Physiology 441 - West Virginia University
... concentrated, creating a gradient favoring entrance into the blood • However, tubular cell membranes not very permeable and only ~50% of the filtered urea is passively reabsorbed • BUN- measured as a crude assessment of kidney function ...
... concentrated, creating a gradient favoring entrance into the blood • However, tubular cell membranes not very permeable and only ~50% of the filtered urea is passively reabsorbed • BUN- measured as a crude assessment of kidney function ...
Time Constants of h Current in Layer II Stellate Cells... along the Dorsal to Ventral Axis of Medial Entorhinal Cortex
... 10.0 dextrose, 26.0 NaHCO3, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 2 CaCl2] oxygenated by bubbling 95% O2/5% CO2 through the solution. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were conducted in horizontal brain slices. To control for slice health, the brain was mounted on either its ventral surface (top-down cut) or dorsal surface ...
... 10.0 dextrose, 26.0 NaHCO3, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 2 CaCl2] oxygenated by bubbling 95% O2/5% CO2 through the solution. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were conducted in horizontal brain slices. To control for slice health, the brain was mounted on either its ventral surface (top-down cut) or dorsal surface ...
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Movement across a Membrane
... the more permeable the membrane will be. (In other words, nonpolar / hydrophobic particles will diffuse more easily through the nonpolar tail region of the membrane.) o Smaller particles will typically diffuse more rapidly than larger particles o O2, H2O, CO2, N2, etc. rapidly diffuse across the lip ...
... the more permeable the membrane will be. (In other words, nonpolar / hydrophobic particles will diffuse more easily through the nonpolar tail region of the membrane.) o Smaller particles will typically diffuse more rapidly than larger particles o O2, H2O, CO2, N2, etc. rapidly diffuse across the lip ...
Fine Gating Properties of Channels Responsible for Persistent
... constants, and the slowest of which are represented by relatively few samples (see Blatz and Magleby, 1986; Sigworth and Sine, 1987; McManus et al., 1987). Hence, logarithmic plots were routinely used for the analysis of intraburst open and closed times as well as burst duration, and in these cases ...
... constants, and the slowest of which are represented by relatively few samples (see Blatz and Magleby, 1986; Sigworth and Sine, 1987; McManus et al., 1987). Hence, logarithmic plots were routinely used for the analysis of intraburst open and closed times as well as burst duration, and in these cases ...
electrochemical processing of regeneration solutions from ion
... In addition, mixtures of salts containing chlorides together with sulfates, as well as hardness cations and sodium ions, are usually present in concentrates and in regeneration solutions. Therefore it is important to develop practical methods of their separation. Ions of hardness salts are separated ...
... In addition, mixtures of salts containing chlorides together with sulfates, as well as hardness cations and sodium ions, are usually present in concentrates and in regeneration solutions. Therefore it is important to develop practical methods of their separation. Ions of hardness salts are separated ...
Protozoa as Model System for Studies of
... The photoreceptor potentials in both ciliates are initiated by light absorption in a cellular photoreceptor system based on hypericin-like chromophores - blepharismin in Blepharisma and stentorin in Stentor. Recent evidence indicates that biochemical processes, which couple the photochemical cycle w ...
... The photoreceptor potentials in both ciliates are initiated by light absorption in a cellular photoreceptor system based on hypericin-like chromophores - blepharismin in Blepharisma and stentorin in Stentor. Recent evidence indicates that biochemical processes, which couple the photochemical cycle w ...
Gemcra! Frimciples
... hole in the negative plate, accelerate, then exit through a smali hole in the posjtive plate. Assume that the holes are small enough nof to affect the elect.ic field orpotentiai. a. What is the electric field strength bet$'een the plates? b. With what speed does an electron exit the electlon gun ifi ...
... hole in the negative plate, accelerate, then exit through a smali hole in the posjtive plate. Assume that the holes are small enough nof to affect the elect.ic field orpotentiai. a. What is the electric field strength bet$'een the plates? b. With what speed does an electron exit the electlon gun ifi ...
The Membrane Skeleton of a Unicellular Consists
... Organization of the Overlapping Region Representative thin sections of isolated cell surface are shown in Fig. 2, a and b, and details are shown diagrammatically in Fig. 3 b. Although the plasma membrane is continuous along the ridge and groove, the membrane skeleton is discontinuous and in fact con ...
... Organization of the Overlapping Region Representative thin sections of isolated cell surface are shown in Fig. 2, a and b, and details are shown diagrammatically in Fig. 3 b. Although the plasma membrane is continuous along the ridge and groove, the membrane skeleton is discontinuous and in fact con ...
The Role of Lipid Domains in Bacterial Cell Processes
... world or from the interiors of other cellular compartments. They maintain a selective permeability for the import and export of water-soluble compounds, enabling the living cell to maintain a stable chemical environment for biological processes. Cell membranes are primarily composed of two crucial s ...
... world or from the interiors of other cellular compartments. They maintain a selective permeability for the import and export of water-soluble compounds, enabling the living cell to maintain a stable chemical environment for biological processes. Cell membranes are primarily composed of two crucial s ...
Charging of Oil-Water Interfaces Due to Spontaneous Adsorption of
... yielding a reasonable value for the adsorption energy of 25kT (kT is the thermal energy). The article is organized as follows: In section 2 the materials and methods for emulsion preparation and analysis are described. In section 3 the experimental results are presented and discussed. The conclusion ...
