
Stimulus-Dependent Synchronization of Neuronal Responses in the
... evoked by the same stimulus are expected to contain such synchronous episodes much more frequently than responses evoked by different stimuli. To test this prediction, we investigated response synchronization in the middle temporal area (area V5 or MT) of alert fixating macaque monkeys. This area is ...
... evoked by the same stimulus are expected to contain such synchronous episodes much more frequently than responses evoked by different stimuli. To test this prediction, we investigated response synchronization in the middle temporal area (area V5 or MT) of alert fixating macaque monkeys. This area is ...
No Direct Projection is Observed from the Substantia Nigra to the
... injection of the retrograde tracer fluoro-gold (FG) into the DVC, FG-labeled neurons were observed in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), lateral hypothalamus (LH), inferior olive (IO), and locus coeruleus (LC). No FG-positive cells were observed in the SN or striatum. Furthermore, after ...
... injection of the retrograde tracer fluoro-gold (FG) into the DVC, FG-labeled neurons were observed in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), lateral hypothalamus (LH), inferior olive (IO), and locus coeruleus (LC). No FG-positive cells were observed in the SN or striatum. Furthermore, after ...
Identification of neural circuits involved in female genital responses
... the brain neurons that innervate the clitoris and vagina. To delineate forebrain input on PRV-labeled cells, the anterograde tracer biotinylated dextran amine was injected in the medial preoptic area (MPO), ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN), or the midbrain periaqueductal gray (PAG) 10 ...
... the brain neurons that innervate the clitoris and vagina. To delineate forebrain input on PRV-labeled cells, the anterograde tracer biotinylated dextran amine was injected in the medial preoptic area (MPO), ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN), or the midbrain periaqueductal gray (PAG) 10 ...
Neuronal subtype specification in the cerebral cortex
... neurons position themselves in the developing neocortex through defined modes of radial and tangential migration6,21–23. The earliest born neurons appear around E10.5 in the mouse and form a layered structure termed the preplate, which is later split into the more superficial marginal zone and the d ...
... neurons position themselves in the developing neocortex through defined modes of radial and tangential migration6,21–23. The earliest born neurons appear around E10.5 in the mouse and form a layered structure termed the preplate, which is later split into the more superficial marginal zone and the d ...
Superior Frontal Gyrus Superior Longitudinal Fasciculus Superior
... intensity) of the sounds to the two ears. Thus for free-field sounds, LSO cells respond well to stimuli presented in the ipsilateral sound field where the level of the sound is greater in the ipsilateral than the contralateral ear and poorly when the sound is in the contralateral sound field. The la ...
... intensity) of the sounds to the two ears. Thus for free-field sounds, LSO cells respond well to stimuli presented in the ipsilateral sound field where the level of the sound is greater in the ipsilateral than the contralateral ear and poorly when the sound is in the contralateral sound field. The la ...
Way SW, McKenna J 3rd, Mietzsch U, Reith RM, Wu HC, Gambello MJ. Loss of Tsc2 in radial glia models the brain pathology of tuberous sclerosis complex in the mouse. Human Molecular Genetics. 2009 Apr 1; 18(7):1252-65.
... Over the past several years, the traditional function of radial glial cells as a mere scaffold for migrating and developing neurons has been expanded to that of neuroglial precursor cells (42). Multiple lineage tracing experiments using Cre transgenic mice and real-time imaging have demonstrated tha ...
... Over the past several years, the traditional function of radial glial cells as a mere scaffold for migrating and developing neurons has been expanded to that of neuroglial precursor cells (42). Multiple lineage tracing experiments using Cre transgenic mice and real-time imaging have demonstrated tha ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... • Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) (Chapter 12) ...
... • Dorsal root ganglia (sensory, somatic) (Chapter 12) ...
48x36 Poster Template
... We will determine whether cilia loss precedes neuro-degeneration and if so, whether there is a causal relationship between cilia loss and neuron cell death. By observing cilia in mice with degenerative diseases, we can better understand the role of cilia in brain function and survival of neurons. ...
... We will determine whether cilia loss precedes neuro-degeneration and if so, whether there is a causal relationship between cilia loss and neuron cell death. By observing cilia in mice with degenerative diseases, we can better understand the role of cilia in brain function and survival of neurons. ...
