Transcription Factor Expression and Notch
... Primar y cultures. Young adult male Sprague Dawley rats (6 –7 weeks of age and weighing 180 –220 gm) were used in all experiments. Adult rats were killed with diethyl ether, and the dorsal part of the spinal cord was exposed by laminectomy. The segments between the fourth thoracic (T4) and sacral le ...
... Primar y cultures. Young adult male Sprague Dawley rats (6 –7 weeks of age and weighing 180 –220 gm) were used in all experiments. Adult rats were killed with diethyl ether, and the dorsal part of the spinal cord was exposed by laminectomy. The segments between the fourth thoracic (T4) and sacral le ...
Neuronal oscillations and brain wave dynamics in a LIF model
... To keep the complexity of this model at an understandable level, it uses the simplest neurological model available: Leaky Integrate and Fire. Generally, each neuron gets input from other neurons, which influences its electrical charge. If the charge reaches a certain threshold, the neuron fires, whi ...
... To keep the complexity of this model at an understandable level, it uses the simplest neurological model available: Leaky Integrate and Fire. Generally, each neuron gets input from other neurons, which influences its electrical charge. If the charge reaches a certain threshold, the neuron fires, whi ...
Neural Mechanisms for Binaural Interactions in the Superior Olivary
... regardless of overall level. Response is small when the ILD is zero, as would occur on the midline. ...
... regardless of overall level. Response is small when the ILD is zero, as would occur on the midline. ...
the spinal cord and the influence of its damage on
... In spinal cord injury, the destruction of nerve fibres that carry motor signals from the brain to the torso and limbs leads to muscle paralysis. Destruction of sensory nerve fibres can lead to loss of sensations such as touch, pressure and temperature. Largely unknown is that the spinal cord control ...
... In spinal cord injury, the destruction of nerve fibres that carry motor signals from the brain to the torso and limbs leads to muscle paralysis. Destruction of sensory nerve fibres can lead to loss of sensations such as touch, pressure and temperature. Largely unknown is that the spinal cord control ...
3 The Third-Person View of the Mind
... difference between the brains of humans and lower animals. Inside the cerebral cortex is white matter, which is used to transport neural activity from one part of the brain to another. It appears lighter than the gray matter because its axons are covered with the fatty myelin sheath, reducing the ti ...
... difference between the brains of humans and lower animals. Inside the cerebral cortex is white matter, which is used to transport neural activity from one part of the brain to another. It appears lighter than the gray matter because its axons are covered with the fatty myelin sheath, reducing the ti ...
BIO 141 Unit 5 Learning Objectives
... Upon your successful completion of this unit, you will be able to do the following. ...
... Upon your successful completion of this unit, you will be able to do the following. ...
Science of Software
... the DNA of a gene to produce a replica. Along the way some codons of base pairs signal the structure of enzymes, amino acids all the way to the proteins of cells, while others indicate a wide variety of sequencing, patterning and ‘on-off’ instructions that we are gradually beginning to understand. W ...
... the DNA of a gene to produce a replica. Along the way some codons of base pairs signal the structure of enzymes, amino acids all the way to the proteins of cells, while others indicate a wide variety of sequencing, patterning and ‘on-off’ instructions that we are gradually beginning to understand. W ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... cells due to their elaborate shapes. In addition to the soma (the cell body), many neurons possess several dendrites and a single axon1 . These processes contribute to the neuron’s overall specific shape. An excitable neuronal membrane forms the surface of the neuron. As shown in Figure 2.1, the neur ...
... cells due to their elaborate shapes. In addition to the soma (the cell body), many neurons possess several dendrites and a single axon1 . These processes contribute to the neuron’s overall specific shape. An excitable neuronal membrane forms the surface of the neuron. As shown in Figure 2.1, the neur ...
Article
... immunofluorescence staining was performed with SC121 and a GFAP antibody that reacts with both mouse and human GFAP. We counted approximately 1000 GFAP-positive cells and 200 SC121-positive human cells in the same cortical field of the cortex of the transplanted Ppt1 / /NSCID brain, revealing only a ...
... immunofluorescence staining was performed with SC121 and a GFAP antibody that reacts with both mouse and human GFAP. We counted approximately 1000 GFAP-positive cells and 200 SC121-positive human cells in the same cortical field of the cortex of the transplanted Ppt1 / /NSCID brain, revealing only a ...
Cell cycles and clonal strings during formation of the
... during gastrulation. The vertical scale shows hours postfertilization (h). Gastrulation begins between 5 and 6 h, and segmentation (somite formation) begins at about 10 h. Cell cycle numbers (c14, c15, c16) are defined by the fertilized egg starting cycle 1, with division 1 occurring at the end of c ...
... during gastrulation. The vertical scale shows hours postfertilization (h). Gastrulation begins between 5 and 6 h, and segmentation (somite formation) begins at about 10 h. Cell cycle numbers (c14, c15, c16) are defined by the fertilized egg starting cycle 1, with division 1 occurring at the end of c ...
Sympathetic nervous system
... • Synaptic Transmission: the process by which nerve impulses are carried across the small gap, the synapse, between one neuron and another. The nerve impulse is an electrical signal which is carried by chemicals called neurotransmitters. • This happens at very high speed e.g. visual information seem ...
... • Synaptic Transmission: the process by which nerve impulses are carried across the small gap, the synapse, between one neuron and another. The nerve impulse is an electrical signal which is carried by chemicals called neurotransmitters. • This happens at very high speed e.g. visual information seem ...
