Chapter_28_HB_Nervous_System
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
A comparison of the distribution and morphology of ChAT
... ABSTRACT: Present knowledge concerning the organization of cholinergic structures of the spinal cord has been derived primarily from studies on small laboratory animals, while there is a complete lack of information concerning its structure in the pig. In the present study we employed choline acetyl ...
... ABSTRACT: Present knowledge concerning the organization of cholinergic structures of the spinal cord has been derived primarily from studies on small laboratory animals, while there is a complete lack of information concerning its structure in the pig. In the present study we employed choline acetyl ...
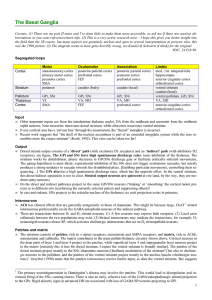
The Basal Ganglia
... neurons. Neither the receipt of reward nor the prediction of reward are necessary conditions for activating dopamine neurons. Nor are they sufficient (the stimulus offset task, and that dopamine neurons respond little to incentive stimuli after overtraining, though one could argue that overtrained b ...
... neurons. Neither the receipt of reward nor the prediction of reward are necessary conditions for activating dopamine neurons. Nor are they sufficient (the stimulus offset task, and that dopamine neurons respond little to incentive stimuli after overtraining, though one could argue that overtrained b ...
Chapter 3 Overlapping circuits for relative value and selective
... not yet been investigated. Here we wished to gain insight into the effects of reward expectancy on neuronal activity in area V1 of macaque monkeys. Moreover, we aimed to investigate the relation between reward expectancy and attention (Maunsell, 2004). The effects of attention are as widespread acro ...
... not yet been investigated. Here we wished to gain insight into the effects of reward expectancy on neuronal activity in area V1 of macaque monkeys. Moreover, we aimed to investigate the relation between reward expectancy and attention (Maunsell, 2004). The effects of attention are as widespread acro ...
Hippocampal region - NeuronDevelopment.org
... since Cajal (1911) and his pupil, Lorente de N6 (1934), carried out their classic slUdies using the Golgi method. In recent years, the cytoarchitecture and connections of the hippocampal region have been further elucidated by the work of Blackstad (1956, 1958), Raisman et al. (1965, 1966) and Hjorth ...
... since Cajal (1911) and his pupil, Lorente de N6 (1934), carried out their classic slUdies using the Golgi method. In recent years, the cytoarchitecture and connections of the hippocampal region have been further elucidated by the work of Blackstad (1956, 1958), Raisman et al. (1965, 1966) and Hjorth ...
Rhythms for Cognition: Communication through
... Challenges for the original CTC hypothesis While there is substantial experimental support, some studies posed challenges to the original CTC formulation that motivated the new CTC formulation. If the two communicating neuronal groups are bidirectionally coupled, I originally proposed zero-phase syn ...
... Challenges for the original CTC hypothesis While there is substantial experimental support, some studies posed challenges to the original CTC formulation that motivated the new CTC formulation. If the two communicating neuronal groups are bidirectionally coupled, I originally proposed zero-phase syn ...
CASE 47
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
5-Autonomic Nervous System
... In anatomy nothing is random. The location of the ganglia is related to its function. ...
... In anatomy nothing is random. The location of the ganglia is related to its function. ...
Slide 1
... perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
... perception, voluntary motor initiation, communication, memory storage, understanding • Each hemisphere connects to contralateral side of the body • There is lateralization of cortical function in the hemispheres ...
Dopamine
... (49–51). There is also evidence that glutamate can release acetylcholine or serotonin in the striatum, which in turn can trigger DA release (43). Glutamate may also stimulate DA release via an action on other local systems, such as those producing NO. NO is known to be released from striatal interne ...
... (49–51). There is also evidence that glutamate can release acetylcholine or serotonin in the striatum, which in turn can trigger DA release (43). Glutamate may also stimulate DA release via an action on other local systems, such as those producing NO. NO is known to be released from striatal interne ...
Document
... (sensory organs designed to respond to electrical fields) clustered at the tip of the spiny anteater’s snout. The researchers made this discovery by exposing small areas of (5) the snout to extremely weak electrical fields and recording the transmission of resulting nervous activity to the brain. Wh ...
... (sensory organs designed to respond to electrical fields) clustered at the tip of the spiny anteater’s snout. The researchers made this discovery by exposing small areas of (5) the snout to extremely weak electrical fields and recording the transmission of resulting nervous activity to the brain. Wh ...
Climbing Neuronal Activity as an Event
... (n; see legend of Fig. 1). For neurons showing stimulus-selective delay activity we averaged over trials with the same pair of sample and test stimuli (see Fig. 1c1). For neurons showing unselective delay activity, different sample stimuli were pooled together (see Fig. 1c2,c3). Bars in Figure 1d re ...
... (n; see legend of Fig. 1). For neurons showing stimulus-selective delay activity we averaged over trials with the same pair of sample and test stimuli (see Fig. 1c1). For neurons showing unselective delay activity, different sample stimuli were pooled together (see Fig. 1c2,c3). Bars in Figure 1d re ...
Down - 서울대 : Biointelligence lab
... This activity packet is stable after removal of the external stimulus when the rotational nodes are inactive Between 20 t 40 , a clockwise rotation activity was applied The activity packet moved in the clockwise direction linearly in this time Movement stops after rotation cell firing ...
... This activity packet is stable after removal of the external stimulus when the rotational nodes are inactive Between 20 t 40 , a clockwise rotation activity was applied The activity packet moved in the clockwise direction linearly in this time Movement stops after rotation cell firing ...
