1 - U-System
... Pyramidal cells- numerous; large, cone-shaped, apex toward cortical surface with long apical dendrite; basal dendrites from base of pyramid and extends horizontally in cortex; principal output neurons of cortex; axon towards white matter Nonpyramidal cells- small, multipolar, short axons; also calle ...
... Pyramidal cells- numerous; large, cone-shaped, apex toward cortical surface with long apical dendrite; basal dendrites from base of pyramid and extends horizontally in cortex; principal output neurons of cortex; axon towards white matter Nonpyramidal cells- small, multipolar, short axons; also calle ...
Untitled
... compartmentalized, synapse specific action of GABA is required in cortical networks for phasic inhibition. However, GABA released at the synaptic cleft diffuses to receptors outside the postsynaptic density and thus tonically activates extrasynaptic GABAA and GABAB receptors, which include subtypes ...
... compartmentalized, synapse specific action of GABA is required in cortical networks for phasic inhibition. However, GABA released at the synaptic cleft diffuses to receptors outside the postsynaptic density and thus tonically activates extrasynaptic GABAA and GABAB receptors, which include subtypes ...
NSCI 525 RWood 1-22-15
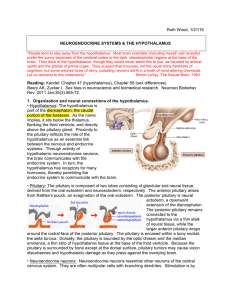
... • Pituitary: The pituitary is composed of two lobes consisting of glandular and neural tissue, derived from the oral ectoderm and neuroectoderm, respectively. The anterior pituitary arises from Rathke’s pouch, an evagination of the oral ectoderm. The posterior pituitary is neural ectoderm, a downwar ...
... • Pituitary: The pituitary is composed of two lobes consisting of glandular and neural tissue, derived from the oral ectoderm and neuroectoderm, respectively. The anterior pituitary arises from Rathke’s pouch, an evagination of the oral ectoderm. The posterior pituitary is neural ectoderm, a downwar ...
Autonomic nervous system
... Joined to ventral rami by white and gray rami communicantes Fusion of ganglia fewer ganglia than spinal nerves ...
... Joined to ventral rami by white and gray rami communicantes Fusion of ganglia fewer ganglia than spinal nerves ...
cranial nerves
... afferents (sensory) to layer IV, (cortical) to layer III efferent to cerebral cortex from layer III; to thalamus from layer VI, to basal ganglia, brain stem. cerebellum and spina l cordfrom layer V pyramidal cells are characteristic cells of cerebral cortex huge Betz cells in layer V of motor cortex ...
... afferents (sensory) to layer IV, (cortical) to layer III efferent to cerebral cortex from layer III; to thalamus from layer VI, to basal ganglia, brain stem. cerebellum and spina l cordfrom layer V pyramidal cells are characteristic cells of cerebral cortex huge Betz cells in layer V of motor cortex ...
Granger causality analysis of state dependent functional connectivity
... Primate feeding behavior is characterized by a series of cycles of different types–ingestion, manipulation, chewing, swallowing [1]. Previous studies employing single electrode recording techniques [2], [3] have shown that majority of neurons in MIo show activity related to rhythmic chewing, preswal ...
... Primate feeding behavior is characterized by a series of cycles of different types–ingestion, manipulation, chewing, swallowing [1]. Previous studies employing single electrode recording techniques [2], [3] have shown that majority of neurons in MIo show activity related to rhythmic chewing, preswal ...
A Neural Mass Model to Simulate Different Rhythms in a Cortical
... interneurons, inhibitory interneurons with slow synaptic kinetics (GABAA,slow ), and inhibitory interneurons with faster synaptic kinetics (GABAA,fast ). In the following, a quantity which belongs to a neural population will be denoted with the subscripts p (pyramidal), e (excitatory interneuron), s ...
... interneurons, inhibitory interneurons with slow synaptic kinetics (GABAA,slow ), and inhibitory interneurons with faster synaptic kinetics (GABAA,fast ). In the following, a quantity which belongs to a neural population will be denoted with the subscripts p (pyramidal), e (excitatory interneuron), s ...
Spinal Sensorimotor System: An Overview
... vertebrae. Running laterally into the body from each of these “segments” are the spinal nerves. A nerve is a bundle of axons running between the central nervous system and peripheral target cells.1 The spinal cord system has four principal classes of nerves as shown below in Table I. Figure 1 illust ...
... vertebrae. Running laterally into the body from each of these “segments” are the spinal nerves. A nerve is a bundle of axons running between the central nervous system and peripheral target cells.1 The spinal cord system has four principal classes of nerves as shown below in Table I. Figure 1 illust ...
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name
... ____________________________ wrap around the nerve fibers when they are myelinated. This results in the impulse skipping from node to node. In myelinated axons and dendrites, the impulse can travel up to 200m/s. In unmyelinated fibers, the impulse can be as slow as 0.5 m/s. This difference in speed ...
... ____________________________ wrap around the nerve fibers when they are myelinated. This results in the impulse skipping from node to node. In myelinated axons and dendrites, the impulse can travel up to 200m/s. In unmyelinated fibers, the impulse can be as slow as 0.5 m/s. This difference in speed ...
22. ANS.Neuroscience
... rami communicantes, which carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers to the sympathetic chain • All the ventral rami receive postganglionic sympathetic fibers from sympathetic chain by a gray ramus • The sympathetic chains carry the preganglionic fibers from T1-L2 levels up to the head and neck and down ...
... rami communicantes, which carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers to the sympathetic chain • All the ventral rami receive postganglionic sympathetic fibers from sympathetic chain by a gray ramus • The sympathetic chains carry the preganglionic fibers from T1-L2 levels up to the head and neck and down ...
