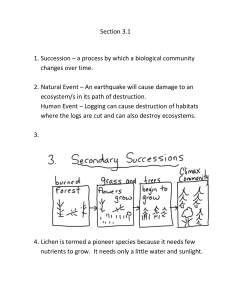
Ecosystems Response Notes
... *Populations form when individuals of the same species share a habitat at the same time.* Habitat is where a population lives. A habitat must support life with food, water, and other resources. ...
... *Populations form when individuals of the same species share a habitat at the same time.* Habitat is where a population lives. A habitat must support life with food, water, and other resources. ...
Slide 1
... Acquiring food /avoidance of predation light A pH A Disease B water A mineral nutrients A turbulence and physical damage. A Pollination B Seed dispersal B ...
... Acquiring food /avoidance of predation light A pH A Disease B water A mineral nutrients A turbulence and physical damage. A Pollination B Seed dispersal B ...
INTERACTIONS AMONG LIVING THINGS
... • Niche - An organism’s way of life. A niche is considered to be an organism’s occupation. Examples: A lion’s niche includes where and how it finds shelter and food, when and how often it reproduces, how it relates to other animals, etc. • Ecosystem - All the living organisms in a given area as well ...
... • Niche - An organism’s way of life. A niche is considered to be an organism’s occupation. Examples: A lion’s niche includes where and how it finds shelter and food, when and how often it reproduces, how it relates to other animals, etc. • Ecosystem - All the living organisms in a given area as well ...
Ecosystems
... A community is a number of different populations interacting with each other. The community of living things interacts with the non-living world around it to form an ecosystem. ...
... A community is a number of different populations interacting with each other. The community of living things interacts with the non-living world around it to form an ecosystem. ...
The highest level of organization is the biosphere, which consists of
... area at the same time is called a population Ø Although all members of the same population share common structural, functional, and behavioural traits, individuals in a population vary slightly in their g ...
... area at the same time is called a population Ø Although all members of the same population share common structural, functional, and behavioural traits, individuals in a population vary slightly in their g ...
Part 7 slides
... Learning Targets 20. Explain how habitat destruction, invasive species, and overexploitation lead to a loss of species. ...
... Learning Targets 20. Explain how habitat destruction, invasive species, and overexploitation lead to a loss of species. ...
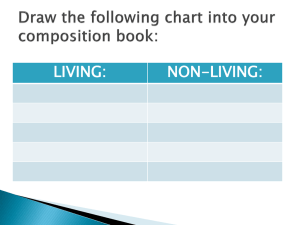
What`s Living? What`s Non-Living?
... particular area ◦ Examples: prairie, mountain stream, ocean, forest ...
... particular area ◦ Examples: prairie, mountain stream, ocean, forest ...
Limiting Factors- Anything that prevents a population sized form
... Limiting Factors- Anything that prevents a population size from increasing. ...
... Limiting Factors- Anything that prevents a population size from increasing. ...
ECOSYSTEMS_1_
... 3) What is a group of the SAME kind of organisms living together in an area called? ...
... 3) What is a group of the SAME kind of organisms living together in an area called? ...
Document
... and extent, the size of the area studied in relation to entire relationship, determine scale. The scale affects what we see. • When one patch meets another, an edge forms. The edges between ecosystems have special properties which are called edge effects. One edge effect is a species diversity. With ...
... and extent, the size of the area studied in relation to entire relationship, determine scale. The scale affects what we see. • When one patch meets another, an edge forms. The edges between ecosystems have special properties which are called edge effects. One edge effect is a species diversity. With ...
Ecosystems Vocabulary
... Habitat-Natural, physical environment of an organism Organism-Any living system Populations-All individuals of a species in a given area Community-Consists of populations of different species that interact ...
... Habitat-Natural, physical environment of an organism Organism-Any living system Populations-All individuals of a species in a given area Community-Consists of populations of different species that interact ...
Habitat Conservation
... Protect native animals and plants in natural communities. In ways such as: -Wildlife and habitat Conservation -Safeguarding biodiversity -Works with local, state, national, and international policy ...
... Protect native animals and plants in natural communities. In ways such as: -Wildlife and habitat Conservation -Safeguarding biodiversity -Works with local, state, national, and international policy ...
