renaissance - Les Cheneaux Community Schools
... • In time Italian Renaissance values spread to other parts of Europe, after hundreds of students from Europe enrolled at Italian universities • When they returned home they took manuscripts by humanist writers, and scholars in the north were ready to welcome this new outlook • The arrival of block-p ...
... • In time Italian Renaissance values spread to other parts of Europe, after hundreds of students from Europe enrolled at Italian universities • When they returned home they took manuscripts by humanist writers, and scholars in the north were ready to welcome this new outlook • The arrival of block-p ...
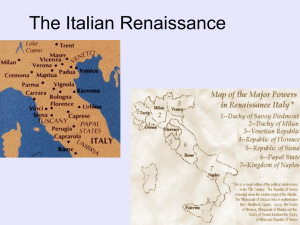
The Italian Renaissance
... Origins of the Renaissance - Economic growth was the basis for the Renaissance - Northern Italy was centrally located and benefited from the crusades and the spice trade - The Renaissance started in Florence and follows the success of the Medici family - Florentine merchants (the Medicis) gained co ...
... Origins of the Renaissance - Economic growth was the basis for the Renaissance - Northern Italy was centrally located and benefited from the crusades and the spice trade - The Renaissance started in Florence and follows the success of the Medici family - Florentine merchants (the Medicis) gained co ...
THE RENAISSANCE
... Renaissance means rebirth Time when ideas of Ancient Greece and Rome (Classical Civilisation) were rediscovered and great advances and new ideas developed in all walks of life – art, architecture, science, medicine, music, literature etc Time when people began to think for themselves instead o ...
... Renaissance means rebirth Time when ideas of Ancient Greece and Rome (Classical Civilisation) were rediscovered and great advances and new ideas developed in all walks of life – art, architecture, science, medicine, music, literature etc Time when people began to think for themselves instead o ...
The Renaissance - New Smyrna Beach High School
... Renaissance By the end of the 14th century, many people across Europe had grown pessimistic about their future and the future of their political state. There was an air of hopelessness about the new century. However, by the end of the 1400s, Europe had experienced great change. The recurring economi ...
... Renaissance By the end of the 14th century, many people across Europe had grown pessimistic about their future and the future of their political state. There was an air of hopelessness about the new century. However, by the end of the 1400s, Europe had experienced great change. The recurring economi ...
Cm2 Fk2 Renaissance Vocabulary
... beginning in the 14th century in Italy, lasting into the 17th century, and marked by a humanistic revival of ...
... beginning in the 14th century in Italy, lasting into the 17th century, and marked by a humanistic revival of ...
Chapter 12 Most Important Thing 2014-15
... the printing press. While the development of humanism and the improvements on education were important, the printing press allowed even your common man to improve his education. Jimmy is how The Italian Renaissance marks a new chapter in history with a new social idea that focuses on the individual' ...
... the printing press. While the development of humanism and the improvements on education were important, the printing press allowed even your common man to improve his education. Jimmy is how The Italian Renaissance marks a new chapter in history with a new social idea that focuses on the individual' ...
Merchants from the Islamic world who traded with Europeans first
... 3. An increased dissatisfaction with religious leadership and the invention of the printing press, both occurring during the Renaissance, led to the spread of religious criticism which ultimately led to the Protestant Reformation. 4. The invention of the printing press; Influence of religious author ...
... 3. An increased dissatisfaction with religious leadership and the invention of the printing press, both occurring during the Renaissance, led to the spread of religious criticism which ultimately led to the Protestant Reformation. 4. The invention of the printing press; Influence of religious author ...
The Renaissance, Reformation, and Exploration
... Wrote The Prince Concerned with political power and how to get it and keep it Rejected the MA view that rulers behave on Christian, ...
... Wrote The Prince Concerned with political power and how to get it and keep it Rejected the MA view that rulers behave on Christian, ...
The Renaissance 1271
... HSS 7.8.1 Describe the way in which the revival of classical learning and the arts fostered a new interest in humanism (i.e., a balance between intellect and religious faith). HSS 7.8.5 Detail advances made in literature, the arts, science, mathematics cartography, engineering and the understanding ...
... HSS 7.8.1 Describe the way in which the revival of classical learning and the arts fostered a new interest in humanism (i.e., a balance between intellect and religious faith). HSS 7.8.5 Detail advances made in literature, the arts, science, mathematics cartography, engineering and the understanding ...
ap european history
... 1. Discuss the meanings of the term renaissance. 2. Explain the economic context for the Renaissance. 3. Describe the new status of the artist in Renaissance Italy. Who were some of the famous literary and artistic figures of the Italian Renaissance? What did they have in common that might be descri ...
... 1. Discuss the meanings of the term renaissance. 2. Explain the economic context for the Renaissance. 3. Describe the new status of the artist in Renaissance Italy. Who were some of the famous literary and artistic figures of the Italian Renaissance? What did they have in common that might be descri ...
Northern Renaissance
... than in this portrait “The Betrothal of the Arnolfini”. • The signature on the back wall 'Jan Van Eyck was here, 1434' and his reflection in the mirror has led many to believe that he was a witness to their marriage. • The carving of Saint Margaret, the patron saint of childbirth, on the bed, and th ...
... than in this portrait “The Betrothal of the Arnolfini”. • The signature on the back wall 'Jan Van Eyck was here, 1434' and his reflection in the mirror has led many to believe that he was a witness to their marriage. • The carving of Saint Margaret, the patron saint of childbirth, on the bed, and th ...
