AthensvSparta - Rachel`s History Classes
... strong farming economy. Though based on fertile land, this farming economy was also a product of cheap forced labor. A large class of serfs called helots (pronounced HEH-lots) farmed the land and allowed the free Spartans to concentrate their efforts on other pursuits. Sparta rose as a powerful city ...
... strong farming economy. Though based on fertile land, this farming economy was also a product of cheap forced labor. A large class of serfs called helots (pronounced HEH-lots) farmed the land and allowed the free Spartans to concentrate their efforts on other pursuits. Sparta rose as a powerful city ...
Democracy in Ancient Athens
... What were the Roles of Men and Women in Athens? In your Duotangs, split a sheet of paper in half and label one side females, and the ...
... What were the Roles of Men and Women in Athens? In your Duotangs, split a sheet of paper in half and label one side females, and the ...
Hellenic History
... a. There was only one king. b. There was no check on royal power. c. There was an assembly called the Apella. d. The system known in classical times began in the 9 th century BCE 8. What treaty of 421 ended the first period of the Peloponnesian War? a. Peace of Nicias b. Peace of Callias c. the King ...
... a. There was only one king. b. There was no check on royal power. c. There was an assembly called the Apella. d. The system known in classical times began in the 9 th century BCE 8. What treaty of 421 ended the first period of the Peloponnesian War? a. Peace of Nicias b. Peace of Callias c. the King ...
to Unit 3 - Ancient Greece Notes
... a. Spartan men served in the military until ________ years old b. Boys began military training at age ______ c. _____________________ ran family estates while men trained or fought d. Spartans showed their strength during the ________________________________ 3. Athens & Sparta ______________________ ...
... a. Spartan men served in the military until ________ years old b. Boys began military training at age ______ c. _____________________ ran family estates while men trained or fought d. Spartans showed their strength during the ________________________________ 3. Athens & Sparta ______________________ ...
Athens and Sparta Reading
... Boys were taught to read, write, do arithmetic, and participate in cultural life, while girls stayed home with their mothers. As Athenian males grew up, they became traders, artisans, and merchants who actively participated in the culture and politics of Athens. When they reached the age of 18, me ...
... Boys were taught to read, write, do arithmetic, and participate in cultural life, while girls stayed home with their mothers. As Athenian males grew up, they became traders, artisans, and merchants who actively participated in the culture and politics of Athens. When they reached the age of 18, me ...
athens
... B. About 750 B.C. nobles, merchants, & manufacturers established an oligarchy (form of government in which a few people have the ruling power) C. Solon (594 B.C.), a rich merchant, wrote a constitution (set of principles & rules for governing) ...
... B. About 750 B.C. nobles, merchants, & manufacturers established an oligarchy (form of government in which a few people have the ruling power) C. Solon (594 B.C.), a rich merchant, wrote a constitution (set of principles & rules for governing) ...
2008 SAN ANTONIO CLASSICAL SOCIETY
... 3) Name the great fortress and palace where Agamemnon was said to be king. a) Mycenae b) Cnossus c) Pylos d) Argos. 4) On what Mycenaean site was the first major finding of Linear B tablets made? a) Mycenae b) Troy c) Pylos d) Argos. 5) Who was said to be the king of this palace in Homer’s Iliad? a) ...
... 3) Name the great fortress and palace where Agamemnon was said to be king. a) Mycenae b) Cnossus c) Pylos d) Argos. 4) On what Mycenaean site was the first major finding of Linear B tablets made? a) Mycenae b) Troy c) Pylos d) Argos. 5) Who was said to be the king of this palace in Homer’s Iliad? a) ...
Archaic Greece 1650 BCE- 700 BCE *Bronze Age *Crete
... Athens: The Arts and Sciences *Drama - ___________ and ___________ *The Sciences: - Pythagoras: Pythagorean Theorum - Archimedes: __________, pulleys and levers -Erastothenes: Calculated Earth’s circumference Art and Architecture *The Parthenon, located on the ____________- place of Worship to Athen ...
... Athens: The Arts and Sciences *Drama - ___________ and ___________ *The Sciences: - Pythagoras: Pythagorean Theorum - Archimedes: __________, pulleys and levers -Erastothenes: Calculated Earth’s circumference Art and Architecture *The Parthenon, located on the ____________- place of Worship to Athen ...
DBQ
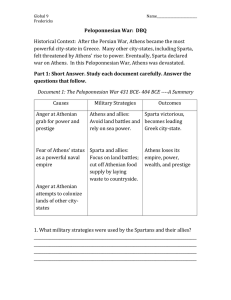
... Sparta and its allies, with the exception of Corinth, were almost exclusively land based powers, able to summon large land armies which were very nearly unbeatable. Under the direction of Pericles, the Athenians pursued a policy of retreat within the city walls of Athens, relying on Athenian maritim ...
... Sparta and its allies, with the exception of Corinth, were almost exclusively land based powers, able to summon large land armies which were very nearly unbeatable. Under the direction of Pericles, the Athenians pursued a policy of retreat within the city walls of Athens, relying on Athenian maritim ...
