Slide 1
... Prior to printing press and Renaissance was little need for books—no one to read them Previously invented by Song Dynasty in China who gained knowledge from Korea— was Gutenberg aware? Ease of printing made it cheaper and able to be mass produced in other languages other than Latin The Bible was the ...
... Prior to printing press and Renaissance was little need for books—no one to read them Previously invented by Song Dynasty in China who gained knowledge from Korea— was Gutenberg aware? Ease of printing made it cheaper and able to be mass produced in other languages other than Latin The Bible was the ...
The Renaissance
... developments in education and art City-States on the Peninsula are not hindered by monarchy or strong influence of papacy. ...
... developments in education and art City-States on the Peninsula are not hindered by monarchy or strong influence of papacy. ...
Renaissance/Reformation Review
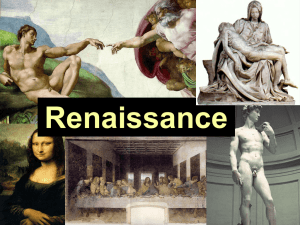
... Humanism Iliad Sistine Chapel Pieta School of Athens Last Supper Florence Patron of the Arts Calvinism Indulgences Printing press Vernacular Anglican Church Linear perspective Secular new interest of Renaissance artists new paint Renaissance man Michelangelo Renaissance buildings Machiavelli Gutenbe ...
... Humanism Iliad Sistine Chapel Pieta School of Athens Last Supper Florence Patron of the Arts Calvinism Indulgences Printing press Vernacular Anglican Church Linear perspective Secular new interest of Renaissance artists new paint Renaissance man Michelangelo Renaissance buildings Machiavelli Gutenbe ...
Renaissance - granbystudents
... ‘Original Sin’ vanities Donatello ‘Sistine Chapel’ Florence Botticelli Roman Catholic 1) _____Latin________ Throughout the Middle Ages, this was the language of the Church and educated nobles. 2) ___Dante____________ He wrote the Divine Comedy in Italian. 3) ____Humanism_________ This philosophy stu ...
... ‘Original Sin’ vanities Donatello ‘Sistine Chapel’ Florence Botticelli Roman Catholic 1) _____Latin________ Throughout the Middle Ages, this was the language of the Church and educated nobles. 2) ___Dante____________ He wrote the Divine Comedy in Italian. 3) ____Humanism_________ This philosophy stu ...
Italian Renaissance
... Shakespeare’s plays are still as popular today as they were when he wrote them Mass production of books was created during this time Christianity radically changed setting off tensions between many Christian groups that still exist today ...
... Shakespeare’s plays are still as popular today as they were when he wrote them Mass production of books was created during this time Christianity radically changed setting off tensions between many Christian groups that still exist today ...
THE RENAISSANCE Essential Question
... Reformation: a 16th-century movement for the reform of abuses in the Roman Catholic Church that ended in the establishment of the Reformed and Protestant Churches Indulgences: The sale of indulgences was a practice where the church acknowledged a donation or other charitable work with a piece of pap ...
... Reformation: a 16th-century movement for the reform of abuses in the Roman Catholic Church that ended in the establishment of the Reformed and Protestant Churches Indulgences: The sale of indulgences was a practice where the church acknowledged a donation or other charitable work with a piece of pap ...
Italian Renaissance Humanism
... Humanism was based on the classics of Greece & Rome. They studied poetry, philosophy, & history. (B) Petrarch used forgotten Latin and he emphasized using pure classical Latin. (A) ...
... Humanism was based on the classics of Greece & Rome. They studied poetry, philosophy, & history. (B) Petrarch used forgotten Latin and he emphasized using pure classical Latin. (A) ...
The Renaissance
... What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? •Renaissance means rebirth of art and learning. •It took place in Italy during 1300 to 1600. ...
... What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? •Renaissance means rebirth of art and learning. •It took place in Italy during 1300 to 1600. ...
Renaissance Powerpoint (from class)
... Plague = End of the Middle Ages 1300s-1600 Same time as Protestant Reformation “rebirth” Explosion of creativity Italy first; Northern Europe later Europe’s Golden Age ...
... Plague = End of the Middle Ages 1300s-1600 Same time as Protestant Reformation “rebirth” Explosion of creativity Italy first; Northern Europe later Europe’s Golden Age ...
Describe the ideal person today. Looking at society as a whole, what
... control of the Holy Land The Black Death – an epidemic of the bubonic plague that swept Europe from 1347-1353, killing about 1/3 of population The Hundred Years’ War – a series of conflicts between England and France from 1337-1453, in which England lost control of most of its territory to ...
