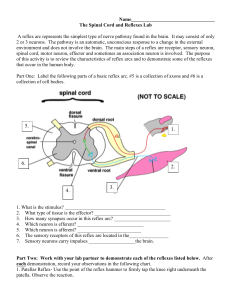
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex ...
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex ...
Action recognition in the premotor cortex
... grip', i.e. opposition of the index finger and thumb. This grip was evoked by small objects, (ii) 'Finger prehension', i.e. opposition of the thumb to the other fingers. The monkeys used finger prehension to pick up middle-size objects from a deep narrow container, (iii) 'Whole hand prehension', i.e ...
... grip', i.e. opposition of the index finger and thumb. This grip was evoked by small objects, (ii) 'Finger prehension', i.e. opposition of the thumb to the other fingers. The monkeys used finger prehension to pick up middle-size objects from a deep narrow container, (iii) 'Whole hand prehension', i.e ...
Medial Prefrontal Cortex Cells Show Dynamic Modulation With the
... The role of the hippocampus during behavior has been thoroughly researched and great progress has been made into unraveling how the hippocampus plays its central role in memory tasks (Eichenbaum, 2004). The prefrontal cortex has been shown to be involved in a range of complex tasks in primates and r ...
... The role of the hippocampus during behavior has been thoroughly researched and great progress has been made into unraveling how the hippocampus plays its central role in memory tasks (Eichenbaum, 2004). The prefrontal cortex has been shown to be involved in a range of complex tasks in primates and r ...
Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to
... The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPTN) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDTN) are major sources of cholinergic projections in the brain stem and contain both cholinergic and glutamatergic neurons (Hallanger and Wainer 1988). PPTN is a part of the reticular activating system, which provides ...
... The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPTN) and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDTN) are major sources of cholinergic projections in the brain stem and contain both cholinergic and glutamatergic neurons (Hallanger and Wainer 1988). PPTN is a part of the reticular activating system, which provides ...
Learning Objectives
... The thumb and the big toe are therefore supplied by cranial dermatomes (C6 and L5 respectively-see dermatome diagram activity 1). The extensor aspect of the lower limb has swung right round to face anteriorly, so the dermatomes will spiral round inwardly on the limb rather than running in parallel ...
... The thumb and the big toe are therefore supplied by cranial dermatomes (C6 and L5 respectively-see dermatome diagram activity 1). The extensor aspect of the lower limb has swung right round to face anteriorly, so the dermatomes will spiral round inwardly on the limb rather than running in parallel ...
Interspike Intervals, Receptive Fields, and Information Encoding in
... Receptive field maps. Cross-correlation of an evoked spike train with the m-sequence stimulus—a process also known as “spike-triggered averaging”—yields a detailed map of the neuron’s spatiotemporal receptive field (see Fig. 4). This map essentially represents the average stimulus preceding each spi ...
... Receptive field maps. Cross-correlation of an evoked spike train with the m-sequence stimulus—a process also known as “spike-triggered averaging”—yields a detailed map of the neuron’s spatiotemporal receptive field (see Fig. 4). This map essentially represents the average stimulus preceding each spi ...
The neural mechanisms of perceptual filling-in
... will be better able to understand how the brain represents the illusory experiences of filling-in, and we might gain insights into the way in which visual experience is represented in the brain. Here, I summarize recent advances in this field, beginning with an introduction to examples of filling-in ...
... will be better able to understand how the brain represents the illusory experiences of filling-in, and we might gain insights into the way in which visual experience is represented in the brain. Here, I summarize recent advances in this field, beginning with an introduction to examples of filling-in ...
Molecular Nature of Spemann`s Organizer: the Role
... terms the organizer is currently thought to be induced as a result of the release of a dorsal growth factor by the Nieuwkoop center blastomeres. This growth factor would then act upon the overlying cells of the marginal zone, inducing them to become organizer tissue. At the late blastula stage, the ...
... terms the organizer is currently thought to be induced as a result of the release of a dorsal growth factor by the Nieuwkoop center blastomeres. This growth factor would then act upon the overlying cells of the marginal zone, inducing them to become organizer tissue. At the late blastula stage, the ...
A Curious Commentary on a Book on Mirror Neurons and Other
... case for expert or novice watchers who do not have to use the visual information to select time-sensitive appropriate action responses. Given these confounds, the sensory experience of players and watchers is simply not equated and the result is perfectly compatible with an action selection account ...
... case for expert or novice watchers who do not have to use the visual information to select time-sensitive appropriate action responses. Given these confounds, the sensory experience of players and watchers is simply not equated and the result is perfectly compatible with an action selection account ...
Perception Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to
... For neural circuits in vivo, however, spiking in both preand postsynaptic cells is likely to be irregular (98), with occasional high-frequency bursts. How well does the STDP window (Fig. 1) account for the effects of complex spike trains? Do all the pre/post spike pairs contribute independently to l ...
... For neural circuits in vivo, however, spiking in both preand postsynaptic cells is likely to be irregular (98), with occasional high-frequency bursts. How well does the STDP window (Fig. 1) account for the effects of complex spike trains? Do all the pre/post spike pairs contribute independently to l ...
