FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain
... “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured by the threshold to obtain some specific behavior (for instance, spatial orientation to a sound). Healthy subjects cycle during a 24-hour period from deep sleep with low arousal and very little ...
... “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured by the threshold to obtain some specific behavior (for instance, spatial orientation to a sound). Healthy subjects cycle during a 24-hour period from deep sleep with low arousal and very little ...
The Nervous System
... adrenaline (also called epinephrine) – prepares body for stressful situations ...
... adrenaline (also called epinephrine) – prepares body for stressful situations ...
CHAPTER 21 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM and SENSES
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
... The Tactile Corpuscles of Meissner are grouped on the skin of the fingertips, lips, and orifices of the body and the nipples. Only stimulated when touched, meissner corpuscles tells the brain the shape and feel of an object in the hand. They adjust constantly to the environment, which is why the br ...
Slide ()
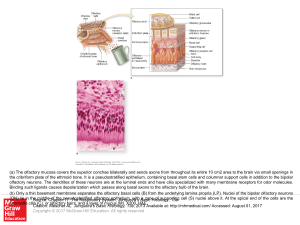
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
File
... LEARNING • Neurons are soft, flexible, living cells • They can change their size, shape, function and connections with other neurons • They are influenced by biological processes and environmental experiences ...
... LEARNING • Neurons are soft, flexible, living cells • They can change their size, shape, function and connections with other neurons • They are influenced by biological processes and environmental experiences ...
Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
The Brain
... • Superior- Helps you know where things are located in space (vision). • Inferior- Processes spatial info for the auditory system (hearing). Substantia nigra (black substance): Critical to control fine motor coordination. - Destruction of black substance causes Parkinson’s Disease. ...
... • Superior- Helps you know where things are located in space (vision). • Inferior- Processes spatial info for the auditory system (hearing). Substantia nigra (black substance): Critical to control fine motor coordination. - Destruction of black substance causes Parkinson’s Disease. ...
3a handout
... Unit 3a:The Nervous System and Biological Psychologists I. Work with the person sitting 3 people down from you (move to your left) to explain what happens in your nervous system in the following situations: a. You pull your hand away from a hot stove. ...
... Unit 3a:The Nervous System and Biological Psychologists I. Work with the person sitting 3 people down from you (move to your left) to explain what happens in your nervous system in the following situations: a. You pull your hand away from a hot stove. ...
Print › psych chapter 2 | Quizlet | Quizlet
... outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. ...
... outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. ...
The Biological Perspective - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... Synaptic Vesicles Neurotransmitters Synaptic Gap or Synapse Receptor Sites How do Neurotransmitters get across the synapse Video ...
... Synaptic Vesicles Neurotransmitters Synaptic Gap or Synapse Receptor Sites How do Neurotransmitters get across the synapse Video ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... • Because of the A- inside and Na+ outside, there is a voltage across the membrane • Inside is 70 mV more negative than outside ...
... • Because of the A- inside and Na+ outside, there is a voltage across the membrane • Inside is 70 mV more negative than outside ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... Earlier columns described how neurons are born and migrate to their final destination within the cerebral cortex. In the next stage of cortical development, axons and dendrites grow and form synapses. From birth to age 6 years, the child's brain grows dramatically (Fig. 1). This growth is not due to ...
... Earlier columns described how neurons are born and migrate to their final destination within the cerebral cortex. In the next stage of cortical development, axons and dendrites grow and form synapses. From birth to age 6 years, the child's brain grows dramatically (Fig. 1). This growth is not due to ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... thalamus—relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness -switchboard that sends incoming info where it needs to go in the brain hypothalamus—links the nervous and endocrine systems via the pituitary ...
... thalamus—relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness -switchboard that sends incoming info where it needs to go in the brain hypothalamus—links the nervous and endocrine systems via the pituitary ...