... control of the Holy Land The Black Death – an epidemic of the bubonic plague that swept Europe from 1347-1353, killing about 1/3 of population The Hundred Years’ War – a series of conflicts between England and France from 1337-1453, in which England lost control of most of its territory to ...
Cultural Achievements of the Italian Renaissance
... Middle Ages. Many of the artists whom are nowadays considered the greatest of all time, lived and worked in Italy during the Renaissance. The painter and sculptor, Michelangelo, is best known for two particular art works. He was commissioned by Pope Julius II to paint the ceiling of the Sistine Chap ...
... Middle Ages. Many of the artists whom are nowadays considered the greatest of all time, lived and worked in Italy during the Renaissance. The painter and sculptor, Michelangelo, is best known for two particular art works. He was commissioned by Pope Julius II to paint the ceiling of the Sistine Chap ...
The Renaissance in Italy 1300
... • 1300-1600 – Explosion in creativity in Europe • Became known as the Renaissance, or “rebirth” ...
... • 1300-1600 – Explosion in creativity in Europe • Became known as the Renaissance, or “rebirth” ...
The ITALIAN Renaissance
... – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “_______________________” (imaginary, ideal society) – ________________________ for not going along with King Henry ...
... – Interested in Early _________________________ and ______________/________________ periods – “_________________ of ___________________” – criticisms of Christian faith • Thomas More – “_______________________” (imaginary, ideal society) – ________________________ for not going along with King Henry ...
The Renaissance in Italy (1375-1527)
... Geography—Italy center of Mediterranean trade; centers of ancient --become the middlemen of Europe Italian towns had expanded into independent city-states Urbanization—25% of Italians took part in civic culture; cities were magnets for trade, ideas, and culture ...
... Geography—Italy center of Mediterranean trade; centers of ancient --become the middlemen of Europe Italian towns had expanded into independent city-states Urbanization—25% of Italians took part in civic culture; cities were magnets for trade, ideas, and culture ...
Renaissance men.
... 9. What is an artistic technique that creates the appearance of three dimensions on a ...
... 9. What is an artistic technique that creates the appearance of three dimensions on a ...
The Renaissance - Basic Information PPT
... – Time period between the years 1350 - 1600 – Means “Rebirth” • Of what? – The Ancient Greek & Roman world ...
... – Time period between the years 1350 - 1600 – Means “Rebirth” • Of what? – The Ancient Greek & Roman world ...
Ch.-17-Review
... - Why was block printing more useful in Europe than in China? - What were the causes of the Reformation? - What were the three main ideas of Luther’s teachings? - What was Henry VIII’s main reason for splitting with the Catholic Church? - What was agreed upon at the Council of Trent? - What years ma ...
... - Why was block printing more useful in Europe than in China? - What were the causes of the Reformation? - What were the three main ideas of Luther’s teachings? - What was Henry VIII’s main reason for splitting with the Catholic Church? - What was agreed upon at the Council of Trent? - What years ma ...
What was the renaissance? Article 4/14 File
... new and different from medieval art work. Paintings were more lifelike and less formal than medieval paintings. Writers tried to understand human nature through their writings. ...
... new and different from medieval art work. Paintings were more lifelike and less formal than medieval paintings. Writers tried to understand human nature through their writings. ...
The Renaissance Chapter 17 Section 1 What was the Renaissance
... Many independent city-states emerged in northern and central Italy that played an important role in Italian politics and art Milan – one of the richest cities Venice-attracted trade from all over the world Florence-controlled by the Medici Family, who became great patrons of the arts All of these ci ...
... Many independent city-states emerged in northern and central Italy that played an important role in Italian politics and art Milan – one of the richest cities Venice-attracted trade from all over the world Florence-controlled by the Medici Family, who became great patrons of the arts All of these ci ...
17.1 Guided Reading Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... Demonstrated piety by wearing rough clothes and ...
... Demonstrated piety by wearing rough clothes and ...
Renaissance Reading Guide
... answers in complete sentences. This means you begin capital letter and end with a period. Restate the question to begin your answer. If you choose to use your own paper please staple this page to it. 1. Where did the Renaissance start? 471 2. The Renaissance was an “explosion” of what? ...
... answers in complete sentences. This means you begin capital letter and end with a period. Restate the question to begin your answer. If you choose to use your own paper please staple this page to it. 1. Where did the Renaissance start? 471 2. The Renaissance was an “explosion” of what? ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.