The Northern and Late Renaissance
... • MUSIC – conservative perfection (Palestrina) & new approaches (madrigals) ...
... • MUSIC – conservative perfection (Palestrina) & new approaches (madrigals) ...
Chapter 14 Test Review Why is Albrecht Dürer often compared to
... Which of the following was an effect of the printing revolution in the 1500s? Luther criticized the Roman Catholic Church for Luther believed that The artists of the Renaissance focused on Copernicus proposed which of the following? Which of the following contributed to the birth of the Renaissance ...
... Which of the following was an effect of the printing revolution in the 1500s? Luther criticized the Roman Catholic Church for Luther believed that The artists of the Renaissance focused on Copernicus proposed which of the following? Which of the following contributed to the birth of the Renaissance ...
Renaissance Class Notes
... (it doesn’t matter how you got there just as long as you got there) Dante - Divine Comedy Chaucer - The Canterbury Tales ...
... (it doesn’t matter how you got there just as long as you got there) Dante - Divine Comedy Chaucer - The Canterbury Tales ...
The Renaissance
... The renaissance changed European culture and society. It brought about a transition from medieval to modern age. As a result the Italian ,French ,German, Spanish and English languages blossomed at this time. ...
... The renaissance changed European culture and society. It brought about a transition from medieval to modern age. As a result the Italian ,French ,German, Spanish and English languages blossomed at this time. ...
Renaissance Vocab List
... a region that included parts of present day northern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands; was an important industrial and financial center of northern Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance humanism ...
... a region that included parts of present day northern France, Belgium, and the Netherlands; was an important industrial and financial center of northern Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance humanism ...
Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet
... Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet For the test you will need to know the following terms/ideas. When completing this review sheet you should know the basic information for each item listed (who, what, when, where, why, how is it important) Renaissance- def. 3 Characteristics of the Renaissance 3 ...
... Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet For the test you will need to know the following terms/ideas. When completing this review sheet you should know the basic information for each item listed (who, what, when, where, why, how is it important) Renaissance- def. 3 Characteristics of the Renaissance 3 ...
File - AP European history Mr. trombetta
... The sentiment in the simple statement above reflects some important changes in European attitudes that began to take place during the 15th century. Although important economic changes had taken place during the late Middle Ages, most people of that era still saw themselves as humble servants of God ...
... The sentiment in the simple statement above reflects some important changes in European attitudes that began to take place during the 15th century. Although important economic changes had taken place during the late Middle Ages, most people of that era still saw themselves as humble servants of God ...
Renaissance
... on city—if it dies, so do you • Patronage: wealthy sponsored art to demonstrate importance & glorify city ...
... on city—if it dies, so do you • Patronage: wealthy sponsored art to demonstrate importance & glorify city ...
renaissance - Montville.net
... _________________ was preserved in the Church & by educated people. ...
... _________________ was preserved in the Church & by educated people. ...
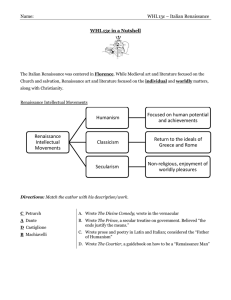
Renaissance Intellectual Movements Humanism Focused on human
... D. Wrote The Courtier, a guidebook on how to be a “Renaissance Man” ...
... D. Wrote The Courtier, a guidebook on how to be a “Renaissance Man” ...
17.1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance (pp. 471-479)
... Name: ___________________________________________ Date: __________________________ Class Period: _____ ...
... Name: ___________________________________________ Date: __________________________ Class Period: _____ ...
Renaissance english music
... madrigal in England, mostly from 1588 to 1627, along with the composers who produced them. The English madrigals were a cappella, predominantly light in style, and generally began as either copies or direct translations of Italian models. Most were for three to six voices. John Dowland[1] (1563 – bu ...
... madrigal in England, mostly from 1588 to 1627, along with the composers who produced them. The English madrigals were a cappella, predominantly light in style, and generally began as either copies or direct translations of Italian models. Most were for three to six voices. John Dowland[1] (1563 – bu ...
The History of Music – An Illustrated History of
... Much of the surviving music left from the Middle Ages is religious, or sacred, because of the sponsorship (patronage) of the church. The later Middle Ages saw the rise of cities, cathedrals, and great works of art and literature. Music held a central place in the cultures of ancient Greece, Ro ...
... Much of the surviving music left from the Middle Ages is religious, or sacred, because of the sponsorship (patronage) of the church. The later Middle Ages saw the rise of cities, cathedrals, and great works of art and literature. Music held a central place in the cultures of ancient Greece, Ro ...
The Renaissance
... Do Now: Examine the sculpture on the right. Write down one thing you can infer from the sculpture about the Renaissance? ...
... Do Now: Examine the sculpture on the right. Write down one thing you can infer from the sculpture about the Renaissance? ...
The Baroque Era
... – Originally a series of dances played for dancing – By the Baroque, suites became independent instrumental pieces no longer intended for dancing – Usually contained four dances – Often unified by key – Differed by tempo and international background – Used binary form ...
... – Originally a series of dances played for dancing – By the Baroque, suites became independent instrumental pieces no longer intended for dancing – Usually contained four dances – Often unified by key – Differed by tempo and international background – Used binary form ...
The History of Music – An Illustrated History of
... Much of the surviving music left from the Middle Ages is religious, or sacred, because of the sponsorship (patronage) of the church. The later Middle Ages saw the rise of cities, cathedrals, and great works of art and literature. Music held a central place in the cultures of ancient Greece, Ro ...
... Much of the surviving music left from the Middle Ages is religious, or sacred, because of the sponsorship (patronage) of the church. The later Middle Ages saw the rise of cities, cathedrals, and great works of art and literature. Music held a central place in the cultures of ancient Greece, Ro ...
The Italian Renaissance
... Renaissance • period from circa 1350 to 1600 during which European scholars revived the learning of ancient Greece and Rome ...
... Renaissance • period from circa 1350 to 1600 during which European scholars revived the learning of ancient Greece and Rome ...
The Baroque Era
... – Originally a series of dances played for dancing – By the Baroque, suites became independent instrumental pieces no longer intended for dancing – Usually contained four dances – Often unified by key – Differed by tempo and international background – Used binary form ...
... – Originally a series of dances played for dancing – By the Baroque, suites became independent instrumental pieces no longer intended for dancing – Usually contained four dances – Often unified by key – Differed by tempo and international background – Used binary form ...
The Renaissance
... What is "The Renaissance" A period of "rebirth" in Europe Reawakening of interest in art, literature, science, and classical civilizations ...
... What is "The Renaissance" A period of "rebirth" in Europe Reawakening of interest in art, literature, science, and classical civilizations ...
- Bright Star Schools
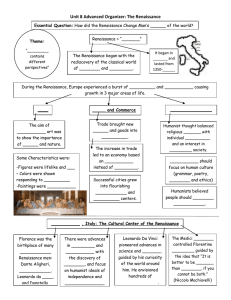
... ___________ , Italy: The Cultural Center of the Renaissance Florence was the birthplace of many ...
... ___________ , Italy: The Cultural Center of the Renaissance Florence was the birthplace of many ...
Renaisance review - Warren County Schools
... gained power and kept it – including the ruler should be feared and loved? ...
... gained power and kept it – including the ruler should be feared and loved? ...
Homework - Manhasset Schools
... Human emotions and experiences are worth studying and understanding. ...
... Human emotions and experiences are worth studying and understanding. ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.