6-1 A Changing Landscape
... Extinction disappearance of a species from all parts of its geographical range Endangered Species species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues ...
... Extinction disappearance of a species from all parts of its geographical range Endangered Species species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues ...
An interaction in which one organism kills and eats
... 2. Commensalism-a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither helped or harmed. Ex. Robin/maple tree 3. Parasitism-a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is harmed. Ex. ...
... 2. Commensalism-a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is neither helped or harmed. Ex. Robin/maple tree 3. Parasitism-a relationship in which one species benefits and the other is harmed. Ex. ...
Flyswatter Review Community - all the populations of organisms
... Trophic Level - The different levels of organisms on a food chain, based on what they consume. Rule of 10 - Each time an eating event occurs, only 10% of that energy is available for use by the consuming organism. Bioaccumulation - The increase of a toxin in an organism over time Biomagnification - ...
... Trophic Level - The different levels of organisms on a food chain, based on what they consume. Rule of 10 - Each time an eating event occurs, only 10% of that energy is available for use by the consuming organism. Bioaccumulation - The increase of a toxin in an organism over time Biomagnification - ...
19-2 Ecology of Organisms
... A. Ecosystem are constantly changing in response to natural disturbances. Older habitants are replaced by new causing further changes in the community. – 1. Primary succession – growth or succession that occurs on surfaces where there is no soil. A. Pioneer Species - the first plants that will grow ...
... A. Ecosystem are constantly changing in response to natural disturbances. Older habitants are replaced by new causing further changes in the community. – 1. Primary succession – growth or succession that occurs on surfaces where there is no soil. A. Pioneer Species - the first plants that will grow ...
Rainforest- OH standards
... Now covering only a small percent of the Earth’s surface, these are some of the most important habitats on the Planet. Students will learn what rain forests are like and meet some rain forest inhabitants. Ohio Science Standards addressed by this Program, organized by grade band and then standard: GR ...
... Now covering only a small percent of the Earth’s surface, these are some of the most important habitats on the Planet. Students will learn what rain forests are like and meet some rain forest inhabitants. Ohio Science Standards addressed by this Program, organized by grade band and then standard: GR ...
Ffridd / Coedcae
... movement of numerous species. Ffridd is a vital component of the landscape, allowing species to adapt to changing conditions by making altitudinal and longitudinal movements, as they seek suitable areas to fulfil their various life-cycles. The importance of this should not be underestimated. This in ...
... movement of numerous species. Ffridd is a vital component of the landscape, allowing species to adapt to changing conditions by making altitudinal and longitudinal movements, as they seek suitable areas to fulfil their various life-cycles. The importance of this should not be underestimated. This in ...
hssv0401t_powerpres
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
File
... Decomposers consume waste and dead organisms. Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and their environment. Symbiosis is any close relationship between 2 species. A consumer is an organism that cannot make its own energy. The maximum rate of increase for a population is its biotic pote ...
... Decomposers consume waste and dead organisms. Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and their environment. Symbiosis is any close relationship between 2 species. A consumer is an organism that cannot make its own energy. The maximum rate of increase for a population is its biotic pote ...
0 Science 10 - Chapter 1.2 Notes
... Ecosystem (pg. 36) Has abiotic components (water, oxygen, nutrients, light, soil) that interact with biotic components (plants, animals, and micro-organisms). Biomes have MANY ecosystems Habitat (pg. 36) The part of the ecosystem where organisms live Water (pg. 37) Is crucial to all organisms becaus ...
... Ecosystem (pg. 36) Has abiotic components (water, oxygen, nutrients, light, soil) that interact with biotic components (plants, animals, and micro-organisms). Biomes have MANY ecosystems Habitat (pg. 36) The part of the ecosystem where organisms live Water (pg. 37) Is crucial to all organisms becaus ...
Ecology Unit Vocabulary List
... Ecologist = scientist who studies relationships between organisms and environments Ecosystem = a community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings Habitat = the specific environment that provides the things an organism needs to live, grow and reproduce Bi ...
... Ecologist = scientist who studies relationships between organisms and environments Ecosystem = a community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings Habitat = the specific environment that provides the things an organism needs to live, grow and reproduce Bi ...
Ecology - My CCSD
... same place at the same time Individual frogs might compete for the same food source Community is a collection of interacting populations A change in one population may cause change in another population more frogs = fewer flies While population and communities interact, they both interact wi ...
... same place at the same time Individual frogs might compete for the same food source Community is a collection of interacting populations A change in one population may cause change in another population more frogs = fewer flies While population and communities interact, they both interact wi ...