Essential Question: How can changes in an organism`s environment
... How can changes in an organism’s environment affect its survival? ...
... How can changes in an organism’s environment affect its survival? ...
Habitat Conservation Planning in Pima County…?
... • The Mission of the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service: working with others to conserve, protect and enhance fish, wildlife, and plants and their habitats for the continuing benefit of the American people ...
... • The Mission of the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service: working with others to conserve, protect and enhance fish, wildlife, and plants and their habitats for the continuing benefit of the American people ...
Student Quiz 6
... • Species: Speciation can happen between two different species, for example like when a horse breeds with a donkey to produce a sterile mule. • Population: There are about 100 thousand zebras living in the savannah. (number not stated to scale; not true) • Habitat: The habitat of wildebeest ...
... • Species: Speciation can happen between two different species, for example like when a horse breeds with a donkey to produce a sterile mule. • Population: There are about 100 thousand zebras living in the savannah. (number not stated to scale; not true) • Habitat: The habitat of wildebeest ...
Student Quiz 6
... • Species: Speciation can happen between two different species, for example like when a horse breeds with a donkey to produce a sterile mule. • Population: There are about 100 thousand zebras living in the savannah. (number not stated to scale; not true) • Habitat: The habitat of wildebeest ...
... • Species: Speciation can happen between two different species, for example like when a horse breeds with a donkey to produce a sterile mule. • Population: There are about 100 thousand zebras living in the savannah. (number not stated to scale; not true) • Habitat: The habitat of wildebeest ...
Appendix A: Pre/Post Test
... 1. The practice of raising fish and other water-dwelling organisms for food is called: A. overfishing. B. aquaculture. C. sustainable yielding. D. selective cutting. 2. The largest population that an environment can support is called its A. carrying capacity. B. limiting factor. C. birth rate. D. de ...
... 1. The practice of raising fish and other water-dwelling organisms for food is called: A. overfishing. B. aquaculture. C. sustainable yielding. D. selective cutting. 2. The largest population that an environment can support is called its A. carrying capacity. B. limiting factor. C. birth rate. D. de ...
LAB MAKE-UP: BIOLOGY 11B
... Sandy Beach. Choose a section of shoreline for each habitat type, both intertidal and nearshore, walk it carefully, and make note of the following: a. Compare the abiotic factors including: wave shock, substrate type, exposure to wind and waves, habitat types. Be specific to the habitats listed b. C ...
... Sandy Beach. Choose a section of shoreline for each habitat type, both intertidal and nearshore, walk it carefully, and make note of the following: a. Compare the abiotic factors including: wave shock, substrate type, exposure to wind and waves, habitat types. Be specific to the habitats listed b. C ...
049539193X_177847
... often have solid substrate on which to cling. 10. Sand and cobble beaches don’t offer a firm substrate. Burrowing animals can quickly be dislodged and into unfavorable places. Only a few organisms (burrowing clams, for example) have evolved adaptations permitting them to succeed in shifting sediment ...
... often have solid substrate on which to cling. 10. Sand and cobble beaches don’t offer a firm substrate. Burrowing animals can quickly be dislodged and into unfavorable places. Only a few organisms (burrowing clams, for example) have evolved adaptations permitting them to succeed in shifting sediment ...
Living Things and the Environment
... Ecosystems contain more than one type of organism All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community To be considered a community the organisms must live together and interact with each other. They may interact by using the same types of shelter, food, or resources. ...
... Ecosystems contain more than one type of organism All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community To be considered a community the organisms must live together and interact with each other. They may interact by using the same types of shelter, food, or resources. ...
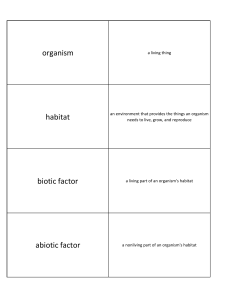
organism habitat biotic factor abiotic factor
... the community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings ...
... the community of organisms that live in a particular area, along with their nonliving surroundings ...
Chapter 2: Living Things in Ecosystems Notes
... C. Section 2.3 (Adapting to the Environment) Goals ...
... C. Section 2.3 (Adapting to the Environment) Goals ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.