Ancient Greece: The Development of Athenian Democracy
... Pericles leads Athens through its Golden Age. The Parthenon was built on the Acropolis during his rule. ...
... Pericles leads Athens through its Golden Age. The Parthenon was built on the Acropolis during his rule. ...
Kerisha Goode Rhetorical Traditions I 2 October 2015 Social
... Social structure under equality is a cultural value that is much respected in ancient Athens. Particularly the inequality of women and slaves is what stands out the most. This value impacted rhetoric’s development in Athens during this period in was such as its legal system, education, and religion ...
... Social structure under equality is a cultural value that is much respected in ancient Athens. Particularly the inequality of women and slaves is what stands out the most. This value impacted rhetoric’s development in Athens during this period in was such as its legal system, education, and religion ...
greek expansion notes
... Established colonies of Athenian citizens in important or rebellious areas Kept Persians out of Aegean Sea Athenian system of weights and measures became standard throughout the empire Delian League members reaped benefits under Pericles, but lost their independence o Athens and Pericles controlled ...
... Established colonies of Athenian citizens in important or rebellious areas Kept Persians out of Aegean Sea Athenian system of weights and measures became standard throughout the empire Delian League members reaped benefits under Pericles, but lost their independence o Athens and Pericles controlled ...
The Glory That Was Greece
... The ancient city of Troy, setting for the Trojan War, was located in modern-day __________. ...
... The ancient city of Troy, setting for the Trojan War, was located in modern-day __________. ...
The Early Greeks notes
... o ___________________ = one ruler who usually inherited power and passed on leadership to his son. o ___________________= where all citizens share in running the government. o __________________ = person who takes power by force and rules with total authority. o __________________= allows for a few ...
... o ___________________ = one ruler who usually inherited power and passed on leadership to his son. o ___________________= where all citizens share in running the government. o __________________ = person who takes power by force and rules with total authority. o __________________= allows for a few ...
7Athens
... most of the interior and many sculptures were destroyed. This building is significant because it represents the grand aspirations of Pericles and his ambition to make Athens the center of the Greek world. When the Delian League, originally a voluntary confederation of Greek city-states bound togethe ...
... most of the interior and many sculptures were destroyed. This building is significant because it represents the grand aspirations of Pericles and his ambition to make Athens the center of the Greek world. When the Delian League, originally a voluntary confederation of Greek city-states bound togethe ...
week-4-reading-questions
... particularly important to either the Athenians or the Corinthians in the debate so far? 6. What are Archidamus’ reasons for avoiding or delaying the war? Are his reasons rooted in ethical or practical considerations? (what about Sthenelaidas’ arguments?) 7. In 1.88, what does Thucydides give as the ...
... particularly important to either the Athenians or the Corinthians in the debate so far? 6. What are Archidamus’ reasons for avoiding or delaying the war? Are his reasons rooted in ethical or practical considerations? (what about Sthenelaidas’ arguments?) 7. In 1.88, what does Thucydides give as the ...
Document
... approved by the Assembly… this group consisted of 6,000 citizens with every one having the right to speak -Proud of their freedom and enjoyed taking part in the process. ...
... approved by the Assembly… this group consisted of 6,000 citizens with every one having the right to speak -Proud of their freedom and enjoyed taking part in the process. ...
Document B: The Athenian Constitution (Modified)
... The following excerpt comes from “The Athenian Constitution,” written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BCE. Aristotle was the leading Greek philosopher of the time, and is credited with writing accounts of the constitutions of 170 different Greek states. At the time that we are ...
... The following excerpt comes from “The Athenian Constitution,” written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BCE. Aristotle was the leading Greek philosopher of the time, and is credited with writing accounts of the constitutions of 170 different Greek states. At the time that we are ...
Warring City
... military state. Boys joined the army at age seven and went through a long period of training as soldiers. ...
... military state. Boys joined the army at age seven and went through a long period of training as soldiers. ...
Epikleros

An epikleros (ἐπίκληρος; plural epikleroi) was an heiress in ancient Athens and other ancient Greek city states, specifically a daughter of a man who had no male heirs. In Sparta, they were called patrouchoi (πατροῦχοι), as they were in Gortyn. Athenian women were not allowed to hold property in their own name; in order to keep her father's property in the family, an epikleros was required to marry her father's nearest male relative. Even if a woman was already married, evidence suggests that she was required to divorce her spouse to marry that relative. Spartan women were allowed to hold property in their own right, and so Spartan heiresses were subject to less restrictive rules. Evidence from other city-states is more fragmentary, mainly coming from the city-states of Gortyn and Rhegium.Plato wrote about epikleroi in his Laws, offering idealized laws to govern their marriages. In mythology and history, a number of Greek women appear to have been epikleroi, including Agariste of Sicyon and Agiatis, the widow of the Spartan king Agis IV. The status of epikleroi has often been used to explain the numbers of sons-in-law who inherited from their fathers-in-law in Greek mythology. The Third Sacred War originated in a dispute over epikleroi.