The ITALIAN Renaissance
... – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “_______________________” (imaginary, ideal society) – ________________________ for not going along with King Henry ...
... – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “_______________________” (imaginary, ideal society) – ________________________ for not going along with King Henry ...
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... Renaissance = Rebirth… educated men/women of Italy bring back to life the culture of classical Greece & Rome. ...
... Renaissance = Rebirth… educated men/women of Italy bring back to life the culture of classical Greece & Rome. ...
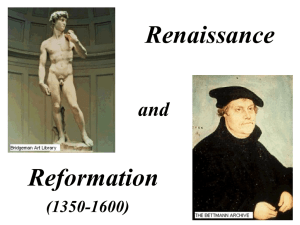
RenaissanceReformati..
... • It was a time of change in Politics, Social Structure, Economics, and Culture. • Changed from an agricultural society to an Urban Society • It was a study of Roman and Greek cultures. ...
... • It was a time of change in Politics, Social Structure, Economics, and Culture. • Changed from an agricultural society to an Urban Society • It was a study of Roman and Greek cultures. ...
Chapter 13.1 – 13.2: Origins of the Renaissance
... • Stressed importance of leading Christian life, but challenged people to think for themselves too • Think about Church teachings, not blindly accept Church orders ...
... • Stressed importance of leading Christian life, but challenged people to think for themselves too • Think about Church teachings, not blindly accept Church orders ...
The Renaissance
... Italian Renaissance Politics • Italian States – Milan, Venice, Florence • Controlled by merchant families • Gained massive wealth & power ...
... Italian Renaissance Politics • Italian States – Milan, Venice, Florence • Controlled by merchant families • Gained massive wealth & power ...
The Renaissance
... wealthy leads to developments in education and art City-States on the Peninsula are not hindered by monarchy or strong influence of papacy. ...
... wealthy leads to developments in education and art City-States on the Peninsula are not hindered by monarchy or strong influence of papacy. ...
High Renaissnce continued
... • Later Neo – Platonists like Plotinus, maintained that the work of Art can directly mirror the Idea itself. That is what the Renaissance was driving for. Some believed that artists could directly access the Ideal forms in the mind of God. (Michelangleo etc). This is what Neo Platonism proposed. • C ...
... • Later Neo – Platonists like Plotinus, maintained that the work of Art can directly mirror the Idea itself. That is what the Renaissance was driving for. Some believed that artists could directly access the Ideal forms in the mind of God. (Michelangleo etc). This is what Neo Platonism proposed. • C ...
The Italian Renaissance Chapter 5 section 1
... Middle Ages, through trade ties info was exchanged…Through merchants, Italian scholars reacquired ancient “lost” wisdom, learning and philosophical ideas. • The “lost” info came primarily from the Byzantine Empire which had kept the Ancient Greek writings and knowledge intact ...
... Middle Ages, through trade ties info was exchanged…Through merchants, Italian scholars reacquired ancient “lost” wisdom, learning and philosophical ideas. • The “lost” info came primarily from the Byzantine Empire which had kept the Ancient Greek writings and knowledge intact ...
Chapter 1 - History With Mr. Wallace
... 8) How was Renaissance art different from the art of the Middle Ages? a) It was more realistic and portrayed some non-religious subjects. b) It was less realistic and only portrayed religious subjects. c) It was always based on Greek and Roman subjects. d) It was usually placed in churches and other ...
... 8) How was Renaissance art different from the art of the Middle Ages? a) It was more realistic and portrayed some non-religious subjects. b) It was less realistic and only portrayed religious subjects. c) It was always based on Greek and Roman subjects. d) It was usually placed in churches and other ...
Leonardo, Michelangelo, Raphael, Donatello (and Petrarch)
... • Cosimo de’ Medici was the wealthiest European of his time • He was virtually dictator of Florence for 30 years through his influence ...
... • Cosimo de’ Medici was the wealthiest European of his time • He was virtually dictator of Florence for 30 years through his influence ...
Renaissance Vocab List
... a region that included parts of present day northern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands; was an important industrial and financial center of northern Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance humanism ...
... a region that included parts of present day northern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands; was an important industrial and financial center of northern Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance humanism ...
The Renaissance (world)
... you will need to research any three from the group below and on the top draw or print a piece they did that represents the techniques of the Renaissance and on the bottom write a paragraph that explains who did it and how their work contributed to the Renaissance movement Jan Van Eyck - Rafael A ...
... you will need to research any three from the group below and on the top draw or print a piece they did that represents the techniques of the Renaissance and on the bottom write a paragraph that explains who did it and how their work contributed to the Renaissance movement Jan Van Eyck - Rafael A ...
