Chapter 14 Questions 14.1 1. Three parts of a niche include food
... A densitydependent limiting factor is affected by the number of individuals in a given area, but a densityindependent limiting factor is not affected by population size. Densitydependent examples include predation, competition and disease. Densityindependent examples include weather, natural ...
... A densitydependent limiting factor is affected by the number of individuals in a given area, but a densityindependent limiting factor is not affected by population size. Densitydependent examples include predation, competition and disease. Densityindependent examples include weather, natural ...
Name Period Date
... Answers can be used more than once, all answers are used. Answer list: sun, plants and animals, hydrogen sulfide, animals, tornado damage, forest fire, flood damage, primary, secondary, 10%, underground, Where carbon is stored out of the carbon cycle, can live on bare rock, asphalt parking lot, glac ...
... Answers can be used more than once, all answers are used. Answer list: sun, plants and animals, hydrogen sulfide, animals, tornado damage, forest fire, flood damage, primary, secondary, 10%, underground, Where carbon is stored out of the carbon cycle, can live on bare rock, asphalt parking lot, glac ...
Answers - SolPass
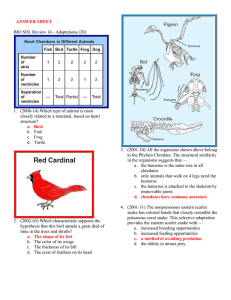
... 8. (2002-35) The picture above shows part of the pectoral girdle and limb of two flying vertebrates known as the bat and the prehistoric pterosaur. Which bone of the pterosaur corresponds to the humerus of the bat? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. (2002-1) Himalayan rabbits are white with black fur on their e ...
... 8. (2002-35) The picture above shows part of the pectoral girdle and limb of two flying vertebrates known as the bat and the prehistoric pterosaur. Which bone of the pterosaur corresponds to the humerus of the bat? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. (2002-1) Himalayan rabbits are white with black fur on their e ...
1.03_Ecological Levels of Organization_11
... Biosphere: The earth’s ecosystem interacting with the physical environment as a whole to maintain a steady state system intermediate in the flow of energy between the high energy input of the sun and the thermal sink of space (merges with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere…). ...
... Biosphere: The earth’s ecosystem interacting with the physical environment as a whole to maintain a steady state system intermediate in the flow of energy between the high energy input of the sun and the thermal sink of space (merges with atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere…). ...
Chapter 12
... some necessities to survive, wildlife also require certain elements from a habitat to survive, such as shelter, food and nest sites. Habitat features include both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Vegetation is the key component to any habitat and all species are dependent on vege ...
... some necessities to survive, wildlife also require certain elements from a habitat to survive, such as shelter, food and nest sites. Habitat features include both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Vegetation is the key component to any habitat and all species are dependent on vege ...
BIO SOL Review 14
... 8. (2002-35) The picture above shows part of the pectoral girdle and limb of two flying vertebrates known as the bat and the prehistoric pterosaur. Which bone of the pterosaur corresponds to the humerus of the bat? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. (2002-1) Himalayan rabbits are white with black fur on their e ...
... 8. (2002-35) The picture above shows part of the pectoral girdle and limb of two flying vertebrates known as the bat and the prehistoric pterosaur. Which bone of the pterosaur corresponds to the humerus of the bat? a. A b. B c. C d. D 9. (2002-1) Himalayan rabbits are white with black fur on their e ...
A niche describes the role or part an organism plays within its
... A plant's or animal's niche, or more correctly, ecological niche, is a way of life that is unique to that species. Niche and habitat are not the same. While many species may share a habitat, this is not true of a niche. Each plant and animal species is a member of a community. The niche describes th ...
... A plant's or animal's niche, or more correctly, ecological niche, is a way of life that is unique to that species. Niche and habitat are not the same. While many species may share a habitat, this is not true of a niche. Each plant and animal species is a member of a community. The niche describes th ...
B20 C3 notes
... • population size and how it changes over time • age distribution • # of females and males, limiting factors on their population • carrying capacity • habitat, niche, range • interactions with other populations and their environment. • succession • zones ...
... • population size and how it changes over time • age distribution • # of females and males, limiting factors on their population • carrying capacity • habitat, niche, range • interactions with other populations and their environment. • succession • zones ...
Unit1 - LiveText
... – All of the individuals of a given species in a specific area or region at a certain time – Contain variation – Example: Females in Colorado Springs in 2009 ...
... – All of the individuals of a given species in a specific area or region at a certain time – Contain variation – Example: Females in Colorado Springs in 2009 ...
Integrated Programme Sec 2 SBGE, LSS Biology Module Topic 3.1
... ii. water with high concentration of salt/minerals (e.g. salt water) can cause living organisms to lose water iii. living organisms need to have special adaptations to prevent water loss iv. freshwater organisms have tendency to gain water Ecology Notes Prepared by Mrs Cheryl Siah ...
