The HR Diagram and Stars Worksheet
... a. Page 622 – Add the Spectral Class below the temperatures. b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 62 ...
... a. Page 622 – Add the Spectral Class below the temperatures. b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 62 ...
Our Sun - STEMpire Central
... a) black dwarf b) red dwarf c) white dwarf d) blue dwarf 3. These objects are bigger than most planets, but just barely too small to ignite nuclear fusion. Don’t be rude and call them “failed stars”! a) black dwarf b) overachieving planets c) brown dwarf d) red supergiants ...
... a) black dwarf b) red dwarf c) white dwarf d) blue dwarf 3. These objects are bigger than most planets, but just barely too small to ignite nuclear fusion. Don’t be rude and call them “failed stars”! a) black dwarf b) overachieving planets c) brown dwarf d) red supergiants ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... 15. A white dwarf star is the dead, remnant core of a star like the Sun at the end of its life. 16. It’s something that might weight as much as half the mass of the Sun but it’s only about the size of the Earth, so it’s an incredibly dense object. It’s dead, there is no nuclear fusion going on any m ...
... 15. A white dwarf star is the dead, remnant core of a star like the Sun at the end of its life. 16. It’s something that might weight as much as half the mass of the Sun but it’s only about the size of the Earth, so it’s an incredibly dense object. It’s dead, there is no nuclear fusion going on any m ...
Chapter 11 Review
... following types of stars. (i) white dwarfs (ii) red giants (iii) supergiants (b) Why is it more difficult to describe the position of a main sequence star than the ones above on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? ...
... following types of stars. (i) white dwarfs (ii) red giants (iii) supergiants (b) Why is it more difficult to describe the position of a main sequence star than the ones above on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram? ...
View the presentation slides
... This means that we can measure the mass of the planet by measuring the speed of the star. The Sun is much heavier than the planets: MJ/MS = 0.001 and ME/MS = 0.000003 (3×10-6) This means that the Sun’s speed is quite small: 12.5 m/s due to Jupiter and 8.4 cm/s due to the Earth. These speeds can be m ...
... This means that we can measure the mass of the planet by measuring the speed of the star. The Sun is much heavier than the planets: MJ/MS = 0.001 and ME/MS = 0.000003 (3×10-6) This means that the Sun’s speed is quite small: 12.5 m/s due to Jupiter and 8.4 cm/s due to the Earth. These speeds can be m ...
Standard Set 2 - Atascadero High School
... different type of fusion is necessary to form elements heavier than iron. This type can be carried out only by adding neutrons to a preexisting heavy element that forms a “seed.” Neutrons are available only during a limited portion of a star’s lifetime, particularly during the brief supernova that o ...
... different type of fusion is necessary to form elements heavier than iron. This type can be carried out only by adding neutrons to a preexisting heavy element that forms a “seed.” Neutrons are available only during a limited portion of a star’s lifetime, particularly during the brief supernova that o ...
The basic premise of the Nebular Model or Theory is that planets var
... was a result of this composition and their size. Use the information on page 166, 476-477 and 486 of the textbook or the chapter notes package to explain why the planets are classified as terrestrial (inner) and Jovian (outer). Nebular Theory ...
... was a result of this composition and their size. Use the information on page 166, 476-477 and 486 of the textbook or the chapter notes package to explain why the planets are classified as terrestrial (inner) and Jovian (outer). Nebular Theory ...
Search for Other Worlds - Science fiction 20 years
... light from a star so that nearby objects, which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare, can be observed. In the past coronagraphs have been developed to view the corona of the Sun, but a new version of similar instruments are being used to find extrasolar planets around nearby stars. C ...
... light from a star so that nearby objects, which otherwise would be hidden in the star's bright glare, can be observed. In the past coronagraphs have been developed to view the corona of the Sun, but a new version of similar instruments are being used to find extrasolar planets around nearby stars. C ...
document
... The Discovery of a Nova A nova, a star’s death, was witnessed in the constellation of Cassiopeia in 1572. Tycho observed the star from different locales on Earth. Discovered that the stars did not change position depending the location on Earth. Result: Stars too far away for stellar parallax ...
