Art History Review (with answers)
... Remember one of the reasons for its fame (stolen, mystery, background, Napoleon, etc.) ...
... Remember one of the reasons for its fame (stolen, mystery, background, Napoleon, etc.) ...
The Renaissance
... Most Renaissance artists lived in the city of Florence Many families in port cities grew wealthy from trading. The city of Florence was ruled by the Medici Family Medici family was very rich and liked art. They wanted Florence to be the most beautiful city in Italy. ...
... Most Renaissance artists lived in the city of Florence Many families in port cities grew wealthy from trading. The city of Florence was ruled by the Medici Family Medici family was very rich and liked art. They wanted Florence to be the most beautiful city in Italy. ...
Jan van Eyck Mona Lisa and Last Supper
... Has a classical education Enrich their life with arts ...
... Has a classical education Enrich their life with arts ...
World Cultures
... About 1450, European scholars became more interested in studying the world around them. Their art became more true to life. They began to explore new lands. The new age in Europe was eventually called “the Renaissance.” Renaissance is a French word that means “rebirth.” Historians consider the Renai ...
... About 1450, European scholars became more interested in studying the world around them. Their art became more true to life. They began to explore new lands. The new age in Europe was eventually called “the Renaissance.” Renaissance is a French word that means “rebirth.” Historians consider the Renai ...
Renaissance
... Renaissance is the period from 14th to 16th centuries, and which preceeds the period of Reformation. It originated in Italy and subsequently spread all across Europe. The Italian Renaissance connects the Western world with the classical knowledge. The learning also spread thanks to the invention of ...
... Renaissance is the period from 14th to 16th centuries, and which preceeds the period of Reformation. It originated in Italy and subsequently spread all across Europe. The Italian Renaissance connects the Western world with the classical knowledge. The learning also spread thanks to the invention of ...
On Pleasure - SCHOOLinSITES
... In the early Renaissance, powerful urban groups commissioned works of art, which remained overwhelmingly religious. In the later fifteenth century, individuals and oligarchs began to sponsor works of art as a means of self glorification. ...
... In the early Renaissance, powerful urban groups commissioned works of art, which remained overwhelmingly religious. In the later fifteenth century, individuals and oligarchs began to sponsor works of art as a means of self glorification. ...
Chapter 11 Objects List PDF
... II. A. 1. “Italian Humanist Writers,” Introduction: Identify the city that was the center of culture in Italy and explain why it was the center of culture. II. A. 1. “Italian Humanist Writers,” Major Thinkers: Match each person with his description. a. Petrarch b. Castiglione c. Machiavelli II. A. 2 ...
... II. A. 1. “Italian Humanist Writers,” Introduction: Identify the city that was the center of culture in Italy and explain why it was the center of culture. II. A. 1. “Italian Humanist Writers,” Major Thinkers: Match each person with his description. a. Petrarch b. Castiglione c. Machiavelli II. A. 2 ...
Renaissance PPT - Mr. Stewart World History
... fortunes in the Italian city-states. • Artists and students sought knowledge and fame. • When these travelers returned home, they brought Renaissance ideas with them. • In time, the ideas of the Renaissance influenced people far from the Italian peninsula. ...
... fortunes in the Italian city-states. • Artists and students sought knowledge and fame. • When these travelers returned home, they brought Renaissance ideas with them. • In time, the ideas of the Renaissance influenced people far from the Italian peninsula. ...
World History Chapter 17 section 1 notes
... patron of the arts and a skilled diplomat. d. Although they were better educated that women of the Middle Ages, they less chance to shape political and economic life. The Printing Press 1. The Renaissance was a time of change in technology. 2. The most exciting invention was the printing press. This ...
... patron of the arts and a skilled diplomat. d. Although they were better educated that women of the Middle Ages, they less chance to shape political and economic life. The Printing Press 1. The Renaissance was a time of change in technology. 2. The most exciting invention was the printing press. This ...
For Blog 1st Renaissance Lesson - Ms. Cannistraci presents the
... and grow if they live in fear of making a mistake. The Renaissance themes where revived from classical Greece and Rome. The word Renaissance means rebirth, it truly was a rebirth of the culture of ancient Greece and Rome. It truly was a blessing that the culture of Greece and Rome was preserved by t ...
... and grow if they live in fear of making a mistake. The Renaissance themes where revived from classical Greece and Rome. The word Renaissance means rebirth, it truly was a rebirth of the culture of ancient Greece and Rome. It truly was a blessing that the culture of Greece and Rome was preserved by t ...
World History Chapter 17 section 1 notes
... “Why was the Renaissance a rebirth?” Chapter 17 section one: The Spirit of the Renaissance p. 327 1. The Renaissance 14th century to 16th century 2. The Word Renaissance comes from the French word “rebirth” The Italian City-States 1. The Renaissance started in the northern Italian city-states about ...
... “Why was the Renaissance a rebirth?” Chapter 17 section one: The Spirit of the Renaissance p. 327 1. The Renaissance 14th century to 16th century 2. The Word Renaissance comes from the French word “rebirth” The Italian City-States 1. The Renaissance started in the northern Italian city-states about ...