... yielding a reasonable value for the adsorption energy of 25kT (kT is the thermal energy). The article is organized as follows: In section 2 the materials and methods for emulsion preparation and analysis are described. In section 3 the experimental results are presented and discussed. The conclusion ...
Lithium chloride ionic association in dilute aqueous solution: a
... conductance [36,37,48,55,74], we know that all electrolytes in dilute aqueous solutions have a general trend to associate or even form stable neutral ion pairs [51] at high temperatures and low pressures due to the decreasing dielectric screening effect, which is prominently regulated by the dielectr ...
... conductance [36,37,48,55,74], we know that all electrolytes in dilute aqueous solutions have a general trend to associate or even form stable neutral ion pairs [51] at high temperatures and low pressures due to the decreasing dielectric screening effect, which is prominently regulated by the dielectr ...
Day 3 - EE Sharif
... conducting an impulse, for each ATP molecule that’s hydrolysed, it is actively transporting 3 molecules Na+ out of the cell and 2 molecules of K+ into the cell, at the same time by means of the sodium-potassium pump. Neural Modeling - Fall 1386 ...
... conducting an impulse, for each ATP molecule that’s hydrolysed, it is actively transporting 3 molecules Na+ out of the cell and 2 molecules of K+ into the cell, at the same time by means of the sodium-potassium pump. Neural Modeling - Fall 1386 ...
Electrical membrane properties of rat subthalamic neurons in an in
... Injections of depolarizing current pulses to STH neurons produced either repetitive or burst discharges. The duration of action potentials was about 1 ms. When neurons with a membrane potential of 40-65 mV were activated by the rejection of current pulses, single or repetitive action potentials were ...
... Injections of depolarizing current pulses to STH neurons produced either repetitive or burst discharges. The duration of action potentials was about 1 ms. When neurons with a membrane potential of 40-65 mV were activated by the rejection of current pulses, single or repetitive action potentials were ...
3 state neurons for contextual processing
... (via NMDA receptors) can bring the neuron into an enabled state. Informational (for instance, cue or positional) input (via AMPA receptors) can fire a neuron only from this enabled state. Where might such an architecture be used? In the CAl region of the hippocampus, pyramidal cells receive two dist ...
... (via NMDA receptors) can bring the neuron into an enabled state. Informational (for instance, cue or positional) input (via AMPA receptors) can fire a neuron only from this enabled state. Where might such an architecture be used? In the CAl region of the hippocampus, pyramidal cells receive two dist ...
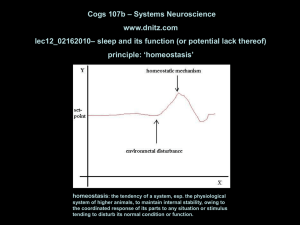
REM-off
... (e.g., NE, HA, ACh, DA, 5-HT). That is, the neuromodulator may change the ‘functional anatomy’ of the brain. For example, when neuron A (presynaptic), having fired an action potential, releases the neurotransmitter glutamate onto neuron B (postsynaptic), ionotropic receptors are activated resulting ...
... (e.g., NE, HA, ACh, DA, 5-HT). That is, the neuromodulator may change the ‘functional anatomy’ of the brain. For example, when neuron A (presynaptic), having fired an action potential, releases the neurotransmitter glutamate onto neuron B (postsynaptic), ionotropic receptors are activated resulting ...
Membrane potential

Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. With respect to the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential range from –40 mV to –80 mV.All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Ion transporter/pump proteins actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradients across the membrane, and ion channels allow ions to move across the membrane down those concentration gradients. Ion pumps and ion channels are electrically equivalent to a set of batteries and resistors inserted in the membrane, and therefore create a voltage difference between the two sides of the membrane.Virtually all eukaryotic cells (including cells from animals, plants, and fungi) maintain a non-zero transmembrane potential, usually with a negative voltage in the cell interior as compared to the cell exterior ranging from –40 mV to –80 mV. The membrane potential has two basic functions. First, it allows a cell to function as a battery, providing power to operate a variety of ""molecular devices"" embedded in the membrane. Second, in electrically excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells, it is used for transmitting signals between different parts of a cell. Signals are generated by opening or closing of ion channels at one point in the membrane, producing a local change in the membrane potential. This change in the electric field can be quickly affected by either adjacent or more distant ion channels in the membrane. Those ion channels can then open or close as a result of the potential change, reproducing the signal.In non-excitable cells, and in excitable cells in their baseline states, the membrane potential is held at a relatively stable value, called the resting potential. For neurons, typical values of the resting potential range from –70 to –80 millivolts; that is, the interior of a cell has a negative baseline voltage of a bit less than one-tenth of a volt. The opening and closing of ion channels can induce a departure from the resting potential. This is called a depolarization if the interior voltage becomes less negative (say from –70 mV to –60 mV), or a hyperpolarization if the interior voltage becomes more negative (say from –70 mV to –80 mV). In excitable cells, a sufficiently large depolarization can evoke an action potential, in which the membrane potential changes rapidly and significantly for a short time (on the order of 1 to 100 milliseconds), often reversing its polarity. Action potentials are generated by the activation of certain voltage-gated ion channels.In neurons, the factors that influence the membrane potential are diverse. They include numerous types of ion channels, some of which are chemically gated and some of which are voltage-gated. Because voltage-gated ion channels are controlled by the membrane potential, while the membrane potential itself is influenced by these same ion channels, feedback loops that allow for complex temporal dynamics arise, including oscillations and regenerative events such as action potentials.