... The Discovery of a Nova A nova, a star’s death, was witnessed in the constellation of Cassiopeia in 1572. Tycho observed the star from different locales on Earth. Discovered that the stars did not change position depending the location on Earth. Result: Stars too far away for stellar parallax ...
Name: ______________________________# __________ Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2
... 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
... 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
STARS
... • These are stars thirty times bigger than our Sun. • Small, very dense object with an extremely strong gravitational pull. • Nothing can escape from it; not even light. ...
... • These are stars thirty times bigger than our Sun. • Small, very dense object with an extremely strong gravitational pull. • Nothing can escape from it; not even light. ...
doc
... So far all we know about stars’ lives is that they are formed within interstellar clouds by contraction under self-gravity, contract until they are hot enough in their cores to burn nuclear fuel, and that the lowest-mass stars live longest. Next we summarize the stages of a star’s life after it begi ...
... So far all we know about stars’ lives is that they are formed within interstellar clouds by contraction under self-gravity, contract until they are hot enough in their cores to burn nuclear fuel, and that the lowest-mass stars live longest. Next we summarize the stages of a star’s life after it begi ...
Stellar Evolution – Test Review Answers
... The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface temperature). In other words, stars that are higher up (brighter) on the main sequence are more massive, larger, and hotter. 19. Describe the beginning of a star’s life. The birth of ...
... The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its luminosity (and also the greater its radius and surface temperature). In other words, stars that are higher up (brighter) on the main sequence are more massive, larger, and hotter. 19. Describe the beginning of a star’s life. The birth of ...
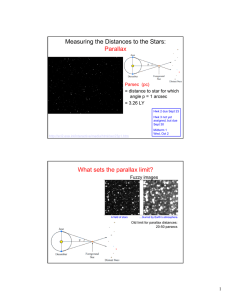
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... • change in luminosity ...
... • change in luminosity ...
Nebula - NICADD
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
... • Any source of light in the night sky that was not a point was called a nebula. ...
Name _________ Date _____________ Period ______ Skills
... d. their size. _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. ...
... d. their size. _____ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. _____ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in the sky ______________________ stars. ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... Sun and have nearly circular orbit. Jupiter is the closest, orbiting at about 5.2 astronomical units. An astronomical unit is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. So Jupiter lies about 5 times as far from the Sun as Earth does, and almost 12 years to complete one orbit. But most of the extrasolar ...
... Sun and have nearly circular orbit. Jupiter is the closest, orbiting at about 5.2 astronomical units. An astronomical unit is the distance from the Earth to the Sun. So Jupiter lies about 5 times as far from the Sun as Earth does, and almost 12 years to complete one orbit. But most of the extrasolar ...
Planet Definition - Porterville College Home
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other Solar System bodies be defined in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape. (This generally a ...
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other Solar System bodies be defined in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape. (This generally a ...
Planet Definition
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other Solar System bodies be defined in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape. (This generally a ...
... The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other Solar System bodies be defined in the following way: (1) A planet is a celestial body that (a) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape. (This generally a ...
The Planets in our Solar System
... • The various temperatures created different elements. • Heavier elements formed closer to the heat of the Sun, lighter elements formed farther from the Sun. ...
... • The various temperatures created different elements. • Heavier elements formed closer to the heat of the Sun, lighter elements formed farther from the Sun. ...
Astronomy 1020 Exam 1 Review Questions
... 10 times bigger than the Sun, what is its luminosity with respect to the Sun? 11. What is more energetic, a blue or a red photon? How about an X-ray versus an infrared photon? Why do you say this? 12. Describe the 3 layers of the solar atmosphere. 13. What are the 3 mechanisms in which heat energy c ...
... 10 times bigger than the Sun, what is its luminosity with respect to the Sun? 11. What is more energetic, a blue or a red photon? How about an X-ray versus an infrared photon? Why do you say this? 12. Describe the 3 layers of the solar atmosphere. 13. What are the 3 mechanisms in which heat energy c ...