Human impacts on ecosystems
... Come from other continents, adjacent countries or from other ecosystems within Canada. Free from predation and competition many invasive species reproduce rapidly and damage, displace or destroy native species ...
... Come from other continents, adjacent countries or from other ecosystems within Canada. Free from predation and competition many invasive species reproduce rapidly and damage, displace or destroy native species ...
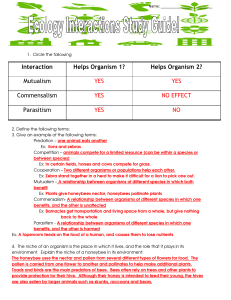
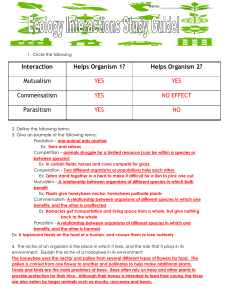
Interaction Helps Organism 1? Helps Organism 2? Mutualism YES
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
Interactions - ScienceGeek.net
... Habitat • All of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives ...
... Habitat • All of the biotic and abiotic factors in the area where an organism lives ...
Woods and Wilds education guide
... The purpose of Woods and Wilds is to depict through movement and dance an exploration of the outdoors. Interdependence, constant change, niche, habitat are described through narratives and movement and connected to Science SOL's. Audience volunteers partner with company dancers during two samples. R ...
... The purpose of Woods and Wilds is to depict through movement and dance an exploration of the outdoors. Interdependence, constant change, niche, habitat are described through narratives and movement and connected to Science SOL's. Audience volunteers partner with company dancers during two samples. R ...
18L- Limiting Factors - Doral Academy Preparatory
... population from ______________ any larger. For example, 10 rabbits may live in a habitat that has enough water, cover and space to support 20 rabbits, but if there is only enough food for ten rabbits, the population will not grow any_____________. In this example, _____________ is the limiting facto ...
... population from ______________ any larger. For example, 10 rabbits may live in a habitat that has enough water, cover and space to support 20 rabbits, but if there is only enough food for ten rabbits, the population will not grow any_____________. In this example, _____________ is the limiting facto ...
Brown Treecreeper
... is the ACT Lowland Woodland Conservation Strategy— Action Plan No. 27 where a full bibliography is available. Action Plans are available from the Environment ACT Website: www.environment.act.gov.au or the Arts, Heritage and Environment Information Centre at 12 Wattle Street, Lyneham ACT. ...
... is the ACT Lowland Woodland Conservation Strategy— Action Plan No. 27 where a full bibliography is available. Action Plans are available from the Environment ACT Website: www.environment.act.gov.au or the Arts, Heritage and Environment Information Centre at 12 Wattle Street, Lyneham ACT. ...
The Habitats and Birds Directives Ciaran O`Keeffe
... • Should also consider areas of value to wildlife even if not designated e.g. pNHAs local Biodiversity Areas, ecological corridors ...
... • Should also consider areas of value to wildlife even if not designated e.g. pNHAs local Biodiversity Areas, ecological corridors ...
Primary succession - No Brain Too Small
... As these conditions change the existing species will be replaced by a new set of species which are now better adapted. Each successive community will be better adapted to the changed environment provided by the previous community. Eventually a climax community is reached and succession will not go a ...
... As these conditions change the existing species will be replaced by a new set of species which are now better adapted. Each successive community will be better adapted to the changed environment provided by the previous community. Eventually a climax community is reached and succession will not go a ...
Levels of Organization in the Ecosystem
... › Example – all of the living organisms (biotic factors) in the environment with the white tail deer, including pine trees, grass, squirrels, moss, mushrooms, and Carolina wrens as well as all of the abiotic (non-living) factors such as rivers, soil, air, and rocks ...
... › Example – all of the living organisms (biotic factors) in the environment with the white tail deer, including pine trees, grass, squirrels, moss, mushrooms, and Carolina wrens as well as all of the abiotic (non-living) factors such as rivers, soil, air, and rocks ...
Ecology Part 2
... leeches ( other than fishing) and mistletoe all have in common? • Parasites- organisms that live on or in another organism • They feed on it without IMMEDIATELY killing it ...
... leeches ( other than fishing) and mistletoe all have in common? • Parasites- organisms that live on or in another organism • They feed on it without IMMEDIATELY killing it ...
Interaction Helps Organism 1? Helps Organism 2? Mutualism YES
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
... The honeybee uses the nectar and pollen from several different types of flowers for food. The pollen is carried from one flower to another and pollinates to help make additional plants. Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection fo ...
Chapter 18
... the same area Includes the abiotic factors Geographic area characterized by certain types of plant and animal communities Earth where life exists ...
... the same area Includes the abiotic factors Geographic area characterized by certain types of plant and animal communities Earth where life exists ...
Ecology …the study of how organisms interact
... organism lives out its life Organisms use a variety of different strategies to live and reproduce in their habitats Habitats can change or disappear from an area through both natural and human causes ...
... organism lives out its life Organisms use a variety of different strategies to live and reproduce in their habitats Habitats can change or disappear from an area through both natural and human causes ...
Keystone species powerpoint
... Some populations of organisms can be removed or lessened with little effect. Why do you think it could have little effect with certain organisms? Some populations of organisms are vital to ecosystems. The event of removing them or lessening them would cause a negative effect. It might stop there or ...
... Some populations of organisms can be removed or lessened with little effect. Why do you think it could have little effect with certain organisms? Some populations of organisms are vital to ecosystems. The event of removing them or lessening them would cause a negative effect. It might stop there or ...
Sc9 - a 1.2 (teacher notes)
... webs represent different types of ongoing relationships between and among all the organisms, within a particular environment. ...
... webs represent different types of ongoing relationships between and among all the organisms, within a particular environment. ...
100
... The largest population of an organism that a given environment can support over time is known as the environment’s __________. ...
... The largest population of an organism that a given environment can support over time is known as the environment’s __________. ...
Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communites
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
4.2_Niches_and_Community
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
... Predators can affect the size of prey populations in a community and determine the places prey can live and feed. ...
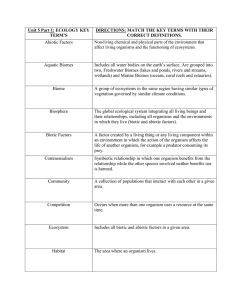
Unit 5 Part 1: ECOLOGY KEY TERM`S DIRECTIONS: MATCH THE
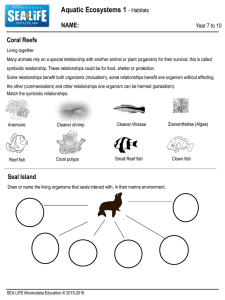
... Includes all water bodies on the earth’s surface. Are grouped into two, Freshwater Biomes (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, wetlands) and Marine Biomes (oceans, coral reefs and estuaries). ...
... Includes all water bodies on the earth’s surface. Are grouped into two, Freshwater Biomes (lakes and ponds, rivers and streams, wetlands) and Marine Biomes (oceans, coral reefs and estuaries). ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.