Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
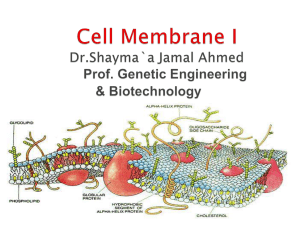
... The plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipids. The membrane has many proteins embedded in it. The arrangement of protein & lipid molecules with in the membrane may suggest different models. The most accepted model is the ...
... The plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipids. The membrane has many proteins embedded in it. The arrangement of protein & lipid molecules with in the membrane may suggest different models. The most accepted model is the ...
Nerve
... increase Hyperpolarization phase: Decline more negative -Cl ions still inside, due to higher conc. outside potential. Microglia:Scavenger Subthreshold cells stimuli get rid no of or foreign local effects, particle B e.g.2mm)& preganglionic autonomic nerve fibers. impulse while response in muscle cel ...
... increase Hyperpolarization phase: Decline more negative -Cl ions still inside, due to higher conc. outside potential. Microglia:Scavenger Subthreshold cells stimuli get rid no of or foreign local effects, particle B e.g.2mm)& preganglionic autonomic nerve fibers. impulse while response in muscle cel ...
Biology for Engineers: Cellular and Systems Neurophysiology
... can be extended (by changing parameter values) to include many other types of voltage-gated ion channels • Voltage-gated ion channels do not only mediate the action potential. They also influence the pattern of action potentials. • Different neurons express different sets of voltageregulated ion cha ...
... can be extended (by changing parameter values) to include many other types of voltage-gated ion channels • Voltage-gated ion channels do not only mediate the action potential. They also influence the pattern of action potentials. • Different neurons express different sets of voltageregulated ion cha ...
8.2 Bellringer..
... Each channel allows the diffusion of a specific substance Ex – only sodium ions can pass through sodium ion channels ...
... Each channel allows the diffusion of a specific substance Ex – only sodium ions can pass through sodium ion channels ...
NMJ-1
... • OPENED Ach CHANNEL ▫ 2 Ach molecules attached to the alpha subunit of receptor ▫ Diameter- 0.65 nanometer ▫ Allows important positive ions—SODIUM, potassium, and calcium to move easily through the opening. ▫ Disallows negative ions, such as chloride to pass through because of strong negative c ...
... • OPENED Ach CHANNEL ▫ 2 Ach molecules attached to the alpha subunit of receptor ▫ Diameter- 0.65 nanometer ▫ Allows important positive ions—SODIUM, potassium, and calcium to move easily through the opening. ▫ Disallows negative ions, such as chloride to pass through because of strong negative c ...
What is the neuron`s resting potential?
... generates and conducts an electrochemical signal. • A given neuron receives electrochemical signals from thousands of adjacent neurons. The terminal buttons of adjacent neurons “synapse” onto the dendrites or cell body of the target neuron. ...
... generates and conducts an electrochemical signal. • A given neuron receives electrochemical signals from thousands of adjacent neurons. The terminal buttons of adjacent neurons “synapse” onto the dendrites or cell body of the target neuron. ...
W09micr430Lec2
... membrane to the outside surface, energy is conserved in the proton gradient that is established; Energy in the proton gradient is both electrical and chemical; The electrical energy exists because a positive charge has been moved across the membrane, creating a charge separation, i.e., the membrane ...
... membrane to the outside surface, energy is conserved in the proton gradient that is established; Energy in the proton gradient is both electrical and chemical; The electrical energy exists because a positive charge has been moved across the membrane, creating a charge separation, i.e., the membrane ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... • Neuron resting potential is ~ -70mV At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration grad ...
... • Neuron resting potential is ~ -70mV At resting potential the neuron is NOT actively transmitting signals Maintained largely because cell membranes are more permeable to K+ than to Na+; more K+ leaves the cell than Na+ enters An ATP powered K+/Na+ pump continually restores the concentration grad ...
Molecular dynamics simulations of membrane
... Due to the limited time and large resources needed to generate MD trajectories of membranes, the latter will be provided to the students. The simulations concern pure planar phospholipid bilayers (membrane constituents) and water described at the atomic level. A set of long trajectories spanning few ...
... Due to the limited time and large resources needed to generate MD trajectories of membranes, the latter will be provided to the students. The simulations concern pure planar phospholipid bilayers (membrane constituents) and water described at the atomic level. A set of long trajectories spanning few ...
Document
... Associated with K+ channel open in the postsynaptic membrane. Occur when axon of presynaptic neuron cause postsynaptic inhibition. ...
... Associated with K+ channel open in the postsynaptic membrane. Occur when axon of presynaptic neuron cause postsynaptic inhibition. ...
