an act of one organism feeding on another Example: A
... amount of their prey species went from 15 to 8. This is becuase the mussles became so pwerful the took over space. ...
... amount of their prey species went from 15 to 8. This is becuase the mussles became so pwerful the took over space. ...
ch04_sec1
... ecosystems, while most of the energy of an ecosystem comes from the sun. • If one part of the ecosystem is destroyed or changes, the entire system will be affected. ...
... ecosystems, while most of the energy of an ecosystem comes from the sun. • If one part of the ecosystem is destroyed or changes, the entire system will be affected. ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... d. The species has many geographically isolated populations, all of them small. e. The species' major food source is an insect population that is declining because of pesticide use. 2. Which of the following may cause a species to become extinct? a. habitat encroachment (e.g., urbanization) b. seaso ...
... d. The species has many geographically isolated populations, all of them small. e. The species' major food source is an insect population that is declining because of pesticide use. 2. Which of the following may cause a species to become extinct? a. habitat encroachment (e.g., urbanization) b. seaso ...
KEYSTONE SPECIES KEEP ECOSYSTEMS TOGETHER
... of its place in the food web, its behavior, or for some other reason. These keystone species affect many of the plants and animals living in an ecosystem. If they disappear, other species may disappear, too, or their populations may change drastically. A KEYSTONE SPECIES MAY BE… ...
... of its place in the food web, its behavior, or for some other reason. These keystone species affect many of the plants and animals living in an ecosystem. If they disappear, other species may disappear, too, or their populations may change drastically. A KEYSTONE SPECIES MAY BE… ...
Unit 9: Ecology A. Definitions 1. biotic(bio = living)
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
File
... with their physical environment (soil, water, climate, and so on). An ecosystem, or ecological system, consists of a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat, such as the soil, water, and weather. ...
... with their physical environment (soil, water, climate, and so on). An ecosystem, or ecological system, consists of a community and all the physical aspects of its habitat, such as the soil, water, and weather. ...
Ecology
... D. Succession: _______________________ through time of changes in community ___________________ Usually described in terms of _____________; unless interrupted (disturbed) succession passes through intermediate stages from pioneer to climax community Primary succession: usually begins with _____ ...
... D. Succession: _______________________ through time of changes in community ___________________ Usually described in terms of _____________; unless interrupted (disturbed) succession passes through intermediate stages from pioneer to climax community Primary succession: usually begins with _____ ...
Adaptations - cloudfront.net
... characteristics of species that allows them to live successfully in the What are environment. some examples Ex : fish have gills so they can breath of under water adaptation? Giraffes have long necks to eat the leaves. ...
... characteristics of species that allows them to live successfully in the What are environment. some examples Ex : fish have gills so they can breath of under water adaptation? Giraffes have long necks to eat the leaves. ...
NOTES ECOLOGY - Pascack Valley Regional High School District
... although many communities never make it to thi step before another disturbance comes to start the process over. ...
... although many communities never make it to thi step before another disturbance comes to start the process over. ...
Ecology terms
... Part of Earth that supports life, top portion of Earth’s crust, all waters on Earth and the surrounding atmosphere ...
... Part of Earth that supports life, top portion of Earth’s crust, all waters on Earth and the surrounding atmosphere ...
Essential Standard 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living
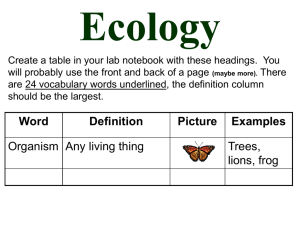
... Organism Within a population, one individual, that has all the characteristics of life, is called an organism. ...
... Organism Within a population, one individual, that has all the characteristics of life, is called an organism. ...
Chap. 16 Ecosystems
... boundaries of an ecosystem are not always obvious, also depends of ecosystem being studied ...
... boundaries of an ecosystem are not always obvious, also depends of ecosystem being studied ...
Everything is Connected powerpoint
... organisms with one another and with their environment. Biotic- The living things in the environment. ...
... organisms with one another and with their environment. Biotic- The living things in the environment. ...
Life Sci.
... An area where organisms interact with each other and with the nonliving things in the environment. ...
... An area where organisms interact with each other and with the nonliving things in the environment. ...
Habitats and Niches
... survive such as food, light, shelter, and water. An organism’s habitat is the area where it can survive because it has these requirements in large enough amounts to support populations of the organism. o A habitat is the environment where an organism lives. ...
... survive such as food, light, shelter, and water. An organism’s habitat is the area where it can survive because it has these requirements in large enough amounts to support populations of the organism. o A habitat is the environment where an organism lives. ...
Chapter 3 Review
... ______________ refers to the ways we use the land around us for urban development, agriculture, industry, mining, and forestry ...
... ______________ refers to the ways we use the land around us for urban development, agriculture, industry, mining, and forestry ...
Endangered Species - Ms. Anderson`s Room 280
... but overuse or human activity has affected the ability of that habitat to support native animals and plants ...
... but overuse or human activity has affected the ability of that habitat to support native animals and plants ...
Chapter 10 – Engage – Page 325 “Relationships
... resources. Sometimes the deer move into areas where they are not normally found. If there is nowhere for deer to move, they are forced to live too close together. Disease can spread easily within populations when this happens. Overpopulation is temporary. When food and other resources eventually r ...
... resources. Sometimes the deer move into areas where they are not normally found. If there is nowhere for deer to move, they are forced to live too close together. Disease can spread easily within populations when this happens. Overpopulation is temporary. When food and other resources eventually r ...
28 Ecosystems - answers
... 1 (a) All the organisms of one species living in a defined area. Population (b) All the organisms living in the same defined area. Community (c) The place where an organism is usually found. Habitat (d) A self-supporting group of organisms and their environment. Ecosystem 2 (a) Animals compete for f ...
... 1 (a) All the organisms of one species living in a defined area. Population (b) All the organisms living in the same defined area. Community (c) The place where an organism is usually found. Habitat (d) A self-supporting group of organisms and their environment. Ecosystem 2 (a) Animals compete for f ...
Habitat – The place in an ecosystem where an organism prefers to live
... Example: forest and a field Benefits of edge to wildlife Edge provides more food and cover for many animals Ex. Negative impacts to wildlife An edge may cut through and limit (fragment) a habitat. Example: A highway through a forest may keep woodland species from crossing. Edge may also increase com ...
... Example: forest and a field Benefits of edge to wildlife Edge provides more food and cover for many animals Ex. Negative impacts to wildlife An edge may cut through and limit (fragment) a habitat. Example: A highway through a forest may keep woodland species from crossing. Edge may also increase com ...
The slow changes of organisms that occurs when the environment
... The slow changes of organisms that occurs when the environment changes. Plant species The main plants that controls the site. (grow in the largest numbers) ...
... The slow changes of organisms that occurs when the environment changes. Plant species The main plants that controls the site. (grow in the largest numbers) ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.