Ch17:2 Reading Guide - W W W . M R S O B R Y A N . W E E B L Y
... Gutenberg, used this same practice to invent his printing press. He produced his first book—the Gutenberg Bible—in 1455 on this press. The technology then spread rapidly. By 1500, presses in Europe had printed nearly 10 million books. Printing made it easier to make many copies of a book. As a resul ...
... Gutenberg, used this same practice to invent his printing press. He produced his first book—the Gutenberg Bible—in 1455 on this press. The technology then spread rapidly. By 1500, presses in Europe had printed nearly 10 million books. Printing made it easier to make many copies of a book. As a resul ...
The Renaissance in Italy
... • Born in Paris / father from Florence • Was sent to Naples to study law but preferred literature. • Personal friend of Petrarch from 1350 until his death. • Boccaccio shares with Petrarch the honor of being the earliest humanist. In their time there were not a dozen men in Italy who could read the ...
... • Born in Paris / father from Florence • Was sent to Naples to study law but preferred literature. • Personal friend of Petrarch from 1350 until his death. • Boccaccio shares with Petrarch the honor of being the earliest humanist. In their time there were not a dozen men in Italy who could read the ...
Renaissance Europe - New Providence School
... • printing press with movable type: Johann Gutenberg, Mainz, mid-15th c. – precursors: rise of schools & literacy (demand for books); invention of cheap paper – by 1500, printing presses running in more than 200 cities in Europe – rulers in church & state now had to deal with more educated, critical ...
... • printing press with movable type: Johann Gutenberg, Mainz, mid-15th c. – precursors: rise of schools & literacy (demand for books); invention of cheap paper – by 1500, printing presses running in more than 200 cities in Europe – rulers in church & state now had to deal with more educated, critical ...
What was the Renaissance?
... During the Renaissance, people had more options than ever before which led to a belief that people can accomplish anything ...
... During the Renaissance, people had more options than ever before which led to a belief that people can accomplish anything ...
HUMAN FIGURES IN SCULPTURES Changes of the human figure
... developments in science and learning caused an explosion of new ideas and ways of living. These changes had an influence on most areas of the arts: literature, music, theatre, but most particularly in the visual arts. This discussion will look closely at the way changes in religion, ideas and behavi ...
... developments in science and learning caused an explosion of new ideas and ways of living. These changes had an influence on most areas of the arts: literature, music, theatre, but most particularly in the visual arts. This discussion will look closely at the way changes in religion, ideas and behavi ...
Renaissance ppt
... During the Renaissance, people had more options than ever before which led to a belief that people can accomplish anything ...
... During the Renaissance, people had more options than ever before which led to a belief that people can accomplish anything ...
CH. 15 The Renaissance and Reformation 1350-1700 A.D.
... • Many were Christian struggled with preparing for the afterlife but also living a joyful life with individual achievment ...
... • Many were Christian struggled with preparing for the afterlife but also living a joyful life with individual achievment ...
The Renaissance
... • Interested in how rulers gained and kept power • He wrote The Prince that is considered the 1st book of modern political science • He advised princes to be powerful, but willing to break rules ...
... • Interested in how rulers gained and kept power • He wrote The Prince that is considered the 1st book of modern political science • He advised princes to be powerful, but willing to break rules ...
The Renaissance, 1400-1500
... Petrarch viewed the 14th Century as a positive and clear break with the “Dark Ages,” celebrating a return/rediscovery of the culture of antiquity (humanism) You have heard what I think of your life and your genius. Are you hoping to hear of your books also; what fate has befallen them, how they ar ...
... Petrarch viewed the 14th Century as a positive and clear break with the “Dark Ages,” celebrating a return/rediscovery of the culture of antiquity (humanism) You have heard what I think of your life and your genius. Are you hoping to hear of your books also; what fate has befallen them, how they ar ...
Bell Ringer - Mr. Benham
... allowed people to invest in art and learning City life led to an exchange of ideas and contributed to the start of the Renaissance More money = more leisure time = learning and interest in the arts ...
... allowed people to invest in art and learning City life led to an exchange of ideas and contributed to the start of the Renaissance More money = more leisure time = learning and interest in the arts ...
Renaissance Renaissance Literature refers to the period in
... Renaissance Literature refers to the period in European literature that began in Italy during the 14th century and spread around Europe through the 17th century. The impact of the Renaissance varied across the continent; countries that were predominantly Catholic or Protestant experienced the Renais ...
... Renaissance Literature refers to the period in European literature that began in Italy during the 14th century and spread around Europe through the 17th century. The impact of the Renaissance varied across the continent; countries that were predominantly Catholic or Protestant experienced the Renais ...
Renaissance Artists
... ■ Brunelleschi was Florence’s greatest architect: –He studied the Roman Pantheon when he built the Cuppolo of Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence –The dome inspired modern building designs ...
... ■ Brunelleschi was Florence’s greatest architect: –He studied the Roman Pantheon when he built the Cuppolo of Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence –The dome inspired modern building designs ...
Renaissance Artists
... ■ Brunelleschi was Florence’s greatest architect: –He studied the Roman Pantheon when he built the Cuppolo of Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence –The dome inspired modern building designs ...
... ■ Brunelleschi was Florence’s greatest architect: –He studied the Roman Pantheon when he built the Cuppolo of Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence –The dome inspired modern building designs ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.