Simulation of signal flow in 3D reconstructions of an anatomically
... flow in the brain. Methods to directly monitor streams of excitation, at subcellular and millisecond resolution, are at present lacking. Here, we describe a pipeline of tools that allow investigating information flow by simulating electrical signals that propagate through anatomically realistic mode ...
... flow in the brain. Methods to directly monitor streams of excitation, at subcellular and millisecond resolution, are at present lacking. Here, we describe a pipeline of tools that allow investigating information flow by simulating electrical signals that propagate through anatomically realistic mode ...
Prenatal and postnatal development of laterally
... in early development. However, they can also represent any other spontaneous activity that includes large patches that are spatially coherent. The patterns consisted of uniform random noise added to a large “disk” of activity representing a local patch of highly responding neurons (a retinal wave). ...
... in early development. However, they can also represent any other spontaneous activity that includes large patches that are spatially coherent. The patterns consisted of uniform random noise added to a large “disk” of activity representing a local patch of highly responding neurons (a retinal wave). ...
BIOL241 Lab tips Labs17-22
... Activity 3 is to learn the anatomy of the 12 cranial nerves, which can be studied from models or links. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11504 The MAJOR part of Lab 19 is the SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION. Detailed info for this can be found in the Lab 19 handout. Tips for Lab 21- An ...
... Activity 3 is to learn the anatomy of the 12 cranial nerves, which can be studied from models or links. http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP11504 The MAJOR part of Lab 19 is the SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION. Detailed info for this can be found in the Lab 19 handout. Tips for Lab 21- An ...
大腦神經解剖與建置
... b. prefrontal cortex (high-order association areas): higher aspects of motor control planning / execution of behaviors that require the integration of information over time分3 more areas: 1.dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex → working memory 2.orbitofrontal cortex 3.anterior cingulate and medial front ...
... b. prefrontal cortex (high-order association areas): higher aspects of motor control planning / execution of behaviors that require the integration of information over time分3 more areas: 1.dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex → working memory 2.orbitofrontal cortex 3.anterior cingulate and medial front ...
Chap 28b - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... Specialization of Ectoderm • Neurulation – First major event of organogenesis – Gives rise to brain and spinal cord – Induced by chemical signals from notochord – Ectoderm over notochord thickens, forming neural plate – Neural plate folds inward as neural groove with neural folds ...
... Specialization of Ectoderm • Neurulation – First major event of organogenesis – Gives rise to brain and spinal cord – Induced by chemical signals from notochord – Ectoderm over notochord thickens, forming neural plate – Neural plate folds inward as neural groove with neural folds ...
Hypophysis
... cells. They are most numerous in the central anterior portion of pars distalis. In humans, the cells contain numerous secretory granules, 350 to 400 nm in diameter that are similar in appearance to the granules of somatotrophs. The cytoplasm often contains lipid droplets and small filaments ranging ...
... cells. They are most numerous in the central anterior portion of pars distalis. In humans, the cells contain numerous secretory granules, 350 to 400 nm in diameter that are similar in appearance to the granules of somatotrophs. The cytoplasm often contains lipid droplets and small filaments ranging ...
A"computational"approach"towards"the"ontogeny"of" mirror"neurons
... Gazzola (2014). This involves the use of an artificial neural network (ANN) to simulate activity in the premotor cortex (PM) and the superior temporal sulcus (STS). The PM coordinates self-performed actions, whereas the STS is a region known to respond to the sight of body movements and the sound of ...
... Gazzola (2014). This involves the use of an artificial neural network (ANN) to simulate activity in the premotor cortex (PM) and the superior temporal sulcus (STS). The PM coordinates self-performed actions, whereas the STS is a region known to respond to the sight of body movements and the sound of ...
the Lateral Lemniscus Powerful, Onset Inhibition in the Ventral
... in 2% O2) prior to injection of urethan. The animal’s temperature was maintained at ⬃37.5°C by a thermostatically controlled heating pad. At the end of the recording session, the animal was intra-cardially perfused with 10% formalin. Brains were removed, postfixed in 10% formalin, and sectioned on a ...
... in 2% O2) prior to injection of urethan. The animal’s temperature was maintained at ⬃37.5°C by a thermostatically controlled heating pad. At the end of the recording session, the animal was intra-cardially perfused with 10% formalin. Brains were removed, postfixed in 10% formalin, and sectioned on a ...
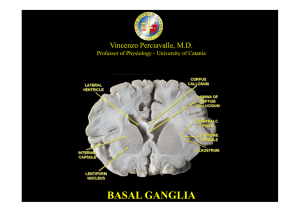
basal ganglia
... the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are colo ...
... the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like those of the globus pallidus, the neurons in pars reticulata are mainly GABAergic. The SNpc is formed by dopaminergic neuron. In humans, these cells are colo ...
Module 18
... • Light-sensitive surface with cells that convert light energy to nerve impulses • At the back of the eyeball • Made up of three layers of cells – Receptor cells (Rods & Cones) – Bipolar cells – Ganglion cells ...
... • Light-sensitive surface with cells that convert light energy to nerve impulses • At the back of the eyeball • Made up of three layers of cells – Receptor cells (Rods & Cones) – Bipolar cells – Ganglion cells ...
video slide
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds major organs have already formed in this pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, chick embryo, which is about 56 hours old and about 2–3 mm l ...
... (a) Early organogenesis. The archenteron forms when lateral folds major organs have already formed in this pinch the embryo away from the yolk. The embryo remains open to the yolk, attached by the yolk stalk, about midway along its length, chick embryo, which is about 56 hours old and about 2–3 mm l ...