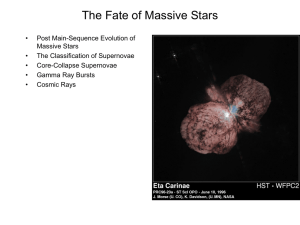
Lecture L24 ASTB21
... radiation pressure of a star and g is the attractive force due to the star's gravitation. If p > g, a microbe that has drifted into space will move away from the star; if p < g, the microbe will fall toward the star. For a microbe to escape into interstellar space from the vicinity of a star like th ...
... radiation pressure of a star and g is the attractive force due to the star's gravitation. If p > g, a microbe that has drifted into space will move away from the star; if p < g, the microbe will fall toward the star. For a microbe to escape into interstellar space from the vicinity of a star like th ...
STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) The basics: GRAVITY vs. PRESSURE
... This may fragment further, so have multiple stages of fragmentation (see Fig. 19.4). 3. Fragmentation ceases—center of fragment dense enough to become opaque to its own radiation, so it heats up, slowing the collapse. (Previously it was transparent and so could stay cool because radiation escaped ea ...
... This may fragment further, so have multiple stages of fragmentation (see Fig. 19.4). 3. Fragmentation ceases—center of fragment dense enough to become opaque to its own radiation, so it heats up, slowing the collapse. (Previously it was transparent and so could stay cool because radiation escaped ea ...
Test - Hampton Science 8A 8B 8C 8D 8E Stars are classified on the
... Stars are classified on the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram according to their absolute magnitude and their surface temperatures at a given time in a star’s life cycle. What classification would a star have if it was very hot and very bright? ...
... Stars are classified on the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram according to their absolute magnitude and their surface temperatures at a given time in a star’s life cycle. What classification would a star have if it was very hot and very bright? ...
ASTR101 Unit 14 Assessment Answer Key 1. It is believed that the
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
... paradox. If other technological civilizations exist, they would tend to spread out and colonize the galaxy. It is estimated that this would take about a million years, a negligible fraction of the age of the galaxy. Since the galaxy does not seem to be colonized, Fermi argued that other technologica ...
Document
... • Aristotle observes that during lunar eclipses the Earth’s shadow on the moon is curved • He assumes it will be curved for all eclipses • A hypothesis that explains this: the earth is round • A prediction of this theory is that the location of the stars in the sky should be different for observers ...
... • Aristotle observes that during lunar eclipses the Earth’s shadow on the moon is curved • He assumes it will be curved for all eclipses • A hypothesis that explains this: the earth is round • A prediction of this theory is that the location of the stars in the sky should be different for observers ...
Two Summers in the UCSC Science Internship Program
... stars are unusual: Stars are known to form in clusters, so it is rare to find a young, recently formed star in isolation. This anomalous behavior makes field stars an exciting and hotly debated subject. One theory proposes that field stars do, in fact, form by themselves; another claims that field s ...
... stars are unusual: Stars are known to form in clusters, so it is rare to find a young, recently formed star in isolation. This anomalous behavior makes field stars an exciting and hotly debated subject. One theory proposes that field stars do, in fact, form by themselves; another claims that field s ...
Shocking Truth about Massive Stars Lidia Oskinova Chandra’s First Decade of Discovery
... Only three WO stars are known in the MW WO is the latest possible evolutionary stage of massive star Core−collapse within 10 000 yr ...
... Only three WO stars are known in the MW WO is the latest possible evolutionary stage of massive star Core−collapse within 10 000 yr ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... (Volume x Luminosity) and Distance from Observer. Betelgeuse, one of the brightest stars in the Universe, does not appear to be as bright as our Sun, because of its ...
... (Volume x Luminosity) and Distance from Observer. Betelgeuse, one of the brightest stars in the Universe, does not appear to be as bright as our Sun, because of its ...
Constellation Part II readingConstellation Part II reading(es)
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
Stellar variability and microvariability II. Spot maps and modelling
... COROT will provide us with an unprecedented view of solar-like activity in late-type MS stars; For at least 40-50 solar analogues and a few hundreds F5V-M0V stars/field, we expect to obtain: • AR evolution time scales and contrast properties; • preferential longitude for AR formation (if any); • sur ...
... COROT will provide us with an unprecedented view of solar-like activity in late-type MS stars; For at least 40-50 solar analogues and a few hundreds F5V-M0V stars/field, we expect to obtain: • AR evolution time scales and contrast properties; • preferential longitude for AR formation (if any); • sur ...
Open clusters
... Open clusters are one of the most common types of multiple star systems. Open clusters usually contain thousands of stars that all formed at about the same time and are all orbit around each other. The average density in an open cluster is 500 times greater than the density of where we are. Imagine ...
... Open clusters are one of the most common types of multiple star systems. Open clusters usually contain thousands of stars that all formed at about the same time and are all orbit around each other. The average density in an open cluster is 500 times greater than the density of where we are. Imagine ...
Blowing Bubbles in Space: The Birth and Death of Practically
... • Planetary nebulae are the final stages in the lives of low-mass stars, such as our Sun. As they reach the ends of their lives, their late RGB superwinds send off large amounts of material into space. Although the nebulae can look like a fireworks display, the process of developing a nebula is (usu ...
... • Planetary nebulae are the final stages in the lives of low-mass stars, such as our Sun. As they reach the ends of their lives, their late RGB superwinds send off large amounts of material into space. Although the nebulae can look like a fireworks display, the process of developing a nebula is (usu ...
22 September: Starlight
... Types of stars, important terms Main Sequence (luminosity class V) Giants (luminosity class III) Supergiants (luminosity class I) White dwarfs What does it all mean? ...
... Types of stars, important terms Main Sequence (luminosity class V) Giants (luminosity class III) Supergiants (luminosity class I) White dwarfs What does it all mean? ...
File
... • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This will continue to shine for billions of years. ...
... • For stars that are part of a binary system or star cluster- NO (on next slide) • The white dwarf is the dense core left behind from the previous red giant. • 1 tsp. of white dwarf matter would have a mass of several tons. • This will continue to shine for billions of years. ...
Unit 1 Cutouts
... 4(B) research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy, including Ptolemy, Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, Neawton, Einstein, and Hubble, and the contribution of women astronaomers, including Maria Mitchell and Henrietta Swan Leavitt; ...
... 4(B) research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy, including Ptolemy, Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, Neawton, Einstein, and Hubble, and the contribution of women astronaomers, including Maria Mitchell and Henrietta Swan Leavitt; ...