37. Of each of the following pairs, circle the one that is m ...
Earth`s Landforms
... Continents and ocean floors form the top of these plates=move and carry continents and ocean floors with them ...
... Continents and ocean floors form the top of these plates=move and carry continents and ocean floors with them ...
What are the processes that cause the Earth`s surface to wear down?
... rocks breaks more particles loosen. ...
... rocks breaks more particles loosen. ...
Science 1st 9 weeks
... I can recognize that Earth has layers, and that geological features are identified with the Earth’s crust. (crust, mantle, core) ...
... I can recognize that Earth has layers, and that geological features are identified with the Earth’s crust. (crust, mantle, core) ...
Pre and Post Test
... 2. An example of mechanical weathering is: A. soil being carried downstream by fast moving water; B. rocks being broken apart by freezing water; C. sand being moved by strong winds; D. rocks being formed by volcanos. ...
... 2. An example of mechanical weathering is: A. soil being carried downstream by fast moving water; B. rocks being broken apart by freezing water; C. sand being moved by strong winds; D. rocks being formed by volcanos. ...
SAGES PhD Proposal - University of Edinburgh
... boulder field over a 1300 m elevation range. The climate differs greatly between these zones and it can be expected that climate change will impact them differently. The central hypothesis of this project is that knowledge of the geomorphological processes that shape the mountain landscape can be co ...
... boulder field over a 1300 m elevation range. The climate differs greatly between these zones and it can be expected that climate change will impact them differently. The central hypothesis of this project is that knowledge of the geomorphological processes that shape the mountain landscape can be co ...
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Greek: γῆ, ge, ""earth""; μορφή, morfé, ""form""; and λόγος, logos, ""study"") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical or chemical processes operating at or near the earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphology is practiced within physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field.