4.2 Notes
... organism lives. Includes both the biotic & abiotic factors Niche: the full range of physical & biological conditions in which an organism lives & the way in which the organism uses those conditions ...
... organism lives. Includes both the biotic & abiotic factors Niche: the full range of physical & biological conditions in which an organism lives & the way in which the organism uses those conditions ...
Eumadicole midges – film stars of the freshwater world
... limited; in many cases we assume that a very fine layer of organic (bacterial/algal) material on the substrate forms the food source. Potential competition for the food is reduced but other components of the aquatic community can also take advantage of this habitat. Similarly, predation pressure from ...
... limited; in many cases we assume that a very fine layer of organic (bacterial/algal) material on the substrate forms the food source. Potential competition for the food is reduced but other components of the aquatic community can also take advantage of this habitat. Similarly, predation pressure from ...
What is population ecology? - Mrs. Cindy Williams Biology website
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
... • What affect population ecology? • density • age • distribution • growth • competition • predation ...
19-2 Ecology of Organisms Habitat- the surrounding area that an
... Examples: plants, food sources, etc. Abiotic factors- the non-living factors that affect organisms. Examples: sunlight levels, precipitation, salinity, Wind levels, temperature, rocks, oxygen concentration, carbon dioxide levels, chemical levels, pH Responses to a Changing EnvironmentCamoflauge- a ...
... Examples: plants, food sources, etc. Abiotic factors- the non-living factors that affect organisms. Examples: sunlight levels, precipitation, salinity, Wind levels, temperature, rocks, oxygen concentration, carbon dioxide levels, chemical levels, pH Responses to a Changing EnvironmentCamoflauge- a ...
ecology Password 14 words
... The class gives the student clues to the vocabulary word onscreen as a clock keeps time. The student tries to guess the word before the buzzer. ...
... The class gives the student clues to the vocabulary word onscreen as a clock keeps time. The student tries to guess the word before the buzzer. ...
Intertidal zone ~ Biome Extension
... tide pools. This applies to starfish, muscles and sea anemones. They do this because the tide pool is rich in nutrients and provides some protection during low tide. Exceptions to this include crabs, hermit crabs and isopods. Their distribution is nearly random as they are mainly found ...
... tide pools. This applies to starfish, muscles and sea anemones. They do this because the tide pool is rich in nutrients and provides some protection during low tide. Exceptions to this include crabs, hermit crabs and isopods. Their distribution is nearly random as they are mainly found ...
Habitats Tour - Potter Park Zoo
... estuaries. Please differentiate between river otters and sea otters. Riparian zones (the plant and animal communities and associated physical features found along bodies of moving water) are unique ecosystems. For a body of water to be suitable for otters it must also have healthy populations of fis ...
... estuaries. Please differentiate between river otters and sea otters. Riparian zones (the plant and animal communities and associated physical features found along bodies of moving water) are unique ecosystems. For a body of water to be suitable for otters it must also have healthy populations of fis ...
Chapter 35 - Science Addict
... In many habitats, the forces that limit population sizes are independent of population density. For example, extreme weather events may decrease populations. For most species, density-dependent factors limit birth rates or increase death rates at least some of the time. This type of population det ...
... In many habitats, the forces that limit population sizes are independent of population density. For example, extreme weather events may decrease populations. For most species, density-dependent factors limit birth rates or increase death rates at least some of the time. This type of population det ...
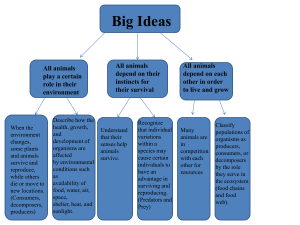
Big Ideas All animals play a certain role in their
... environment changes, some plants and animals survive and reproduce, while others die or move to new locations. (Consumers, decomposers, producers) ...
... environment changes, some plants and animals survive and reproduce, while others die or move to new locations. (Consumers, decomposers, producers) ...
Effects of Catastrophic Events Notes • Tornadoes
... animals.; Fish can breed in areas where flood water stays for an extended duration. Flooding forces many wild and domestic animals from their natural habitats/homes Wildfires Effect on Ecosystem Destroy acres of forests; Burned vegetation in watersheds, leading to erosion; Habitat destruction and an ...
... animals.; Fish can breed in areas where flood water stays for an extended duration. Flooding forces many wild and domestic animals from their natural habitats/homes Wildfires Effect on Ecosystem Destroy acres of forests; Burned vegetation in watersheds, leading to erosion; Habitat destruction and an ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.