Mind, Brain & Behavior
... There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the bran ...
... There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines (punching bags). Don’t be fooled by the bran ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
C48 Nervous System
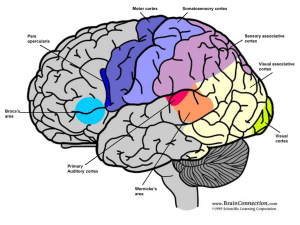
... Sensory input – signals from sensory receptors via sensory neurons, ex. light-detecting cells in eyes Integration – interpreting signals and forming responses (carried out by central nervous system (CNS), brain and spinal cord in vertebrates) via interneurons Motor input – conduction of signal ...
... Sensory input – signals from sensory receptors via sensory neurons, ex. light-detecting cells in eyes Integration – interpreting signals and forming responses (carried out by central nervous system (CNS), brain and spinal cord in vertebrates) via interneurons Motor input – conduction of signal ...
Stimulus space topology and geometry from neural activity
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
... generated in our brains. How do we do this? Many studies have investigated how the electrical activity of neurons (action potentials) is related to outside stimuli, and maps of these relationships – often called receptive fields – are routinely computed from data collected in neuroscience experiment ...
Nerve cord
... structure for receiving and passing on information. Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
... structure for receiving and passing on information. Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
nervous system
... At the end of axon, the Ca+ gates open, this causes a rush of Ca+ which makes the vacuoles contain neurotransmitters to fuse w/ the synaptic knob and open ...
... At the end of axon, the Ca+ gates open, this causes a rush of Ca+ which makes the vacuoles contain neurotransmitters to fuse w/ the synaptic knob and open ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
Design a Neuron
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
Name
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ r ...
... In order to trigger a neural impulse, excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must exceed a certain intensity, called a ________________________. Increasing a stimulus above this level will not increase the neural impulse's intensity. This phenomenon is called an ______-______-________________ r ...
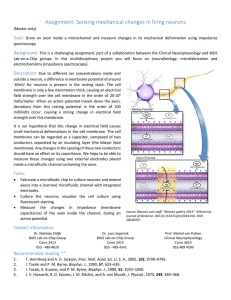
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... Description: Due to different ion concentrations inside and outside a neuron, a difference in membrane potential of around -65mV for neurons is present in the resting state. The cell membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of ...
... Description: Due to different ion concentrations inside and outside a neuron, a difference in membrane potential of around -65mV for neurons is present in the resting state. The cell membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
Biological Basis of Behavior
... - Myelin sheath - fatty material that covers the axon and insulates it which increases conduction speed - Nodes of ranvier -spaces between the myelin sheath where information can become depolarized ( get lost) ...
... - Myelin sheath - fatty material that covers the axon and insulates it which increases conduction speed - Nodes of ranvier -spaces between the myelin sheath where information can become depolarized ( get lost) ...
Neural Basis of the Oblique Effect
... • Combination of alternatives were confirmed: – The effect exists only for a subpopulation of cells: simple cells in V1 with high spatial frequency. – There are more cells tuned for cardinal orientations and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning ...
... • Combination of alternatives were confirmed: – The effect exists only for a subpopulation of cells: simple cells in V1 with high spatial frequency. – There are more cells tuned for cardinal orientations and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning ...
neuron
... • arborisation (branching) increases receptive area of the cell (100 000 contacts and more) • dendritic spines (site of synapse - postsynaptic membrane, actin microfilaments • neurofilaments (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H), other cytoskeleton units, proteosynthetic apparatus except GA • always non- myelinated ...
... • arborisation (branching) increases receptive area of the cell (100 000 contacts and more) • dendritic spines (site of synapse - postsynaptic membrane, actin microfilaments • neurofilaments (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H), other cytoskeleton units, proteosynthetic apparatus except GA • always non- myelinated ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... How does the Synapse carry the signal? 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the sign ...
... How does the Synapse carry the signal? 1. Electrical current travels down the axon 2. Vesicles with chemicals move toward the membrane what is that called? 3. Chemicals are released and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the sign ...
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... – Neurons are the information processors – Glia provide metabolic and structural support to the neurons ...
... – Neurons are the information processors – Glia provide metabolic and structural support to the neurons ...
Neurons: What They`re Made Of and How They
... Once the chemicals cross the synaptic cleft, they bind to special receptors on the dendrites. When bound, these receptors open channels in the cell membrane that allow positively charged particles (called ions) to enter the cell, changing the internal chemistry. This change, if great enough, will ca ...
... Once the chemicals cross the synaptic cleft, they bind to special receptors on the dendrites. When bound, these receptors open channels in the cell membrane that allow positively charged particles (called ions) to enter the cell, changing the internal chemistry. This change, if great enough, will ca ...
Name
... 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic ne ...
... 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic ne ...