Spinal Cord - eCurriculum
... matter, and supportive neuroglial cells. The gray matter is divided into dorsal (posterior), lateral and ventral (anterior) horns, and the intermediate zone. The white matter of the spinal cord consists of myelinated tracts, and supportive neuroglial cells (fibrous astrocytes, interfasicular oligode ...
... matter, and supportive neuroglial cells. The gray matter is divided into dorsal (posterior), lateral and ventral (anterior) horns, and the intermediate zone. The white matter of the spinal cord consists of myelinated tracts, and supportive neuroglial cells (fibrous astrocytes, interfasicular oligode ...
neurology_lab6_13_4_2011 - Post-it
... ☻Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body (3)- Cerebrocerebellum ☻latral zone ...
... ☻Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body (3)- Cerebrocerebellum ☻latral zone ...
ANS.Neuroscience.09
... rami communicantes, which carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers to the sympathetic chain • All the ventral rami receive postganglionic sympathetic fibers from sympathetic chain by a gray ramus • The sympathetic chains carry the preganglionic fibers from T1-L2 levels up to the head and neck and down ...
... rami communicantes, which carry preganglionic sympathetic fibers to the sympathetic chain • All the ventral rami receive postganglionic sympathetic fibers from sympathetic chain by a gray ramus • The sympathetic chains carry the preganglionic fibers from T1-L2 levels up to the head and neck and down ...
Signals from the notochord and floor plate regulate
... transcripts are absent from floor plate cells and the adjacent ventrally located neuroepithelial cells. The zebrafish homologue of Pax-6, pax[zf-a], exhibits a similar pattern of expression in the mid-lateral spinal cord of the early embryo (Krauss et al., 1991a; Pueschel et al., 1992). The spinal c ...
... transcripts are absent from floor plate cells and the adjacent ventrally located neuroepithelial cells. The zebrafish homologue of Pax-6, pax[zf-a], exhibits a similar pattern of expression in the mid-lateral spinal cord of the early embryo (Krauss et al., 1991a; Pueschel et al., 1992). The spinal c ...
The Neuromodulatory Basis of Emotion
... this modulation at the neural level (23). It is clear however that drug reward involves a complex circuitry including the hypothalamus, the ventral pallidum, amygdala, hippocampus and the tegmental nucleus, and that each of these structures are preferentially modulated by different neuromodulatory s ...
... this modulation at the neural level (23). It is clear however that drug reward involves a complex circuitry including the hypothalamus, the ventral pallidum, amygdala, hippocampus and the tegmental nucleus, and that each of these structures are preferentially modulated by different neuromodulatory s ...
Dopamine is one of major neurotransmitters in the brain
... differences between these pathways because they have opposing roles in a balanced circuit; elucidating the mechanisms that give rise to those roles may aid in the treatment of diseases like schizophrenia and substance abuse where that circuit is out of balance. I propose that the three mesocortical ...
... differences between these pathways because they have opposing roles in a balanced circuit; elucidating the mechanisms that give rise to those roles may aid in the treatment of diseases like schizophrenia and substance abuse where that circuit is out of balance. I propose that the three mesocortical ...
The role of exogenous heart-RNA in development of the chick
... effect was carried out on in vitro cultures of the control and heart-RNAtreated presumptive forebrain. 13 of the 17 control explants developed into brain vesicle (76 %), 1 developed into a smaller vesicle with the neurocoel filled with cells (6 %) and 3 remained as a solid mass of cells. In contrast ...
... effect was carried out on in vitro cultures of the control and heart-RNAtreated presumptive forebrain. 13 of the 17 control explants developed into brain vesicle (76 %), 1 developed into a smaller vesicle with the neurocoel filled with cells (6 %) and 3 remained as a solid mass of cells. In contrast ...
Estimating Fast Neural Input Using Anatomical and
... have a direct connection to (T). Some of those neurons may also send collaterals elsewhere, hence contributing to the indirect activity. Right: synapse specific recordings allows quantification of the direct input to the target neuron exclusively while sparing indirect paths. (C) Functional connecti ...
... have a direct connection to (T). Some of those neurons may also send collaterals elsewhere, hence contributing to the indirect activity. Right: synapse specific recordings allows quantification of the direct input to the target neuron exclusively while sparing indirect paths. (C) Functional connecti ...
Learning Objectives
... 26. Compare the structures and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27. Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 28. Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 29. Describe the structures ...
... 26. Compare the structures and functions of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27. Distinguish between the functions of the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. 28. Describe the embryonic development of the vertebrate brain. 29. Describe the structures ...
Primate Globus Pallidus and Subthalamic Nucleus: Functional
... 2. In GPe (n = 249), GPi (n = 15l), and movements were found throughout the rosSTN (n = 153), 47, 29, and 28% of the cells, trocaudal extent of the nucleus, but were respectively, discharged in relation to active most numerous at the rostra1 and caudal arm movements, 10, 11, and 15% to leg poles. Ne ...
... 2. In GPe (n = 249), GPi (n = 15l), and movements were found throughout the rosSTN (n = 153), 47, 29, and 28% of the cells, trocaudal extent of the nucleus, but were respectively, discharged in relation to active most numerous at the rostra1 and caudal arm movements, 10, 11, and 15% to leg poles. Ne ...
this worksheet - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Neuron Shapes and click Continue to return to the main screen. Click the Change button and then select the neuron whose shape you want to change. Click on the desired shape from the window that opens to the left of the screen. Let’s play around first with making different types of circuits. Design a ...
... Neuron Shapes and click Continue to return to the main screen. Click the Change button and then select the neuron whose shape you want to change. Click on the desired shape from the window that opens to the left of the screen. Let’s play around first with making different types of circuits. Design a ...