Guidelines for the Analysis of Twentieth
... A. Many 20th-Century pieces set up their own formal worlds and categories. Be sensitive to structural repetition, but do not expect pieces to fit into the formal norms of traditional tonal music. B. 20th-century composers often tend to avoid the literal restatement of material—to emphasize continual ...
... A. Many 20th-Century pieces set up their own formal worlds and categories. Be sensitive to structural repetition, but do not expect pieces to fit into the formal norms of traditional tonal music. B. 20th-century composers often tend to avoid the literal restatement of material—to emphasize continual ...
Artemis 3-19 Notes
... the form determines when musical themes are heard and how they are developed throughout the piece. There are simple forms – popular music often uses a verse/chorus/verse/chorus pattern – and complex forms – a Mozart symphony uses a sophisticated system of exposition, development, and recapitulation, ...
... the form determines when musical themes are heard and how they are developed throughout the piece. There are simple forms – popular music often uses a verse/chorus/verse/chorus pattern – and complex forms – a Mozart symphony uses a sophisticated system of exposition, development, and recapitulation, ...
An orchestra may be arranged differently, depending on the music
... Kettledrum: A large metal bowl, usually made out of copper or brass, with a parchment stretched across the top that can be tightened or loosened (with a foot pedal) to create different pitches when hit with a drumstick. A set of kettledrums (also known as timpani) is usually played by one person. Th ...
... Kettledrum: A large metal bowl, usually made out of copper or brass, with a parchment stretched across the top that can be tightened or loosened (with a foot pedal) to create different pitches when hit with a drumstick. A set of kettledrums (also known as timpani) is usually played by one person. Th ...
Thursday March 7, 2013, 8:00 pm Kulas Recital Hall Concert No
... 2012. It consists of 7 short movements. The piece uses a Chinese scale: A, B, C-sharp, E and F-sharp. I used only these five notes during the whole piece (except the last “out of scale” long note D natural in the violin part), but each note itself can be in many variants (nature, sharp, flat, double ...
... 2012. It consists of 7 short movements. The piece uses a Chinese scale: A, B, C-sharp, E and F-sharp. I used only these five notes during the whole piece (except the last “out of scale” long note D natural in the violin part), but each note itself can be in many variants (nature, sharp, flat, double ...
indian raga - Life Learning Cloud
... The notes in a Rag vary – some have 5 notes like a pentatonic scale whilst others have 7 or 8 notes ...
... The notes in a Rag vary – some have 5 notes like a pentatonic scale whilst others have 7 or 8 notes ...
Unit A: Instrumental Techniques
... the rhythmic values of the following notes and rests: whole, half, quarter, eighth, and dotted quarter, dotted half, sixteenth, dotted 8th, triplet (eighth and quarter), syncopation and tied rhythms. B. Correctly identify the names of lines and spaces in a clef relative to their instrument. C. Ident ...
... the rhythmic values of the following notes and rests: whole, half, quarter, eighth, and dotted quarter, dotted half, sixteenth, dotted 8th, triplet (eighth and quarter), syncopation and tied rhythms. B. Correctly identify the names of lines and spaces in a clef relative to their instrument. C. Ident ...
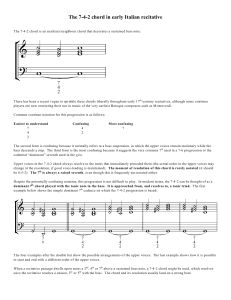
The 7-4-2 chord in early Italian recitative
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
... The second form is confusing because it normally refers to a bass suspension, in which the upper voices remain stationary while the bass descends a step. The third form is the most confusing because it suggests the very common 7 th used in a 7-6 progression or the cadential “dominant” seventh used i ...
20th Century Music Week
... Debussy has often been described as an ‘Impressionist’ composer due to the similarities which his music had (blurred/hazy lines, no clear centre or focus) with the Impressionist artists and movement. ...
... Debussy has often been described as an ‘Impressionist’ composer due to the similarities which his music had (blurred/hazy lines, no clear centre or focus) with the Impressionist artists and movement. ...
Students can
... articulation for a variety of musical styles b) Finger/Slide technique exercises in semiquaver patterns using varying articulations ...
... articulation for a variety of musical styles b) Finger/Slide technique exercises in semiquaver patterns using varying articulations ...
Helen Jane Long
... Worked for the children’s shows “Blue Peter” and “Live and kicking” Worked with many composers Served as a music score assistant for composer Howard Shore on the trilogy: The Lord of the ...
... Worked for the children’s shows “Blue Peter” and “Live and kicking” Worked with many composers Served as a music score assistant for composer Howard Shore on the trilogy: The Lord of the ...
Akrotiri Music Curriculum Overview 2016 2017
... to devise non-standard and recognise and use standard symbols to indicate when to play and rest (rhythmic notation) to recognise a semibreve and quavers (WOPPS) (as well as crotchets, minim and crotchet rests to use and apply the terms duration (beat/rhythm), pitch, texture, structure, dynamics and ...
... to devise non-standard and recognise and use standard symbols to indicate when to play and rest (rhythmic notation) to recognise a semibreve and quavers (WOPPS) (as well as crotchets, minim and crotchet rests to use and apply the terms duration (beat/rhythm), pitch, texture, structure, dynamics and ...
Notations used in Sound/Path/Field
... notation, but impressionistically, not necessarily exactly. In such notations, vertical space from bottom to top indicates pitch from low to high. On the next page is an example from the string score, the section called "Side to side resound" starting at 1:23. The header for the section is given, bu ...