Review Energy limitation as a selective pressure on the evolution of
... Evolution of animal morphology, physiology and behaviour is shaped by the selective pressures to which they are subject. Some selective pressures act to increase the benefits accrued whilst others act to reduce the costs incurred, affecting the cost/benefit ratio. Selective pressures therefore produ ...
... Evolution of animal morphology, physiology and behaviour is shaped by the selective pressures to which they are subject. Some selective pressures act to increase the benefits accrued whilst others act to reduce the costs incurred, affecting the cost/benefit ratio. Selective pressures therefore produ ...
Brain Computer Interface Seminar Report
... controls the right half of the body and vice versa. Each hemisphere can be divided into four lobes, the frontal, the parietal, the occipital and the temporal (see figure 2.3). The cortex can also by divide in certain areas each of which is specialized for a different function. Especially the sensori ...
... controls the right half of the body and vice versa. Each hemisphere can be divided into four lobes, the frontal, the parietal, the occipital and the temporal (see figure 2.3). The cortex can also by divide in certain areas each of which is specialized for a different function. Especially the sensori ...
GAP-43 Expression in Primary Sensory Neurons following Central
... nerve section, even though vacant synaptic sites were produced in unstained laminae by this procedure. This indicates that the location of GAP-43 immunolabeling in the central terminals of primed sensory cells may not depend only on the location of vacant synaptic sites. We conclude that distinct co ...
... nerve section, even though vacant synaptic sites were produced in unstained laminae by this procedure. This indicates that the location of GAP-43 immunolabeling in the central terminals of primed sensory cells may not depend only on the location of vacant synaptic sites. We conclude that distinct co ...
Evolutionary Neurotheology - UTK-EECS
... characteristics of the aperture, but obscure others, which are exposed by complex and naturalistic scenes. So also with consciousness. The structure of consciousness cannot be observed independently of its content, but trained “observers” may distinguish characteristics more dependent on consciousne ...
... characteristics of the aperture, but obscure others, which are exposed by complex and naturalistic scenes. So also with consciousness. The structure of consciousness cannot be observed independently of its content, but trained “observers” may distinguish characteristics more dependent on consciousne ...
Bridging Cytoarchitectonics and Connectomics in Human Cerebral
... Cytoarchitectonic mappings of the human cortex were taken from the 1925 Von Economo and Koskinas work Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen (Von Economo and Koskinas, 1925) [translated Cytoarchitectonics of the Adult Human Cerebral Cortex (Triarhou, 2008)]. As described in the ...
... Cytoarchitectonic mappings of the human cortex were taken from the 1925 Von Economo and Koskinas work Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen (Von Economo and Koskinas, 1925) [translated Cytoarchitectonics of the Adult Human Cerebral Cortex (Triarhou, 2008)]. As described in the ...
17-Basal ganglion
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
... Originates from the pars compacta of the ipsilateral substantia nigra of the midbrain tegmentum to caudate nucleus and putamen. The neurons of pars compacta contain the dark pigment neuromelanin. Their transmitter is the monoamine dopamine which has both excitatory and inhibitory effects upon striat ...
Anat3_08_Autonomic_Nervous_System1
... Somatic motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles to produce both voluntary and involuntary movements. When a somatic motor neuron stimulates a muscle, it contracts; the effect is excitation. If it fails to stimulate a muscle it becomes paralyzed. A few skeletal muscles, such as those in the middle e ...
... Somatic motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles to produce both voluntary and involuntary movements. When a somatic motor neuron stimulates a muscle, it contracts; the effect is excitation. If it fails to stimulate a muscle it becomes paralyzed. A few skeletal muscles, such as those in the middle e ...
PDF
... principles have been used in computational modeling (Favorov and Kursun, 2011), applied in developing synthetic neural modeling (Edelman et al., 1992), and used in developing machines with memory capabilities (Edelman, 2007). At the level of neuronal activation, binding by neural synchrony (Legendy, ...