Plants and Pollinators
... • Movement of K+ out of cell repolarizes the cell • The inside of the cell once again becomes more negative than the outside ...
... • Movement of K+ out of cell repolarizes the cell • The inside of the cell once again becomes more negative than the outside ...
Slide ()
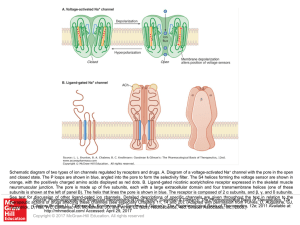
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
The Nervous System
... – Action potentials jump from node to node, thereby speeding the propagation of the impulse. ...
... – Action potentials jump from node to node, thereby speeding the propagation of the impulse. ...
Homeostasis - the ability or tendency of an organism or cell to
... of the cellular membrane, often by viral or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A solution containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate". Turgid – When the cytoplasm and water vacuoles of a cell are filled, the cell membrane will push against the cell and the cell is desc ...
... of the cellular membrane, often by viral or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A solution containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate". Turgid – When the cytoplasm and water vacuoles of a cell are filled, the cell membrane will push against the cell and the cell is desc ...
Cholera - KingsfieldBiology
... (upto 6l a day) causing severe dehydration. Water tainted with V. Cholerae is ingested, usually through water contaminated with effluent Produce flagellin to produce flagellum to move through mucus of small intestine. ...
... (upto 6l a day) causing severe dehydration. Water tainted with V. Cholerae is ingested, usually through water contaminated with effluent Produce flagellin to produce flagellum to move through mucus of small intestine. ...
Movements Through Cell Membranes
... Receptor-mediated endocytosis: moves very specific kinds of particles into the cell. Where proteins from within the cell become receptors on the membrane waiting for specific molecules outside the cell (ligands). ...
... Receptor-mediated endocytosis: moves very specific kinds of particles into the cell. Where proteins from within the cell become receptors on the membrane waiting for specific molecules outside the cell (ligands). ...
Central Nervous System
... potential that spread over the entire surface of the cell – Occurs when a graded potential causes depolarization of the plasma membrane to a level called threshold – Occur in an all-or-none fashion and are of the same magnitude, no matter how strong the stimulus – Occurs in three phases ...
... potential that spread over the entire surface of the cell – Occurs when a graded potential causes depolarization of the plasma membrane to a level called threshold – Occur in an all-or-none fashion and are of the same magnitude, no matter how strong the stimulus – Occurs in three phases ...
Membrane potential

Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. With respect to the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential range from –40 mV to –80 mV.All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Ion transporter/pump proteins actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradients across the membrane, and ion channels allow ions to move across the membrane down those concentration gradients. Ion pumps and ion channels are electrically equivalent to a set of batteries and resistors inserted in the membrane, and therefore create a voltage difference between the two sides of the membrane.Virtually all eukaryotic cells (including cells from animals, plants, and fungi) maintain a non-zero transmembrane potential, usually with a negative voltage in the cell interior as compared to the cell exterior ranging from –40 mV to –80 mV. The membrane potential has two basic functions. First, it allows a cell to function as a battery, providing power to operate a variety of ""molecular devices"" embedded in the membrane. Second, in electrically excitable cells such as neurons and muscle cells, it is used for transmitting signals between different parts of a cell. Signals are generated by opening or closing of ion channels at one point in the membrane, producing a local change in the membrane potential. This change in the electric field can be quickly affected by either adjacent or more distant ion channels in the membrane. Those ion channels can then open or close as a result of the potential change, reproducing the signal.In non-excitable cells, and in excitable cells in their baseline states, the membrane potential is held at a relatively stable value, called the resting potential. For neurons, typical values of the resting potential range from –70 to –80 millivolts; that is, the interior of a cell has a negative baseline voltage of a bit less than one-tenth of a volt. The opening and closing of ion channels can induce a departure from the resting potential. This is called a depolarization if the interior voltage becomes less negative (say from –70 mV to –60 mV), or a hyperpolarization if the interior voltage becomes more negative (say from –70 mV to –80 mV). In excitable cells, a sufficiently large depolarization can evoke an action potential, in which the membrane potential changes rapidly and significantly for a short time (on the order of 1 to 100 milliseconds), often reversing its polarity. Action potentials are generated by the activation of certain voltage-gated ion channels.In neurons, the factors that influence the membrane potential are diverse. They include numerous types of ion channels, some of which are chemically gated and some of which are voltage-gated. Because voltage-gated ion channels are controlled by the membrane potential, while the membrane potential itself is influenced by these same ion channels, feedback loops that allow for complex temporal dynamics arise, including oscillations and regenerative events such as action potentials.