C. Jacob Burkhardt
... • In accordance with Renaissance ideals, “virtu” refers to: striving for excellence and being a virtuous person or... • those excelling gifts which God gave to the to the soul of man, greatest and preeminent above all other earthly animals." • The man of virtù ( think “virtuoso”), aims at reasoned a ...
... • In accordance with Renaissance ideals, “virtu” refers to: striving for excellence and being a virtuous person or... • those excelling gifts which God gave to the to the soul of man, greatest and preeminent above all other earthly animals." • The man of virtù ( think “virtuoso”), aims at reasoned a ...
Chapter 17 Section 2: The Northern Renaissance
... printing press – Invention used to mass produce written work – First printed work = BIBLE – Only 46 copies remain of Gutenberg Bible ...
... printing press – Invention used to mass produce written work – First printed work = BIBLE – Only 46 copies remain of Gutenberg Bible ...
Renaissance Art
... Middle East led to the rise of Italian city-states. Wealthy merchants were active civic leaders. ...
... Middle East led to the rise of Italian city-states. Wealthy merchants were active civic leaders. ...
The Renaissance
... 1. A wealthy merchant developed in each Italian city-state 2. Merchants dominated politics 3. Merchants did not inherit social rank- used their wits to survive 4. This lead to the rise of importance of individual merit 5. The Medici banking family came to dominate Florence a. Had branch offices all ...
... 1. A wealthy merchant developed in each Italian city-state 2. Merchants dominated politics 3. Merchants did not inherit social rank- used their wits to survive 4. This lead to the rise of importance of individual merit 5. The Medici banking family came to dominate Florence a. Had branch offices all ...
6. How did the new Renaissance worldview shape
... The importance of education 17. Test Conclusions: The Renaissance and Scientific Revolution are often described as eras of human progress. Evaluate whether this is an accurate description. Answers may agree with this description because great discoveries were made, advancing science and enrichin ...
... The importance of education 17. Test Conclusions: The Renaissance and Scientific Revolution are often described as eras of human progress. Evaluate whether this is an accurate description. Answers may agree with this description because great discoveries were made, advancing science and enrichin ...
Origins of the Rensaissance
... The Renaissance began around 1300 A.D. and lasted until around 1600 A.D. o It was a time of cultural awakening for Europe ...
... The Renaissance began around 1300 A.D. and lasted until around 1600 A.D. o It was a time of cultural awakening for Europe ...
Italy: birthplace of the Renaissance
... • Wealthiest, most powerful class • Earned social rank • Individual achievement important (See Medici Family) ...
... • Wealthiest, most powerful class • Earned social rank • Individual achievement important (See Medici Family) ...
The Renaissance - Linn-Benton Community College
... Giotto (Father of Western painting) (know his form / content) Cimabue (Maniera Greca) (the end of an era) Observation, naturalism. expression Pietro Cavallini “Last Judgment” c1290 Duccio- spatial complexity P. Lorenzetti “Birth of a Virgin” Ambrogio Lorenzetti ‘Good Government’/Bad Government -firs ...
... Giotto (Father of Western painting) (know his form / content) Cimabue (Maniera Greca) (the end of an era) Observation, naturalism. expression Pietro Cavallini “Last Judgment” c1290 Duccio- spatial complexity P. Lorenzetti “Birth of a Virgin” Ambrogio Lorenzetti ‘Good Government’/Bad Government -firs ...
The Renaissance
... 2. Which does NOT describe the Renaissance time period? a. focused on human life and accomplishments b. concerned with heaven and hell more than in Middle Ages c. period of exploration and adventure d. period of exceptional human creativity 3. Which of the following does NOT describe the intellectua ...
... 2. Which does NOT describe the Renaissance time period? a. focused on human life and accomplishments b. concerned with heaven and hell more than in Middle Ages c. period of exploration and adventure d. period of exceptional human creativity 3. Which of the following does NOT describe the intellectua ...
MC Review: The Renaissance
... 15 One reason the Renaissance began in Italy was that Italian city-states (1) defeated the Spanish Armada (2) were unified as a nation under the Pope (3) were unaffected by the Commercial Revolution (4) dominated key Mediterranean trade routes 16 In The Prince, Machiavelli advises rulers to (1) seek ...
... 15 One reason the Renaissance began in Italy was that Italian city-states (1) defeated the Spanish Armada (2) were unified as a nation under the Pope (3) were unaffected by the Commercial Revolution (4) dominated key Mediterranean trade routes 16 In The Prince, Machiavelli advises rulers to (1) seek ...
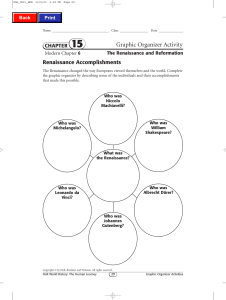
Graphic Organizer Activity
... terms of lofty ideals but in the William Michelangelo? way it actually worked. His Shakespeare? Michelangelo was a brilmost famous work is Shakespeare wrote and proliant painter and sculptor. He The Prince. duced plays written in English helped to design St. Peter’s in which he portrayed personalBas ...
... terms of lofty ideals but in the William Michelangelo? way it actually worked. His Shakespeare? Michelangelo was a brilmost famous work is Shakespeare wrote and proliant painter and sculptor. He The Prince. duced plays written in English helped to design St. Peter’s in which he portrayed personalBas ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.