Drosophila melanogaster
... Drosophila counterpart of NMU and its receptor signaling modulate post-mating food preference decisions in female. To investigate molecular and neural mechanisms underlying the post-mating food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8 ...
... Drosophila counterpart of NMU and its receptor signaling modulate post-mating food preference decisions in female. To investigate molecular and neural mechanisms underlying the post-mating food preference switch, we manipulated activities of neurons producing hugin peptides or its two receptors, CG8 ...
Advances in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
... Progress in the clinical management of erectile disorders, and specifically erectile dysfunction (ED), has gained substantially from basic science advances in the field. Unquestionably, the advance of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor therapy quickly followed the basic scientific description of n ...
... Progress in the clinical management of erectile disorders, and specifically erectile dysfunction (ED), has gained substantially from basic science advances in the field. Unquestionably, the advance of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitor therapy quickly followed the basic scientific description of n ...
9/7/2012 1 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me
... • Impulse travels to dorsal horn to block afferent sensory fibers ...
... • Impulse travels to dorsal horn to block afferent sensory fibers ...
Nervous System
... • Largest amount of serotonin is found in the intestinal mucosa. • Although the CNS contains less than 2% of the total serotonin in the body, serotonin plays a very important role in a range of brain functions. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. ...
... • Largest amount of serotonin is found in the intestinal mucosa. • Although the CNS contains less than 2% of the total serotonin in the body, serotonin plays a very important role in a range of brain functions. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. ...
21-1
... temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. ...
... temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 degrees F. ...
Nervous System
... • Largest amount of serotonin is found in the intestinal mucosa. • Although the CNS contains less than 2% of the total serotonin in the body, serotonin plays a very important role in a range of brain functions. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. ...
... • Largest amount of serotonin is found in the intestinal mucosa. • Although the CNS contains less than 2% of the total serotonin in the body, serotonin plays a very important role in a range of brain functions. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. ...
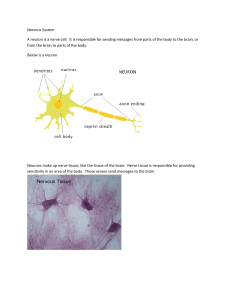
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... The Nervous system is responsible for sensing everything we sense and all the things that make our body work properly and protect us from our environment. The nervous system is why we can tell hot and cold, hard or soft, see, talk, cry etc. Below is a very rough picture of the nervous system. In rea ...
... The Nervous system is responsible for sensing everything we sense and all the things that make our body work properly and protect us from our environment. The nervous system is why we can tell hot and cold, hard or soft, see, talk, cry etc. Below is a very rough picture of the nervous system. In rea ...
Tinkering with the Biochemistry of Life: Viruses, Prions, and Peptide
... 1. Exhibits Watson-Crick base pairing and forms double helices with other PNA, DNA, and RNA 2. Binds more strongly to DNA and RNA 3. Is not easily recognized by proteases and nucleases ...
... 1. Exhibits Watson-Crick base pairing and forms double helices with other PNA, DNA, and RNA 2. Binds more strongly to DNA and RNA 3. Is not easily recognized by proteases and nucleases ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
A. Sensation
... 1. ability to recognize specific information about a touch sensation plus the shape, size, and texture and to make two-point discrimination b. stereognosis 1. ability to recognize by feel the size, shape and texture of an object ...
... 1. ability to recognize specific information about a touch sensation plus the shape, size, and texture and to make two-point discrimination b. stereognosis 1. ability to recognize by feel the size, shape and texture of an object ...
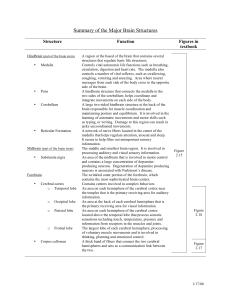
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... Processes and distributes almost all of the sensory and motor information going to and from the cerebral cortex. It is thought to be involved in regulating levels of awareness, attention, motivation and emotional aspects of sensation. A peanut-sized structure that regulates behavior important for su ...
... Processes and distributes almost all of the sensory and motor information going to and from the cerebral cortex. It is thought to be involved in regulating levels of awareness, attention, motivation and emotional aspects of sensation. A peanut-sized structure that regulates behavior important for su ...
Epilepsy & Membrane Potentials
... channels (K+, Ca2+, Na+) on receptor membrane = Graded Receptor Potential ...
... channels (K+, Ca2+, Na+) on receptor membrane = Graded Receptor Potential ...