... ii. water with high concentration of salt/minerals (e.g. salt water) can cause living organisms to lose water iii. living organisms need to have special adaptations to prevent water loss iv. freshwater organisms have tendency to gain water Ecology Notes Prepared by Mrs Cheryl Siah ...
• Many organisms have evolved as specialists. They might: Occupy
... Each of the organisms in this ecosystem has a particular way of fitting into the oak tree environment - they each occupy a niche within the ecosystem. For example the blue tits and the squirrels, though they both inhabit the same tree, do not directly compete for food: the squirrels feed on acorns, ...
... Each of the organisms in this ecosystem has a particular way of fitting into the oak tree environment - they each occupy a niche within the ecosystem. For example the blue tits and the squirrels, though they both inhabit the same tree, do not directly compete for food: the squirrels feed on acorns, ...
Habitat Action Fact Sheet
... native prairies, wetlands, and forests. Rising real estate prices next to such “amenities” are one measure of that change. (Schools also value native habitat for field study research.) Native habitat also brings real economic benefits: • Slows runoff, allowing half or more of rainfall to infiltrate ...
... native prairies, wetlands, and forests. Rising real estate prices next to such “amenities” are one measure of that change. (Schools also value native habitat for field study research.) Native habitat also brings real economic benefits: • Slows runoff, allowing half or more of rainfall to infiltrate ...
Population Dynamics
... Density – independent factors are those that affect all populations regardless of their density. Most density – independent factors are abiotic: temperature, flood, drought, storms, and habitat disruption. ...
... Density – independent factors are those that affect all populations regardless of their density. Most density – independent factors are abiotic: temperature, flood, drought, storms, and habitat disruption. ...
Habitat Fragmentation and Invasive Species
... Habitat: the natural environment in which an organism lives, included food and shelter ...
... Habitat: the natural environment in which an organism lives, included food and shelter ...
native species
... Energy in Ecosystems Within ecosystems energy flows from the radiant energy of the sun through organisms as chemical energy this is ultimately transformed into heat energy. ...
... Energy in Ecosystems Within ecosystems energy flows from the radiant energy of the sun through organisms as chemical energy this is ultimately transformed into heat energy. ...
key - Scioly.org
... A. The host is generally larger than the parasite. B. An efficient parasite usually kills its host. C. Smaller parasites often live as endoparasites within the body of the host. D. Ectoparasites are attached to the outside of the host's body by specialized organs. E. Some organisms and all viruses a ...
... A. The host is generally larger than the parasite. B. An efficient parasite usually kills its host. C. Smaller parasites often live as endoparasites within the body of the host. D. Ectoparasites are attached to the outside of the host's body by specialized organs. E. Some organisms and all viruses a ...
Ecology ppt.
... • Extinction of a species occurs when it ceases to exist; may follow environmental change - if the species does not evolve • Evolution and extinction are affected by: – large scale movements of continents – gradual climate changes due to continental drift or orbit changes – rapid climate changes due ...
... • Extinction of a species occurs when it ceases to exist; may follow environmental change - if the species does not evolve • Evolution and extinction are affected by: – large scale movements of continents – gradual climate changes due to continental drift or orbit changes – rapid climate changes due ...
Ecology EOC Review
... because they can contaminate groundwater and other water sources. –Biological magnification – concentrations of a harmful substance increase in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food web or a food chain. »Ex. algae pick up toxin from water they live in – plankton eat much algae to survive – sm ...
... because they can contaminate groundwater and other water sources. –Biological magnification – concentrations of a harmful substance increase in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food web or a food chain. »Ex. algae pick up toxin from water they live in – plankton eat much algae to survive – sm ...
Ecosystems: What are they?
... can be categorized into types based on light, depth, temperature, and salinity (Table 2.1). Earth as a whole is the largest scale ecosystem, called the biosphere. ...
... can be categorized into types based on light, depth, temperature, and salinity (Table 2.1). Earth as a whole is the largest scale ecosystem, called the biosphere. ...
The Zoo Can Come to You!
... Meet the Vertebrates - Explore the differences between the vertebrates. Animal Appreciation - Learn how to act around animals. Rainforests - Discover the amazing biodiversity that exists in the rainforests. Going, Going, Gone - More and more species are at risk do to human impact. How can you be par ...
... Meet the Vertebrates - Explore the differences between the vertebrates. Animal Appreciation - Learn how to act around animals. Rainforests - Discover the amazing biodiversity that exists in the rainforests. Going, Going, Gone - More and more species are at risk do to human impact. How can you be par ...
Presentation
... • 1. There is an upper and lower limit for any environmental factor • 2. Tolerance: ability of an organism to survive when subjected to biotic or abiotic factors ...
... • 1. There is an upper and lower limit for any environmental factor • 2. Tolerance: ability of an organism to survive when subjected to biotic or abiotic factors ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.