Chapter 48
... • Concept 48.5: The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized • In all vertebrates, the nervous system – Shows a high degree of cephalization and distinct CNS and PNS components ...
... • Concept 48.5: The vertebrate nervous system is regionally specialized • In all vertebrates, the nervous system – Shows a high degree of cephalization and distinct CNS and PNS components ...
13-1 CHAPTER 13 SYNAPSES The nervous system consists of
... often an accumulation of some electrondense (appears dark in electron micrographs) material near the thickened membrane. On the presynaptic side, there is normally an accumulation of mitochondria in the bouton and, in electron micrographs, a large number of spherical or irregularly shaped structure ...
... often an accumulation of some electrondense (appears dark in electron micrographs) material near the thickened membrane. On the presynaptic side, there is normally an accumulation of mitochondria in the bouton and, in electron micrographs, a large number of spherical or irregularly shaped structure ...
University of Birmingham Drosophila neurotrophins reveal a
... molecules promoting neuronal survival in vertebrates. They also control cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation, and they are required for axonal and dendritic elaborations, synaptic plasticity, excitability, and long-term potentiation (LTP, the basis of memory and learning) [2–5]. NTs under ...
... molecules promoting neuronal survival in vertebrates. They also control cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation, and they are required for axonal and dendritic elaborations, synaptic plasticity, excitability, and long-term potentiation (LTP, the basis of memory and learning) [2–5]. NTs under ...
Spinal cord
... • Spinal cord anatomy in cross section (continued) • Spinal nerve • Contains axons of both sensory and motor neurons • Sensory enter CNS through dorsal root ...
... • Spinal cord anatomy in cross section (continued) • Spinal nerve • Contains axons of both sensory and motor neurons • Sensory enter CNS through dorsal root ...
to receive a reprint - Institute for Learning and Brain Sciences
... syntactic processing is particularly well established in the literature. For example, high-capacity individuals are more sensitive to syntactic ambiguities (e.g., MacDonald et al. 1992; Pearlmutter and MacDonald 1995; Long and Prat 2008) and are better able to parse complex syntactic structures (e.g ...
... syntactic processing is particularly well established in the literature. For example, high-capacity individuals are more sensitive to syntactic ambiguities (e.g., MacDonald et al. 1992; Pearlmutter and MacDonald 1995; Long and Prat 2008) and are better able to parse complex syntactic structures (e.g ...
File - Shabeer Dawar
... • Every skeletal muscle fiber has a motor end plate at the site where an axonal ending comes in close association with the fiber. • As the myelinated nerves fiber reach a muscle they divide into several branches each passes to different muscle fibers, terminating there at the motor end plate. • Clos ...
... • Every skeletal muscle fiber has a motor end plate at the site where an axonal ending comes in close association with the fiber. • As the myelinated nerves fiber reach a muscle they divide into several branches each passes to different muscle fibers, terminating there at the motor end plate. • Clos ...
chapter 27 Reproduction
... 27.12 Organs start to form after gastrulation Organs develop from the three embryonic layers. – The stiff notochord forms the main axis of the body and is later replaced by the vertebral column in most chordates. – The neural tube develops above the notochord and will become the – brain and – spi ...
... 27.12 Organs start to form after gastrulation Organs develop from the three embryonic layers. – The stiff notochord forms the main axis of the body and is later replaced by the vertebral column in most chordates. – The neural tube develops above the notochord and will become the – brain and – spi ...
Network mechanisms of grid cells
... Figure 1. Inhibition-based attractor network model for grid cells. (a) A hexagonal grid pattern forms spontaneously (here over a period of 500 ms) on a twodimensional neuronal lattice consisting of stellate cells that have all-or-none inhibitory connections with each other. Neurons are arranged on t ...
... Figure 1. Inhibition-based attractor network model for grid cells. (a) A hexagonal grid pattern forms spontaneously (here over a period of 500 ms) on a twodimensional neuronal lattice consisting of stellate cells that have all-or-none inhibitory connections with each other. Neurons are arranged on t ...
Reproduction and Development
... 27.12 Organs start to form after gastrulation Organs develop from the three embryonic layers. – The stiff notochord forms the main axis of the body and is later replaced by the vertebral column in most chordates. – The neural tube develops above the notochord and will become the – brain and – spi ...
... 27.12 Organs start to form after gastrulation Organs develop from the three embryonic layers. – The stiff notochord forms the main axis of the body and is later replaced by the vertebral column in most chordates. – The neural tube develops above the notochord and will become the – brain and – spi ...
USF Hyperbaric Biomedical Research Laboratory
... equipment used to measure cellular function in real time via electrophysiology, polarography, fluorescence microscopy and atomic force microscopy during experimental perturbations of barometric pressure and gas partial pressures. The mission of the USF-HBRL is to identify the molecular and cellular ...
... equipment used to measure cellular function in real time via electrophysiology, polarography, fluorescence microscopy and atomic force microscopy during experimental perturbations of barometric pressure and gas partial pressures. The mission of the USF-HBRL is to identify the molecular and cellular ...