Pasko Rakic`s Autobiography
... channels on the surface of migrating neurons and radial glial cells that contribute jointly to cell orientation, recognition of migratory pathways through differential cell adhesion and also regulate the rate of their nuclear movement by controlling the dynamics of cytoskeletal proteins. We found t ...
... channels on the surface of migrating neurons and radial glial cells that contribute jointly to cell orientation, recognition of migratory pathways through differential cell adhesion and also regulate the rate of their nuclear movement by controlling the dynamics of cytoskeletal proteins. We found t ...
Quiz - psychm5
... ____ 17. Ellie had a right hemisphere stroke. During her rehabilitation period, her family and the hospital staff noticed that she placed all articles on the right side of the dresser and did not notice an article if it were placed on the left side until it was brought to her attention. Even when ea ...
... ____ 17. Ellie had a right hemisphere stroke. During her rehabilitation period, her family and the hospital staff noticed that she placed all articles on the right side of the dresser and did not notice an article if it were placed on the left side until it was brought to her attention. Even when ea ...
Nervous System Chap49
... 33. These neurons control the timing of sleep periods characterized by rapid eye movements (REMs) and by vivid dreams. 34. Sleep is essential and may play a role in the consolidation of learning and memory 35. Emotions: Limbic System 36. Generation and experience of emotions involve many brain struc ...
... 33. These neurons control the timing of sleep periods characterized by rapid eye movements (REMs) and by vivid dreams. 34. Sleep is essential and may play a role in the consolidation of learning and memory 35. Emotions: Limbic System 36. Generation and experience of emotions involve many brain struc ...
An Introduction to Neuroscience
... MIT open courseware: 901 An Introduction to Neuroscience http://ocw.mit.edu Belmonte and Thoroughman Introduction to Neuroscience ...
... MIT open courseware: 901 An Introduction to Neuroscience http://ocw.mit.edu Belmonte and Thoroughman Introduction to Neuroscience ...
Psychology 312: Essay Questions Test 1 G9 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Describe in detail two methods for determining the absolute threshold. Why do we see light, as opposed to other forms of electromagnetic radiation? Give at least two reasons. These reasons may include th ...
... -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Describe in detail two methods for determining the absolute threshold. Why do we see light, as opposed to other forms of electromagnetic radiation? Give at least two reasons. These reasons may include th ...
Nervous Systems
... In mammals, circadian rhythms are coordinated by a group of neurons in the hypothalamus called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. o The SCN acts as a pacemaker, synchronizing the biological clock in cells throughout the body to the natural cycles of day length. o By surgically removing the SCN from ...
... In mammals, circadian rhythms are coordinated by a group of neurons in the hypothalamus called the suprachiasmatic nucleus or SCN. o The SCN acts as a pacemaker, synchronizing the biological clock in cells throughout the body to the natural cycles of day length. o By surgically removing the SCN from ...
... • These vesicles move to and fuse with the membrane at surface of the axon terminal. The neurotransmitters within the vesicles are then released (by exocytosis) into the synaptic cleft. • The neurotransmitter then diffuses across the cleft and binds to receptor molecules on the dendrites of the next ...
Teacher Resource - Dale - American Physiological Society
... To improve the quality of astronauts' sleep, neuroscientist George C. Brainard, PhD, is researching the effects of space flight on circadian rhythms (podcast with lessons and more). ...
... To improve the quality of astronauts' sleep, neuroscientist George C. Brainard, PhD, is researching the effects of space flight on circadian rhythms (podcast with lessons and more). ...
Neurons
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
... information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks called SYNAPTIC VESICLES Vesicles fuse together with the membrane and spill contents into the synaptic gap They may bind to certain areas at various receptor sites ...
All rights reserved. AP Biology Interaction among Living Systems
... C. A is a coenzyme or cofactor; B is an inhibitor D. A is a regulatory protein that promotes the enzyme's synthesis; B is a regulatory protein that inhibits the enzyme's synthesis. 16. A researcher investigating bluegill sunfish observes that Daphnia, which are crustaceans, make up a large part of ...
... C. A is a coenzyme or cofactor; B is an inhibitor D. A is a regulatory protein that promotes the enzyme's synthesis; B is a regulatory protein that inhibits the enzyme's synthesis. 16. A researcher investigating bluegill sunfish observes that Daphnia, which are crustaceans, make up a large part of ...
Previously in Cell Bio
... gains access to cytosol how can the information be transmitted? Extracellular domain ...
... gains access to cytosol how can the information be transmitted? Extracellular domain ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.