Star Types
... and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
... and quite bright. Ex. Betelgeuse is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun but is only 3,500K on the surface. It’s radius is 1,000 times that of the Sun. ...
Homework PHY121 (Astronomy
... Stars in a constellation or an asterism appear to be in about the same direction as seen from Earth. They are part of a grouping of stars on the celestial sphere which has a shape which suggested a particular object, animal or person to the people in ancient cultures. Most stars in such groupings, h ...
... Stars in a constellation or an asterism appear to be in about the same direction as seen from Earth. They are part of a grouping of stars on the celestial sphere which has a shape which suggested a particular object, animal or person to the people in ancient cultures. Most stars in such groupings, h ...
star brightness
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
... it would appear over 38 our in times fainter than uld be daytime sky! In fact, it wo in night sky, which is the ma the in n cyo Pro as t as fain g) Do all Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not singl ...
10.4 Observing the Universe
... For a long time, people have looked up in the sky and seen patterns that they named after characters in stories, animals, and other common things. Many of the names given to these groups of stars by ancient cultures remain today and are called constellations. Astronomers use constellations to locate ...
... For a long time, people have looked up in the sky and seen patterns that they named after characters in stories, animals, and other common things. Many of the names given to these groups of stars by ancient cultures remain today and are called constellations. Astronomers use constellations to locate ...
STARS
... The greater a stars mass, the greater is the amount of its nuclear fuel. However, the more massive stars are fuel guzzlers. They shine much brighter than less massive stars and use up their fuel very fast. So the more massive stars have shorter lives. Our sun will last about 10 billion years ( we a ...
... The greater a stars mass, the greater is the amount of its nuclear fuel. However, the more massive stars are fuel guzzlers. They shine much brighter than less massive stars and use up their fuel very fast. So the more massive stars have shorter lives. Our sun will last about 10 billion years ( we a ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... 3. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be that the stars exhibit an apparent motion over a period of months that is similar to the apparent motion of the red plate in this investigation. In the case of the stars, the change in the observer’s location is the result of the earth’s orbit around t ...
... 3. Answers will vary. A typical answer would be that the stars exhibit an apparent motion over a period of months that is similar to the apparent motion of the red plate in this investigation. In the case of the stars, the change in the observer’s location is the result of the earth’s orbit around t ...
How Stars Form Powerpoint
... Stars of Other Masses Remember - Main Sequence is a band, rather than a line, because stars of the same mass can have different compositions. Most important: Stars do not move along the Main Sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
... Stars of Other Masses Remember - Main Sequence is a band, rather than a line, because stars of the same mass can have different compositions. Most important: Stars do not move along the Main Sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
White Dwarf Stars - University of California Observatories
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
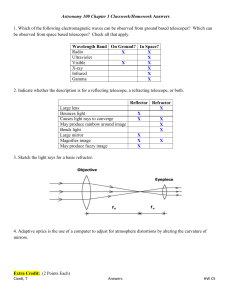
Astronomy 100 Chapter 5 Classwork/Homework Answers 1. Which
... Magnifies image X X May produce fuzzy image X 3. Sketch the light rays for a basic refractor. ...
... Magnifies image X X May produce fuzzy image X 3. Sketch the light rays for a basic refractor. ...
Earth in space
... away from the earth… If the shift had been towards the blue end of the spectrum, the galaxies would be moving towards the earth ...
... away from the earth… If the shift had been towards the blue end of the spectrum, the galaxies would be moving towards the earth ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... particularly in cool stars. The structure of the Sun and its Teff can be reproduced with =1.6, But nothing definite known about this value for other stars. In Schaller et al. they estimate from the average location of the red giant branch of 75 clusters, and obtained best fit for =1.6 0.1. N ...
... particularly in cool stars. The structure of the Sun and its Teff can be reproduced with =1.6, But nothing definite known about this value for other stars. In Schaller et al. they estimate from the average location of the red giant branch of 75 clusters, and obtained best fit for =1.6 0.1. N ...
The Life of a Star
... • As long as they have hydrogen atoms to fuse into helium atoms they just keep on releasing lots of energy. ...
... • As long as they have hydrogen atoms to fuse into helium atoms they just keep on releasing lots of energy. ...