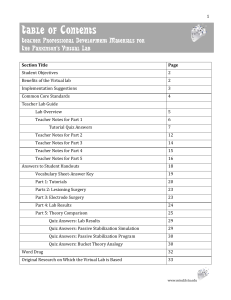
Table of Contents - The Mind Project
... In addition to role-playing and being able to collect data to interpret, this virtual lab, allows students to see how the research process works, on a bigger, grander scale. Students learn that there is a cellular phenomenon that scientists do not understand. Data show that Parkinson’s patients have ...
... In addition to role-playing and being able to collect data to interpret, this virtual lab, allows students to see how the research process works, on a bigger, grander scale. Students learn that there is a cellular phenomenon that scientists do not understand. Data show that Parkinson’s patients have ...
Chapter 9b final
... Effects of exercise on SWS Not related Effects of brain activity on SWS Increased SWS following cognitive task ...
... Effects of exercise on SWS Not related Effects of brain activity on SWS Increased SWS following cognitive task ...
Differential Temporal Storage Capacity in the Baseline Activity of
... Neurons in visuomotor areas such as FEF or the lateral intraparietal area often exhibit sustained activation in the absence of visual stimulation, such as in memory-guided saccade tasks (e.g., Chafee and Goldman-Rakic 2000; Lawrence et al. 2005; Thompson et al. 2005). Conversely, neurons in V4 and o ...
... Neurons in visuomotor areas such as FEF or the lateral intraparietal area often exhibit sustained activation in the absence of visual stimulation, such as in memory-guided saccade tasks (e.g., Chafee and Goldman-Rakic 2000; Lawrence et al. 2005; Thompson et al. 2005). Conversely, neurons in V4 and o ...
Parkinson`s Disease Rigidity Quantification Kylen Bares1, Eddie
... Additional ways to improve our design regard convenience and comfort for the patient using it. Our device may not work for certain people with arms of enormous size because a person’s arm, if too big, may not fit into the arm frame. Addressing the problem may involve refining our device to make it ...
... Additional ways to improve our design regard convenience and comfort for the patient using it. Our device may not work for certain people with arms of enormous size because a person’s arm, if too big, may not fit into the arm frame. Addressing the problem may involve refining our device to make it ...
Patterns of neuronal migration in the embryonic cortex
... in the MZ before turning again to enter the cortical plate to reach their final positions [36]. Interestingly, a proportion of tangentially migrating neurons from all cortical layers were observed to undergo ventricle-directed migration to the VZ in slice-culture preparations [37]. Upon reaching the ...
... in the MZ before turning again to enter the cortical plate to reach their final positions [36]. Interestingly, a proportion of tangentially migrating neurons from all cortical layers were observed to undergo ventricle-directed migration to the VZ in slice-culture preparations [37]. Upon reaching the ...
Developmental origin of shark electrosensory organs
... Kuratani and Horigome 2000). We detected Sox8 and HNK1-positive cells in both mechanosensory and electrosensory placodes at stage 32 (Fig. 2, C and D). Histological analysis over the course of ampullary organ development revealed that Sox8 and HNK1 positive cells were positioned initially at the api ...
... Kuratani and Horigome 2000). We detected Sox8 and HNK1-positive cells in both mechanosensory and electrosensory placodes at stage 32 (Fig. 2, C and D). Histological analysis over the course of ampullary organ development revealed that Sox8 and HNK1 positive cells were positioned initially at the api ...
Limitations in anti-obesity drug development: the critical role of
... glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), which stimulates the pancreas to secrete insulin; both GLP1 and insulin are thought to reduce food intake by acting directly on the brain. In pancreatic β‑cells, the hormone amylin is released together with insulin in response to a meal. Amylin is a potent satiety sig ...
... glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), which stimulates the pancreas to secrete insulin; both GLP1 and insulin are thought to reduce food intake by acting directly on the brain. In pancreatic β‑cells, the hormone amylin is released together with insulin in response to a meal. Amylin is a potent satiety sig ...
Flow-metabolism coupling in human visual, motor, and
... CMRO2ⴚCBF coupling ratios in the three regions (PVC: 0.34 ⴞ 0.03; PMC: 0.24 ⴞ 0.03; and SMA: 0.40 ⴞ 0.02). Part of this difference emerges from the calculated values of the hypercapnic calibration constant M in each region (MPVC ⴝ 6.6 ⴞ 3.4, MPMC ⴝ 4.3 ⴞ 3.5, and MSMA ⴝ 7.2 ⴞ 4.1), while a relativel ...
... CMRO2ⴚCBF coupling ratios in the three regions (PVC: 0.34 ⴞ 0.03; PMC: 0.24 ⴞ 0.03; and SMA: 0.40 ⴞ 0.02). Part of this difference emerges from the calculated values of the hypercapnic calibration constant M in each region (MPVC ⴝ 6.6 ⴞ 3.4, MPMC ⴝ 4.3 ⴞ 3.5, and MSMA ⴝ 7.2 ⴞ 4.1), while a relativel ...
spinal cord - Zanichelli
... Ions channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier, so action potential jumps from one node to the other and travels faster in a saltatory conduction. ...
... Ions channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier, so action potential jumps from one node to the other and travels faster in a saltatory conduction. ...
IV. Model Application: the UAV Autonomous Learning in Unknown
... recent years since they provide new opportunities to achieve the goal of General Intelligence. The neural network architecture of the brain supports the realization of cognitive behaviors at multiple scales. Although spiking neural networks have been adopted for cognitive behavior simulation and cre ...
... recent years since they provide new opportunities to achieve the goal of General Intelligence. The neural network architecture of the brain supports the realization of cognitive behaviors at multiple scales. Although spiking neural networks have been adopted for cognitive behavior simulation and cre ...