solutions - Berkeley MCB
... This is where the retinal ganglion cell axons leave the retina and therefore there are no photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. la ...
... This is where the retinal ganglion cell axons leave the retina and therefore there are no photoreceptors (and thus no response to light) at this location. 3) The fovea allows for increase visual acuity by which of the following specializations: a. high ratio of photoreceptors to ganglion cells b. la ...
Brain Function and Organization via Imaging
... boutons and dendrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters: released across synapse by arrival of action potential. Received by post-synaptic dendrites. ...
... boutons and dendrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters: released across synapse by arrival of action potential. Received by post-synaptic dendrites. ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... Neurotransmitters (p.55-58): Discuss the impact of different neurotransmitters on our body and behavior. ...
... Neurotransmitters (p.55-58): Discuss the impact of different neurotransmitters on our body and behavior. ...
Topic: Nervous system Reading: Chapter 38 Main concepts
... • There may be over 1000 different olfactory receptor proteins in in the receptors cells. • Pain • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medic ...
... • There may be over 1000 different olfactory receptor proteins in in the receptors cells. • Pain • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medic ...
Nervous System
... LOBES OF THE BRAIN FRONTAL LOBE: In charge of speech, movement, emotions, problem solving, memory OCCIPITAL LOBE: In charge of vision PARIETAL LOBE: In charge of touch, temperature and pain TEMPORAL LOBE: In charge of hearing ...
... LOBES OF THE BRAIN FRONTAL LOBE: In charge of speech, movement, emotions, problem solving, memory OCCIPITAL LOBE: In charge of vision PARIETAL LOBE: In charge of touch, temperature and pain TEMPORAL LOBE: In charge of hearing ...
Lecture 3. Hormone action - receptors
... Cell membrane is impermeable to the majority of ions: ion movement through transmembrane protein “tunnels” (ion channels) ...
... Cell membrane is impermeable to the majority of ions: ion movement through transmembrane protein “tunnels” (ion channels) ...
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body - Nicole
... which sends the impulse directly to salivary glands beneath the tongue. Ex2) palmar reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s hand, the hand will automatically grasp in response Ex3)rooting reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s cheek, the baby will turn its head towards the touch ...
... which sends the impulse directly to salivary glands beneath the tongue. Ex2) palmar reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s hand, the hand will automatically grasp in response Ex3)rooting reflex – if you touch a newborn baby’s cheek, the baby will turn its head towards the touch ...
A synaptic memory trace for cortical receptive field plasticity
... learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordination across diverse brain regions, including the activation of subcortical neuromodulator sy ...
... learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordination across diverse brain regions, including the activation of subcortical neuromodulator sy ...
PGRx: An Interactive Software System for Integrating Clinical
... Costs of Adverse Drug Responses (ADR) According to a survey published in the Journal of American Pharmacists Association in 2001, the cost of drug-related mortality and morbidity in the US was estimated at over $175 billion in 2000. ADRs represents approximately 10% of all health care costs in ...
... Costs of Adverse Drug Responses (ADR) According to a survey published in the Journal of American Pharmacists Association in 2001, the cost of drug-related mortality and morbidity in the US was estimated at over $175 billion in 2000. ADRs represents approximately 10% of all health care costs in ...
Monoclonal Antibody To Human GPR50
... G-Protein Coupled Receptor 50; Melatonin-related Receptor; H9; UniProt: Q13585 GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unkn ...
... G-Protein Coupled Receptor 50; Melatonin-related Receptor; H9; UniProt: Q13585 GPR50 or melatonin-related receptor is a 617 amino acid protein that belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, containing one disulfide bond. GPR50 does not bind melatonin and its endogenous ligand is still unkn ...
How the Brain Works And Why it Probably Doesn`t Work this way!
... • Because most pathways in the human CNS are myelinated, MS can involve different pathways in different patients; while patients may show very individual patterns of demyelination (and therefore different signs/symptoms), there are some sites that appear to be more commonly affected; for example, th ...
... • Because most pathways in the human CNS are myelinated, MS can involve different pathways in different patients; while patients may show very individual patterns of demyelination (and therefore different signs/symptoms), there are some sites that appear to be more commonly affected; for example, th ...
MARCH 2017 PBAC MEETING – ITEMS AWAITING TGA
... The PBAC recommendation cannot be made public until the TGA outcome is known. ...
... The PBAC recommendation cannot be made public until the TGA outcome is known. ...
Intro-biological
... of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning such as thought, and the cerebellum which maintains coordination. The brain stem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body' ...
... of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning such as thought, and the cerebellum which maintains coordination. The brain stem includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla, and controls lower level functioning such as respiration and digestion. The spinal cord connects the brain and the body' ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the limbic system). The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum. The hindbrain is made of the cerebellum, pons and ...
... The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the limbic system). The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum. The hindbrain is made of the cerebellum, pons and ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... brain could lose neurons, but not grow new ones. But new studies showed that the hippocampus, a brain structure that plays a vital role in forming new memories, has the ability to generate new neurons throughout the lifespan. Studies since this discovery have shown that stress, exercise, environment ...
... brain could lose neurons, but not grow new ones. But new studies showed that the hippocampus, a brain structure that plays a vital role in forming new memories, has the ability to generate new neurons throughout the lifespan. Studies since this discovery have shown that stress, exercise, environment ...
Neuron-target interaction 1. Synapse formation between presynaptic
... leads to cell death. Target cells secrete a variety of neurotrophic factors. Neurotrophins Cytokines such as CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) ...
... leads to cell death. Target cells secrete a variety of neurotrophic factors. Neurotrophins Cytokines such as CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on the basilar membrane in the cochlea transduce movements along the basilar membrane into neural signa ...
... When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on the basilar membrane in the cochlea transduce movements along the basilar membrane into neural signa ...
Welcome to Biochemistry/Endocrinology
... Redrawn based on figure from Alberts, B., et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed. New York: Garland Science, 2002. Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 7e edited by Thomas M. Devlin © 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc . ...
... Redrawn based on figure from Alberts, B., et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed. New York: Garland Science, 2002. Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 7e edited by Thomas M. Devlin © 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Inc . ...
Exercise 3 key
... amino group transfer from alanine to ketoglutarate to form Glutamate and pyruvate. YOl.ftext on pg 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). ...
... amino group transfer from alanine to ketoglutarate to form Glutamate and pyruvate. YOl.ftext on pg 721 shows the mechanism for stage I of this reaction; the transformation of the amino acid to the keto acid (we also did this in lecture). ...
Slide ()
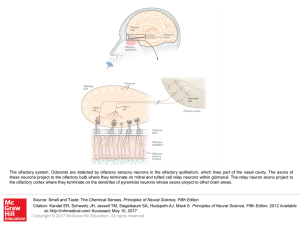
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Cell Communication
... the a-adrenergic receptor. The Kd for binding of epinephrine to this receptor is ~0.6 mM. Which of the following compounds might be good candidate drugs for high blood pressure? Kd for binding to the a-adrenergic ...
... the a-adrenergic receptor. The Kd for binding of epinephrine to this receptor is ~0.6 mM. Which of the following compounds might be good candidate drugs for high blood pressure? Kd for binding to the a-adrenergic ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.