... notation, but impressionistically, not necessarily exactly. In such notations, vertical space from bottom to top indicates pitch from low to high. On the next page is an example from the string score, the section called "Side to side resound" starting at 1:23. The header for the section is given, bu ...
Brass Long term Plan
... Play at a reliable mf (without overblowing) Singing - songs - aural skills ...
... Play at a reliable mf (without overblowing) Singing - songs - aural skills ...
presentation
... Harmony should consist of chords that fit with the current melody note Harmony usually split into four voices, each with distinct vocal ranges: soprano, alto, tenor, and bass The “leading tone” (ti, or 7) must resolve to 1/do in the soprano ...
... Harmony should consist of chords that fit with the current melody note Harmony usually split into four voices, each with distinct vocal ranges: soprano, alto, tenor, and bass The “leading tone” (ti, or 7) must resolve to 1/do in the soprano ...
Texture and Melody
... ! A passing note is a notes in a melody that connects two notes that are part of the harmony ! For example, in a melody you might have C followed by E; these two notes are recognisable ...
... ! A passing note is a notes in a melody that connects two notes that are part of the harmony ! For example, in a melody you might have C followed by E; these two notes are recognisable ...
http://circle.adventist.org/files/download/Glossary_Musical_Terms.pdf
... brace a bracket connecting two or more staffs in a musical score. brass instruments a group of wind instruments made of brass and other metals and played by blowing through a cup-shaped or funnel-shaped mouthpiece; the chief brass instruments of the orchestra are the trumpet, trombone, French horn, ...
... brace a bracket connecting two or more staffs in a musical score. brass instruments a group of wind instruments made of brass and other metals and played by blowing through a cup-shaped or funnel-shaped mouthpiece; the chief brass instruments of the orchestra are the trumpet, trombone, French horn, ...
doc - Philharmonia Orchestra
... culture. There’s a passage around about Figure 12 that he gives the vibraphone along with the other keyboard instruments – example – so the same pattern repeated several times across the beat, across the bar, as if there is no particular pulse, just repeated sounds. It’s not just in repeated rhythmi ...
... culture. There’s a passage around about Figure 12 that he gives the vibraphone along with the other keyboard instruments – example – so the same pattern repeated several times across the beat, across the bar, as if there is no particular pulse, just repeated sounds. It’s not just in repeated rhythmi ...
A CONTOUR-BASED JAZZ WALKING BASS GENERATOR
... the walking bass technique, there are several other aspects regarding the notes, rhythm and articulations that have an important role in a good performance. These aspects, here referred to as ornaments, are little nuances and additions to the phrases that dont change nor define the main contents of ...
... the walking bass technique, there are several other aspects regarding the notes, rhythm and articulations that have an important role in a good performance. These aspects, here referred to as ornaments, are little nuances and additions to the phrases that dont change nor define the main contents of ...
Basic Music Theory
... scale. The notes in the chromatic A scale are A, A# (Bb), B, C, C#(Db), D, D# (Eb), E, F, F# (Gb), G, and G# (Ab). Most of the music we play is based on the major scale, which consists of only 7 notes out of the chromatic scale (the 8th note shown below is the same as the first note, which is an "oc ...
... scale. The notes in the chromatic A scale are A, A# (Bb), B, C, C#(Db), D, D# (Eb), E, F, F# (Gb), G, and G# (Ab). Most of the music we play is based on the major scale, which consists of only 7 notes out of the chromatic scale (the 8th note shown below is the same as the first note, which is an "oc ...
Absolute music. Music that makes no intentional reference to a non
... melody in one "voice," all subsequent "voices" must imitate that melody exactly (note for note), or with only minimal adjustments. The melody must be composed so that it sounds "correct" when played "against" itself. The imitations may begin on the same pitch, or on another pitch (in which case all ...
... melody in one "voice," all subsequent "voices" must imitate that melody exactly (note for note), or with only minimal adjustments. The melody must be composed so that it sounds "correct" when played "against" itself. The imitations may begin on the same pitch, or on another pitch (in which case all ...
Theory of Music Grade 1 - Trinity College London
... Section 1 (20 marks) Put a tick (P ) in the box next to the correct answer. ...
... Section 1 (20 marks) Put a tick (P ) in the box next to the correct answer. ...
Elements of Music Worksheet Name: August 9th, 2011 Fine Arts List
... 40. A _______________ is an apparatus which produces ticking sounds or flashes of light at any desired musical speed. The metronome setting indicates the exact number of beats per minute. 41. After hearing a piece of music, we usually remember its ___________ best 42. Melody is: 43. A ______________ ...
... 40. A _______________ is an apparatus which produces ticking sounds or flashes of light at any desired musical speed. The metronome setting indicates the exact number of beats per minute. 41. After hearing a piece of music, we usually remember its ___________ best 42. Melody is: 43. A ______________ ...
Choral_Music_Glossary
... Melisma – a sequence where the pitches change, but the vowel sound stays the same; also known as a “run” Melody – the main musical theme in a musical piece or song Meter – tells you how to count the music; defines rhythmic structure Metronome marking – the number of beats per minute ...
... Melisma – a sequence where the pitches change, but the vowel sound stays the same; also known as a “run” Melody – the main musical theme in a musical piece or song Meter – tells you how to count the music; defines rhythmic structure Metronome marking – the number of beats per minute ...
Polyrhythm

Polyrhythm is the simultaneous use of two or more conflicting rhythms, that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic conflict may be the basis of an entire piece of music (cross-rhythm), or a momentary disruption. Polyrhythms can be distinguished from irrational rhythms, which can occur within the context of a single part; polyrhythms require at least two rhythms to be played concurrently, one of which is typically an irrational rhythm.