The Italian Renaissance I. Background A. Renaissance means
... 2. Questioning the structures of medieval society which block social advancement D. Educated people reject medieval values and look to the classical past for ideas II. Italy’s Advantages…why Italy? A. Northern Europe locked in war (100 Years war) B. Italy had three distinct advantages: 1. Thriving C ...
... 2. Questioning the structures of medieval society which block social advancement D. Educated people reject medieval values and look to the classical past for ideas II. Italy’s Advantages…why Italy? A. Northern Europe locked in war (100 Years war) B. Italy had three distinct advantages: 1. Thriving C ...
4.8 dark ages to renissance
... • increased rationale and secular thinking (humanism) • new technology (printing press) ...
... • increased rationale and secular thinking (humanism) • new technology (printing press) ...
The Italian Renaissance
... Renaissance • period from circa 1350 to 1600 during which European scholars revived the learning of ancient Greece and Rome ...
... Renaissance • period from circa 1350 to 1600 during which European scholars revived the learning of ancient Greece and Rome ...
Renaissance - granbystudents
... 17) __Original Sin______ This Church teaching was a constant reminder that human beings were flawed. 18) ___Brunelleschi_____ This architect is famous for his Roman style dome and for discovering perspective. 19) ___Savonarola_______ This priest hated all that the Medici stood for and eventually cau ...
... 17) __Original Sin______ This Church teaching was a constant reminder that human beings were flawed. 18) ___Brunelleschi_____ This architect is famous for his Roman style dome and for discovering perspective. 19) ___Savonarola_______ This priest hated all that the Medici stood for and eventually cau ...
RENAISSANCE
... Rebirth • Philosophical and Artistic movement • Emphasis on human reasoning • Begins in Italy – Florence, Milan, Naples, Rome, Venice – Lorenzo de Medici, ruler and patron of arts – Isabella d Este, filled her palace with artwork ...
... Rebirth • Philosophical and Artistic movement • Emphasis on human reasoning • Begins in Italy – Florence, Milan, Naples, Rome, Venice – Lorenzo de Medici, ruler and patron of arts – Isabella d Este, filled her palace with artwork ...
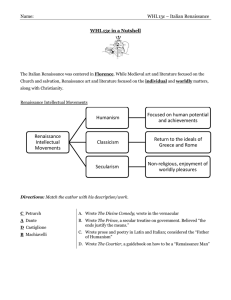
Renaissance Intellectual Movements Humanism Focused on human
... Church and salvation, Renaissance art and literature focused on the individual and worldly matters, along with Christianity. Renaissance Intellectual Movements ...
... Church and salvation, Renaissance art and literature focused on the individual and worldly matters, along with Christianity. Renaissance Intellectual Movements ...
The ITALIAN Renaissance
... - What book do you think was printed the most? Northern Renaissance: Writers • Desiderius Erasmus – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “________________ ...
... - What book do you think was printed the most? Northern Renaissance: Writers • Desiderius Erasmus – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “________________ ...
THE RENAISSANCE Essential Question
... Reformation: a 16th-century movement for the reform of abuses in the Roman Catholic Church that ended in the establishment of the Reformed and Protestant Churches Indulgences: The sale of indulgences was a practice where the church acknowledged a donation or other charitable work with a piece of pap ...
... Reformation: a 16th-century movement for the reform of abuses in the Roman Catholic Church that ended in the establishment of the Reformed and Protestant Churches Indulgences: The sale of indulgences was a practice where the church acknowledged a donation or other charitable work with a piece of pap ...
social context ppt File
... Galen and Arabic texts on medicine Ibn-Sina’s (Avicenna) Al Kanun 70 books in all. ...
... Galen and Arabic texts on medicine Ibn-Sina’s (Avicenna) Al Kanun 70 books in all. ...
The Renaissance
... Christians fled to the West • These refugees brought with them classical scholarship that had originally been lost to the West • Medieval artists who originally strove to suggest strong spiritual characters started exploring ways to suggest actual figures standing in realistic landscapes during the ...
... Christians fled to the West • These refugees brought with them classical scholarship that had originally been lost to the West • Medieval artists who originally strove to suggest strong spiritual characters started exploring ways to suggest actual figures standing in realistic landscapes during the ...
Chapter 13 Part 4
... BUT the vast majority of the population were untouched by the Renaissance. Only 6% were urban dwellers BUT Renaissance men belief that all things were possible if one willed it Life not just to be endured; but enjoyed ...
... BUT the vast majority of the population were untouched by the Renaissance. Only 6% were urban dwellers BUT Renaissance men belief that all things were possible if one willed it Life not just to be endured; but enjoyed ...