... principles have been used in computational modeling (Favorov and Kursun, 2011), applied in developing synthetic neural modeling (Edelman et al., 1992), and used in developing machines with memory capabilities (Edelman, 2007). At the level of neuronal activation, binding by neural synchrony (Legendy, ...
Prevalent Presence of Periodic Actin-spectrin-based
... relatively small soma size. We also used general neuronal markers MAP2 and NeuN to exclude glial cells from our analysis. All neuronal subtypes were cultured for at least 10 days in vitro until a distinctly long axon had projected from the soma to ensure sufficient axon specification. The neurons we ...
... relatively small soma size. We also used general neuronal markers MAP2 and NeuN to exclude glial cells from our analysis. All neuronal subtypes were cultured for at least 10 days in vitro until a distinctly long axon had projected from the soma to ensure sufficient axon specification. The neurons we ...
Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]
... study the olfactory system of a terrestrial snail. This animal, as do all gastropod molluscs (Croll, 1983) uses olfaction as the principal sensory modality for perception at a distance (Chase et al., 1978; Chase and Croll, 1981; Chase, 1982). Several recent reports have described associative conditi ...
... study the olfactory system of a terrestrial snail. This animal, as do all gastropod molluscs (Croll, 1983) uses olfaction as the principal sensory modality for perception at a distance (Chase et al., 1978; Chase and Croll, 1981; Chase, 1982). Several recent reports have described associative conditi ...
pax proteins in embryogenesis and their role in nervous system
... roof plate and two alar (dorsal) plates, but to lack floor and basal (ventral) plates 29. The alar plate of the diencephalon is characterized by the expression of Pax6. Pax6 expression in human embryos also characterizes the infundibulum, the evagination of the floor plate of the diencephalon and ...
... roof plate and two alar (dorsal) plates, but to lack floor and basal (ventral) plates 29. The alar plate of the diencephalon is characterized by the expression of Pax6. Pax6 expression in human embryos also characterizes the infundibulum, the evagination of the floor plate of the diencephalon and ...
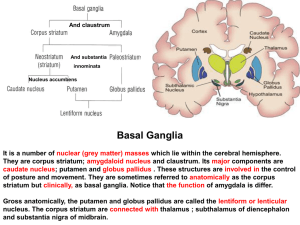
Basal Ganglia
... However under normal conditions this does not happens and the Indirect Pathway is not able to overcome the strong STR brake on GPi/SNr over the Direct Pathway. ...
... However under normal conditions this does not happens and the Indirect Pathway is not able to overcome the strong STR brake on GPi/SNr over the Direct Pathway. ...
Minireview - Leslie Vosshall
... Shortly after the papers above were published, Daisuke Yamamoto and coworkers documented exactly this phenomenon: a small group of central brain neurons called mAL likely involved in taste sensation depends on fru function for survival, and these cells are programmed to die in normal females (Kimura ...
... Shortly after the papers above were published, Daisuke Yamamoto and coworkers documented exactly this phenomenon: a small group of central brain neurons called mAL likely involved in taste sensation depends on fru function for survival, and these cells are programmed to die in normal females (Kimura ...
Lateral olfactory processing
... mammalian olfactory bulb and its insect analog, the antennal lobe. These results are now beginning to elaborate which of these circuit motifs are operative in early olfactory processing and what role they play in odor coding (Aungst et al 2003; McGann et al. 2005; Olsen et al. 2007; Shang et al. 200 ...
... mammalian olfactory bulb and its insect analog, the antennal lobe. These results are now beginning to elaborate which of these circuit motifs are operative in early olfactory processing and what role they play in odor coding (Aungst et al 2003; McGann et al. 2005; Olsen et al. 2007; Shang et al. 200 ...
Sten Grillner
... belt, with the belt speed set on low, the two limbs generated alternating locomotor movements. But when the speed was increased, the coordination of the limbs changed to in phase locomotor movements like in a gallop. This thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated ...
... belt, with the belt speed set on low, the two limbs generated alternating locomotor movements. But when the speed was increased, the coordination of the limbs changed to in phase locomotor movements like in a gallop. This thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated ...

















![Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017009313_1-932f7069dbfdd3fd3915bbe942d02b0f-300x300.png)