Chapter 18 review answers
... 20. Copernicus, he theorized that if the starts were nearby there position would shift like the planets’ positions do as the Earth travels around the sun. Since they did not, they must be very far away. 21. Sir Isaac Newton explained why the planets orbit the sun and why the moons orbit planets, for ...
... 20. Copernicus, he theorized that if the starts were nearby there position would shift like the planets’ positions do as the Earth travels around the sun. Since they did not, they must be very far away. 21. Sir Isaac Newton explained why the planets orbit the sun and why the moons orbit planets, for ...
Ayres-Kepler-ASC
... stellar activity by exploiting two complementary aspects of the precision photometry: spot modulations (surface activity, rotation & diff rotation, flares) and asteroseismology (rotation, diff rotation [?], internal structure, age, ...
... stellar activity by exploiting two complementary aspects of the precision photometry: spot modulations (surface activity, rotation & diff rotation, flares) and asteroseismology (rotation, diff rotation [?], internal structure, age, ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... - Stars are classified by their size, brightness, color, temperature, spectrum and age. ...
... - Stars are classified by their size, brightness, color, temperature, spectrum and age. ...
File - Mr. Goodyear Astronomy
... Step 5 Helium Flash / Red Giant – as hydrogen in core of star decreases and helium in core rises, the star starts to become unstable and equilibrium breaks down, gravity takes over – causing greater pressure on core and causes helium flash or fusion (new energy He C ) Star grows: increase energy ov ...
... Step 5 Helium Flash / Red Giant – as hydrogen in core of star decreases and helium in core rises, the star starts to become unstable and equilibrium breaks down, gravity takes over – causing greater pressure on core and causes helium flash or fusion (new energy He C ) Star grows: increase energy ov ...
Our Star - the Sun
... the Earth moves along its orbit Parallax measurements made from orbit, above the blurring effects of the atmosphere, are much more accurate than those made with Earth-based telescopes Stellar parallaxes can only be measured for stars within a few hundred parsecs ...
... the Earth moves along its orbit Parallax measurements made from orbit, above the blurring effects of the atmosphere, are much more accurate than those made with Earth-based telescopes Stellar parallaxes can only be measured for stars within a few hundred parsecs ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 6 - A tour of the planets 6 - 1 Lecture 6
... Jupiter’s, a mass of 0.7 Jupiter’s (density = 300-500 kg/m3) but an orbital radius of 0.047 AU, astonishingly small. The mass distribution is (2008 data from http://exoplanet.eu) 0 - 2 Jupiter masses: 63% 2 - 4 Jupiter masses: 17% 4 - 6 Jupiter masses: 7% Issues: • The conventional model of our sola ...
... Jupiter’s, a mass of 0.7 Jupiter’s (density = 300-500 kg/m3) but an orbital radius of 0.047 AU, astonishingly small. The mass distribution is (2008 data from http://exoplanet.eu) 0 - 2 Jupiter masses: 63% 2 - 4 Jupiter masses: 17% 4 - 6 Jupiter masses: 7% Issues: • The conventional model of our sola ...
here - Stargazers Club
... Wobble method - an orbiting planet will pull on its star, causing it to wobble as it rotates. We can detect this wiggle in the light we receive from it Most planets found are the size of Jupiter Big dog/small dog pulling on owner is like the Earth on sun - extremely hard to detect Transit Method - a ...
... Wobble method - an orbiting planet will pull on its star, causing it to wobble as it rotates. We can detect this wiggle in the light we receive from it Most planets found are the size of Jupiter Big dog/small dog pulling on owner is like the Earth on sun - extremely hard to detect Transit Method - a ...
Geocentric vs. Heliocentric
... Lots of data! – Decades worth. He made the most precise observations that had yet been made by devising the best instruments available before the invention of the telescope. Decided by measurement and observation, NOT BY DOGMA His observations of planetary motion, particularly that of Mars, provided ...
... Lots of data! – Decades worth. He made the most precise observations that had yet been made by devising the best instruments available before the invention of the telescope. Decided by measurement and observation, NOT BY DOGMA His observations of planetary motion, particularly that of Mars, provided ...