Nervous System
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
Alzheimer`s Disease review: targets for early intervention
... partially involved in excitotoxicity. NMDA are a class of glutamate-binding receptors that have been targeted for therapy. They are unique because their ion channels are blocked by Mg2+. Not only must glutamate bind to these receptors, but Mg2+ must be removed before positivelycharged ions can enter ...
... partially involved in excitotoxicity. NMDA are a class of glutamate-binding receptors that have been targeted for therapy. They are unique because their ion channels are blocked by Mg2+. Not only must glutamate bind to these receptors, but Mg2+ must be removed before positivelycharged ions can enter ...
C48 Nervous System
... connective tissue. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – nerves that communicate motor and sensory signals between CNS and rest of body. 2 classes of nervous system cells: Neurons – conduct messages, functional unit of nervous ...
... connective tissue. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – nerves that communicate motor and sensory signals between CNS and rest of body. 2 classes of nervous system cells: Neurons – conduct messages, functional unit of nervous ...
bioii ch10 ppt
... gastrointestinal tract, platelets and the central nervous system. This chemical is also known as the “happiness hormone”, because it arouses feelings of pleasure and well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with increased carbohydrate cravings, depression, sleep deprivations and hypersensi ...
... gastrointestinal tract, platelets and the central nervous system. This chemical is also known as the “happiness hormone”, because it arouses feelings of pleasure and well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with increased carbohydrate cravings, depression, sleep deprivations and hypersensi ...
FOUNDATION MODULE 2012 SELF ASSESMENT BCQs 6TH
... b. Beta-blockers block beta receptors causing decrease in heart rate*** ...
... b. Beta-blockers block beta receptors causing decrease in heart rate*** ...
6 - smw15.org
... • Taste and smell axons converge in the endopiriform cortex • Receptors for taste are modified skin cells • Taste receptors have excitable membranes that release neurotransmitters to excite neighboring neurons • Taste receptors are replaced every 10 to 14 days ...
... • Taste and smell axons converge in the endopiriform cortex • Receptors for taste are modified skin cells • Taste receptors have excitable membranes that release neurotransmitters to excite neighboring neurons • Taste receptors are replaced every 10 to 14 days ...
the central nervous system
... The brain carries out most of the functions for the body while the spinal cord acts more like a liaison between the body and the brain. Most information is brought to the brain by moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain a ...
... The brain carries out most of the functions for the body while the spinal cord acts more like a liaison between the body and the brain. Most information is brought to the brain by moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain a ...
Presentation - Stamm`s Lab
... anthelmintic used for pinworm treatment. It also significantly improves exon5 Vb inclusion. Pyrvinium pamoate has been known to bind DNA with intercalation, while it is unclear whether and how this compounds interacts with RNA. I am interested in understanding how this compound and other possible ca ...
... anthelmintic used for pinworm treatment. It also significantly improves exon5 Vb inclusion. Pyrvinium pamoate has been known to bind DNA with intercalation, while it is unclear whether and how this compounds interacts with RNA. I am interested in understanding how this compound and other possible ca ...
Phys Chapter 59 [4-20
... In these people, things that can increase the excitability enough to cause an attack include strong emotional stimuli, alkalosis from overbreathing, drugs, fever, and loud noises or flashing lights o Even in people not genetically predisposed, certain types of traumatic lesions in almost any part ...
... In these people, things that can increase the excitability enough to cause an attack include strong emotional stimuli, alkalosis from overbreathing, drugs, fever, and loud noises or flashing lights o Even in people not genetically predisposed, certain types of traumatic lesions in almost any part ...
Document
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
... Nucleus raphe magnus neurons release serotonin at their nerve endings. Neurons with cell bodies located within the spinal cord that are stimulated by input from nucleus raphe magnus neurons release -endorphin at their nerve endings. d. All of the above are true. 10. Massaging the skin or applicatio ...
The nervous system
... The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are cellular extensions with many branches, and metaphorically this o ...
... The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are cellular extensions with many branches, and metaphorically this o ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.